Content Menu
● Introduction to Hot Melt Extrusion
>> Working Principle of Hot Melt Extrusion
● Criteria for Polymer Selection
>> 1. Thermoplastic Properties
>> 2. Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
>> 3. Thermal Stability
>> 4. Melt Viscosity
>> 5. Hygroscopicity
>> 6. Solubility
>> 7. Regulatory Requirements
● Commonly Used Polymers in HME
● Hot Melt Extrusion Pharmaceutical Equipment
>> Features of Twin-Screw Extruders
● Applications of Hot Melt Extrusion
● Challenges and Future Directions
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the primary factors to consider when selecting a polymer for HME?
>> 2. How does the glass transition temperature (Tg) affect the HME process?
>> 3. What are the advantages of using twin-screw extruders in HME?
>> 4. Can HME be used for controlled release formulations?
>> 5. How does HME improve drug solubility?
● Citations:
Hot melt extrusion (HME) is a versatile and widely used technology in the pharmaceutical industry for the development of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs), controlled release systems, and other specialized drug formulations. The process involves melting and mixing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with polymers and other excipients to create a uniform product with enhanced solubility and stability. The choice of polymer is crucial in HME, as it directly affects the physical stability, solubility, and release characteristics of the final product.
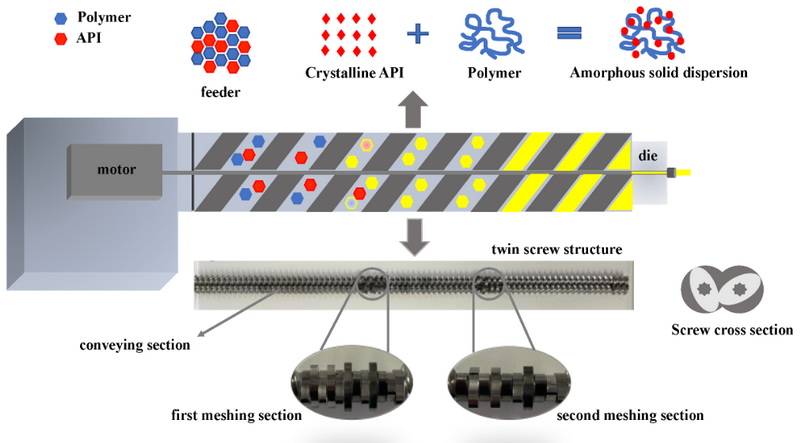
Introduction to Hot Melt Extrusion
Hot melt extrusion is a continuous process that offers several advantages over traditional batch processing methods, including improved product uniformity, reduced dust generation, and increased manufacturing efficiency. It is particularly beneficial for poorly soluble drugs, as it allows for the formation of solid solutions at the molecular level, enhancing drug bioavailability.
Working Principle of Hot Melt Extrusion
The HME process involves several key steps:
1. Feeding: The API and polymer are fed into the extruder.
2. Melting: The materials are melted and softened in the heated barrel.
3. Mixing: The molten mixture is thoroughly mixed under high shear forces.
4. Extrusion: The uniform mixture is forced through a die to form the desired shape.
5. Cooling and Shaping: The extrudate is cooled and shaped as needed.
Criteria for Polymer Selection
Selecting the right polymer for HME involves considering several critical factors:
1. Thermoplastic Properties
Polymers must exhibit thermoplastic behavior, meaning they can soften and deform when heated. This property is essential for processing through HME equipment.
2. Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
The polymer's Tg should be within the range of 50°C to 180°C, compatible with the processing temperature but allowing for efficient extrusion. Tg can be adjusted using plasticizers if necessary.
3. Thermal Stability
The chosen polymer must remain stable and not undergo decomposition or degradation at the temperatures used during extrusion.
4. Melt Viscosity
Polymers with moderate to low melt viscosity are preferred for HME, as they improve flowability and processability.
5. Hygroscopicity
Low hygroscopicity is desirable to minimize the impact of moisture on the stability and performance of the final ASD.
6. Solubility
The polymer should be able to dissolve or be compatible with the drug substance, enhancing drug dispersion and dissolution within the polymer matrix.
7. Regulatory Requirements
Ensure the selected polymer complies with relevant regulatory standards, especially if it will be used in a pharmaceutical product.
Commonly Used Polymers in HME
Several polymers are commonly used in HME due to their favorable properties:
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): High molecular weight, but often too rigid for HME.
- PVP/VA (Copovidone): A copolymer of vinylpyrrolidone and vinyl acetate, offering a lower Tg and better suitability for HME.
- Soluplus: An amphiphilic copolymer with excellent solubilization capacity.
- Eudragit: Various grades are used for different release profiles.
