Content Menu
● Introduction to Metal Extrusion Equipment
● The Metal Extrusion Process: Step by Step
>> 1. Preparation of the Metal Billet
>> 2. Loading into the Extrusion Press
>> 3. Application of Pressure
>> 4. Metal Flow Through the Die
>> 5. Cooling and Post-Processing
>> 6. Cutting and Finishing
● Types of Metal Extrusion Equipment
● Key Components of Metal Extrusion Equipment
● Applications and Advantages of Metal Extrusion
>> Applications
>> Advantages
● Factors Affecting the Extrusion Process
● Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Metal Extrusion Equipment
>> Routine Maintenance
>> Regular Maintenance
>> Common Troubleshooting Issues
● Safety Considerations in Metal Extrusion Operations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the difference between direct and indirect metal extrusion equipment?
>> 2. What metals can be processed using metal extrusion equipment?
>> 3. How is the die maintained in metal extrusion equipment?
>> 4. What are common problems encountered in metal extrusion equipment, and how are they solved?
>> 5. What safety precautions are necessary when operating metal extrusion equipment?
● Citations:
Metal extrusion equipment is at the heart of a transformative manufacturing process that enables the creation of complex, continuous metal profiles with remarkable efficiency and precision. From automotive components to architectural frameworks, the products shaped by metal extrusion equipment are essential to modern industry. This comprehensive guide explores what metal extrusion equipment is, how it operates, its types, applications, and the best practices for its maintenance and troubleshooting.
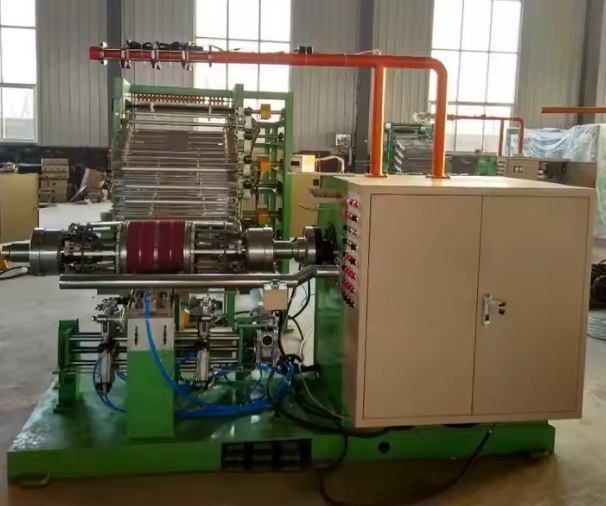

Introduction to Metal Extrusion Equipment
Metal extrusion equipment refers to the specialized machinery used to force metal billets or slugs through a shaped die, producing objects with a continuous cross-sectional profile. This equipment is fundamental in industries requiring high-strength, lightweight, and intricately shaped metal components, such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics[4][9][15].
The process itself is a mechanical deformation technique, where compressive forces push the metal through a die, resulting in elongated products like tubes, rods, and custom profiles[4][10]. The versatility of metal extrusion equipment allows manufacturers to create profiles that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with other metal forming methods.
The Metal Extrusion Process: Step by Step
Understanding how metal extrusion equipment works requires a stepwise look at the process:
1. Preparation of the Metal Billet
The process begins with cutting raw metal into billets or slugs of appropriate size. These billets are then preheated (for hot extrusion) to make them malleable but not molten, ensuring optimal flow through the die[2][11].
2. Loading into the Extrusion Press
The preheated billet is loaded into the extrusion press. The press can be mechanical or hydraulic, depending on the scale and requirements of the operation[10][15].
3. Application of Pressure
A ram or plunger applies immense compressive force to the billet, pushing it against the die opening. The pressure must be sufficient to cause plastic deformation, allowing the metal to flow through the die and assume its shape[3][10].
4. Metal Flow Through the Die
As the metal is forced through the die, it takes on the cross-sectional profile defined by the die's geometry. The process can be direct (the metal moves in the same direction as the ram) or indirect (the die moves towards the stationary billet)[9][12].
5. Cooling and Post-Processing
The extruded profile exits the die and is quickly cooled, often using water or air jets, to solidify its shape and enhance its mechanical properties. Additional treatments, such as straightening, cutting, or heat treatment, may follow to achieve the desired final characteristics[2][4][11].
6. Cutting and Finishing
The continuous extruded product is cut into specified lengths and may undergo further finishing processes like machining, surface treatment, or assembly[15].
Types of Metal Extrusion Equipment
Metal extrusion equipment can be classified based on several criteria, including the direction of force application, operating temperature, and mechanical design. The primary types are:
| Type of Equipment | Description | Typical Applications |
| Direct (Forward) Extrusion | The billet and ram move in the same direction; the die is stationary96. | Most common, hot/cold metals |
| Indirect (Backward) Extrusion | The die moves towards the stationary billet; metal flows in the opposite direction of the ram96. | Lower friction, thin profiles |
| Hot Extrusion | Performed at elevated temperatures, increasing metal malleability and reducing required force415. | Aluminum, copper, steel |
| Cold Extrusion | Performed at or near room temperature for improved strength and surface finish415. | Steel, aluminum, magnesium |
| Hydraulic Extrusion Presses | Use hydraulic cylinders to generate extrusion force; suitable for high-pressure applications110. | Large-scale production |
| Mechanical Extrusion Presses | Use mechanical means (screws, gears) to apply force; often used for smaller or continuous operations15. | Small to medium production |
Key Components of Metal Extrusion Equipment
Modern metal extrusion equipment is a sophisticated assembly of several critical components, each contributing to the process's efficiency and precision:
- Extrusion Press: The main machine that houses the billet and applies the extrusion force, typically via a hydraulic or mechanical system[1][10].
- Die: A hardened steel tool with an opening that defines the shape of the extruded product. Die design is crucial for profile accuracy and longevity[1][4].
- Ram/Plunger: The moving part that pushes the billet through the die, generating the necessary compressive force[10][15].
- Container/Barrel: The chamber in which the billet is placed before extrusion[1][10].
- Heating System: Used in hot extrusion to bring the billet and sometimes the die to the required temperature, ensuring optimal metal flow[2][11].
- Cooling System: Rapidly cools the extruded profile to maintain shape and improve mechanical properties[2][4].
- Control System: Modern machines use PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) for precise control of pressure, temperature, and movement, enhancing repeatability and safety[1].
- Cutting and Handling Equipment: For cutting the continuous extrudate into desired lengths and transporting finished products[15].
Applications and Advantages of Metal Extrusion
Applications
Metal extrusion equipment is indispensable in a range of industries:
- Automotive: Production of lightweight, high-strength components such as frames, rails, and engine parts[4].
- Construction: Window frames, door profiles, structural supports, and roofing elements[4][11].
- Aerospace: Aircraft frames, seat tracks, and structural components requiring precision and strength[4].
- Electronics: Heat sinks, connectors, and enclosures[4].
- Consumer Goods: Furniture, appliances, and sports equipment.
Advantages
- Complex Shapes: Ability to create intricate, continuous profiles that would be difficult with other methods[4][10].
- Material Efficiency: Minimal waste compared to subtractive processes[4].
- Mechanical Properties: Enhanced strength and surface finish, especially with cold extrusion[4].
- Versatility: Applicable to a wide range of metals, including aluminum, copper, magnesium, and steel[1][4][11].
- High Production Rates: Suitable for mass production of seamless tubes, rods, and complex profiles[6].
Factors Affecting the Extrusion Process
The quality and efficiency of metal extrusion depend on several critical factors:
- Material Properties: The metal's ductility, strength, and temperature response influence extrusion success[6].
- Billet Temperature: Proper preheating ensures smooth flow and prevents defects[2][4].
- Die Design and Condition: Well-designed, well-maintained dies produce accurate profiles and extend tool life[4].
- Extrusion Speed: Too high a speed can cause surface defects; too low increases costs and reduces throughput[4].
- Lubrication: Reduces friction and wear on equipment, especially in hot extrusion[6].
- Press Force: Adequate and consistent force is necessary for uniform extrusion[10].
- Cooling Rate: Rapid, uniform cooling prevents warping and improves mechanical properties[2][4].
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Metal Extrusion Equipment
Proper maintenance is essential for the reliable operation and longevity of metal extrusion equipment. Maintenance can be divided into routine and regular (scheduled) activities[8][14]:
Routine Maintenance
- Regular cleaning of the machine and components.
- Lubrication of moving parts.
- Checking and tightening fasteners.
- Monitoring and adjusting control instruments.
Regular Maintenance
- Conducted every 2,500–5,000 hours of operation.
- Inspection and measurement of wear on critical components (screw, barrel, die).
- Replacement or repair of worn parts.
- Disassembly and cleaning of major assemblies[8][14].
Common Troubleshooting Issues
- Abnormal Noise/Vibration: Often due to worn bearings, gears, or poor lubrication. Replace or lubricate as needed[13].
- Low Output: May result from blocked feed throats, worn screws/dies, or incorrect temperature settings. Clean, repair, or adjust as necessary[7].
- Die Build-Up or Surface Defects: Caused by die wear or improper temperature; refinish die surfaces and adjust settings[7].
- Cooling Issues: Inadequate cooling can lead to warping or incomplete profiles; check cooling system and water flow[13].
- Safety Hazards: Always ensure proper handling of heavy components, electrical safety, and use of lifting equipment during maintenance[8][14].
Safety Considerations in Metal Extrusion Operations
Operating metal extrusion equipment involves significant mechanical, thermal, and electrical hazards. Key safety practices include:
- Ensuring all personnel are trained in equipment operation and emergency procedures.
- Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and heat-resistant clothing.
- Implementing lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance.
- Regularly inspecting and maintaining safety guards and emergency stops.
- Keeping the work area clean and free from obstructions[8][14].
Conclusion
Metal extrusion equipment is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the efficient production of complex, high-strength metal profiles for a vast array of industries. By understanding the equipment's operation, types, maintenance requirements, and safety considerations, manufacturers can optimize their processes for quality, efficiency, and longevity. Whether producing lightweight automotive components, robust construction materials, or precision aerospace parts, metal extrusion equipment delivers unmatched versatility and performance.