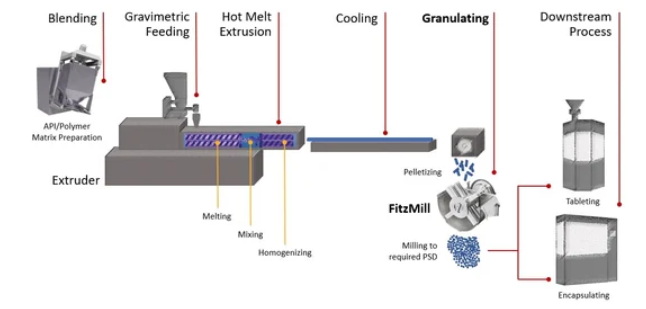
Hot Melt Extrusion Pharmaceutical Equipment
The choice of hot melt extrusion pharmaceutical equipment is crucial for efficient and consistent production. Twin-screw extruders are widely used due to their ability to generate high shear forces, ensuring uniform mixing and dispersion of the API within the polymer matrix.
Features of Twin-Screw Extruders
- Multi-stage Temperature Control: Allows for precise control over different zones of the extruder.
- Modular Screw Design: Enables customization based on material properties.
- Easy Disassembly and Cleaning: Essential for compliance with GMP regulations.
Applications of Hot Melt Extrusion
HME is versatile and can be used for various pharmaceutical applications:
- Amorphous Solid Dispersions (ASDs): Enhance solubility of poorly soluble drugs.
- Controlled Release Systems: Tailor drug release profiles.
- Taste Masking: Improve palatability of bitter drugs.
- Transdermal Patches: Formulate drugs for dermal delivery.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its advantages, HME faces challenges such as limited availability of approved polymers for pharmaceutical use and the need for extensive compatibility studies. Future research should focus on developing new polymers and optimizing processing conditions to expand the range of drugs that can be formulated using HME.
Conclusion
Selecting the right polymer for hot melt extrusion is a critical step in developing effective pharmaceutical formulations. By understanding the key criteria for polymer selection and leveraging the capabilities of hot melt extrusion pharmaceutical equipment, manufacturers can create products with improved solubility, stability, and release characteristics.
FAQ
1. What are the primary factors to consider when selecting a polymer for HME?
When selecting a polymer for HME, consider thermoplastic properties, glass transition temperature (Tg), thermal stability, melt viscosity, hygroscopicity, solubility, and regulatory compliance.
2. How does the glass transition temperature (Tg) affect the HME process?
The Tg of a polymer should be compatible with the processing temperature, allowing for efficient extrusion. Polymers with Tg between 50°C and 180°C are generally suitable.
3. What are the advantages of using twin-screw extruders in HME?
Twin-screw extruders offer high shear forces, uniform mixing, easier feeding, improved dispersing capacities, and a lower risk of overheating, making them ideal for high drug loading and fast dissolution requirements.
4. Can HME be used for controlled release formulations?
Yes, HME can be used to produce controlled release formulations by adjusting the drug-to-polymer ratio and selecting polymers that provide the desired release profile.
5. How does HME improve drug solubility?
HME improves drug solubility by forming solid solutions at the molecular level, which enhances the dissolution rate of poorly soluble drugs.
Citations:
[1] https://www.crystalpharmatech.com/asd-column-how-to-select-polymers-in-hotmelt-extrusion-process.html
[2] https://www.pharmtech.com/view/selecting-excipients-for-enhancing-solubility-of-hot-melt-extrusion-formulations
[3] https://compoundingextruder.com/pharma-hot-melt-extruder/
[4] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CT33vHgSVLs
[5] https://www.vjinstruments.com/products/hotmeltextruder/
[6] https://www.thermofisher.com/hk/zt/home/industrial/manufacturing-processing/improving-pharmaceutical-biotech-manufacturing-processes-production-methods/technologies/hot-melt-extrusion.html
[7] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4efDzsuPh6A
[8] https://ascendiacdmo.com/hot-melt-extrusion-formulation-manufacturing
[9] https://www.fitzpatrick-mpt.com/news-and-events/how-to-mill-hot-melt-extrusion-without-destroying-product-quality
[10] https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/12/9/795
[11] https://www.crystalpharmatech.com/uploads/file/20240808/optimizing-polymer-selection-for-amorphous-solid-dispersion-in-hot-melt-extrusion-processes.pdf
[12] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4766118/
[13] https://www.bioduro.com/hot-melt-extrusion-to-prepare-amorphous-solid-dispersions-key-concepts-and-common-misperceptions.html
[14] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6160992/
[15] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32842703/






