FAQ
1. What is the difference between direct and indirect metal extrusion equipment?
Direct extrusion equipment pushes the billet in the same direction as the ram, with the die fixed at the opposite end. This is the most common method but requires higher force due to friction between the billet and container. Indirect extrusion equipment moves the die towards the stationary billet, reducing friction and required force but complicating the support of the extrudate[9][6][12].
2. What metals can be processed using metal extrusion equipment?
Metal extrusion equipment is suitable for a wide range of metals, including aluminum, copper, magnesium, titanium, steel, and their alloys. The choice depends on the application's requirements for strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and formability[1][4][11].
3. How is the die maintained in metal extrusion equipment?
Die maintenance involves regular inspection for wear, timely replacement, and proper storage. Worn or damaged dies can compromise profile quality, so careful handling and periodic refurbishment are essential for optimal results[4][14].
4. What are common problems encountered in metal extrusion equipment, and how are they solved?
Common issues include abnormal noise or vibration (usually due to worn parts or poor lubrication), low output (from blockages or worn screws), die build-up (from die wear or improper temperature), and cooling issues (from inadequate water flow). Solutions involve regular maintenance, cleaning, part replacement, and adjustment of process parameters[7][13][8].
5. What safety precautions are necessary when operating metal extrusion equipment?
Operators should be trained, use proper PPE, follow lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance, and ensure all safety guards are in place. Regular inspection of electrical, thermal, and mechanical systems is vital to prevent accidents and ensure safe operation[8][14].
Citations:
[1] https://www.cdocast.com/metal-extrusion-machine/
[2] https://www.gabrian.com/what-is-aluminum-extrusion-process/
[3] https://paulmurphyplastics.com/industry-news-blog/extrusion-process-working-types-application-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[4] https://ferrero-industrial.com/en/metal-extrusion-what-it-is-and-how-to-do-it-best/
[5] https://technical.europe.misumi-ec.com/en/support/solutions/articles/76000046645-aluminum-extrusions-general-questions
[6] https://testbook.com/objective-questions/mcq-on-extrusion--5eea6a0d39140f30f369e2ec
[7] https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/extruder-machine-troubleshooting-for-engineers-pptx/271771887
[8] http://www.chinaextruders.com/m/article/mojmFqLp6gSj.html
[9] https://fractory.com/metal-extrusion/
[10] https://testbook.com/mechanical-engineering/extrusion-process-and-types
[11] https://www.impol.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-aluminum-extrusion/
[12] https://www.sanfoundry.com/mechanical-metallurgy-questions-answers-extrusion-equipments/
[13] https://www.haisiextrusion.com/Solutions-to-the-four-major-fault-problems-of-the-extruder-id43687177.html
[14] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/nine-main-points-aluminum-extrusion-press-machine-maintenance-
[15] https://www.globalspec.com/learnmore/manufacturing_process_equipment/manufacturing_equipment_components/extrusion_machines
[16] https://www.alibaba.com/showroom/metal-hot-extrusion-machine.html
[17] https://engineeringproductdesign.com/knowledge-base/metal-extrusion/
[18] https://www.aluminum-extrusion-machine.com
[19] https://femltd.com/2022/12/27/what-is-metal-extrusion/
[20] https://salamanderfabs.com/latest-news/what-is-metal-extrusion/
[21] https://www.machine4aluminium.com/parts-of-aluminum-extrusion-machine-and-its-function/
[22] https://www.sms-group.com/plants/extrusion
[23] https://www.impol.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-aluminum-extrusion/
[24] https://fractory.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Metal-extrusion.jpg?sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjZu6nRk_iMAxUps1YBHegBCCgQ_B16BAgHEAI
[25] https://www.idc-online.com/technical_references/pdfs/mechanical_engineering/Types_of_extrusion.pdf
[26] https://community.xometry.com/kb/articles/761-metal-extrusion-frequently-asked-questions
[27] https://xingdimc.en.made-in-china.com/product-group/ObBmFUqvnrGf/Metal-Extrusion-1.html
[28] https://aec.org/faqs
[29] https://www.uniqueextrusions.com/aluminum-extrusion-faq/
[30] https://starext.com/frequently-asked-questions-about-aluminum-extrusions
[31] https://edmolimited.co.uk/education/frequently-asked-questions/aluminium-extrusion/
[32] https://spectraaluminum.com/frequently-asked-questions-about-aluminum-extrusion/
[33] https://www.ryerson.com/metal-resources/metal-market-intelligence/5-questions-on-aluminum-extrusions
[34] https://starext.com/news/aluminum-extrusion-finishing-fabrication-frequently-asked-questions-faq
[35] https://kdmfab.com/metal-extrusion/
[36] https://www.elastron.com/blog/12-extrusion-defects-and-troubleshooting/
[37] https://www.outashi.com/blog/tips-maintenance-aluminum-extrusion-press-id25.html
[38] https://www.odmetals.com/pages/faqs-what-is-custom-aluminum-extrusion
[39] https://omnexus.specialchem.com/selection-guide/an-in-depth-look-at-extrusion






















