Content Menu
● Understanding Aluminum Extrusion
● Key Factors in Design Optimization
>> Material Selection
>> Die Design
>> Profile Design
>> Wall Thickness
>> Draft Angles
>> Tolerances
>> Surface Finish
>> Post-Processing Considerations
● Best Practices for Design Optimization
>> Collaborate with Extrusion Experts
>> Utilize CAD Software
>> Prototype Testing
>> Consider Sustainability
>> Continuous Improvement
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What is the most common aluminum alloy used for extrusion?
>> 2. How does wall thickness affect the extrusion process?
>> 3. What role do draft angles play in extrusion?
>> 4. Can CAD software help in optimizing extrusion designs?
>> 5. What are some post-processing steps for extruded aluminum profiles?
Aluminum extrusion is a manufacturing process that involves shaping aluminum alloy into a desired cross-sectional profile by forcing it through a die. This process is widely used in various industries due to aluminum's lightweight, strength, and corrosion resistance. However, to achieve the best results in aluminum extrusion, it is crucial to optimize the design of the components being extruded. This article will explore various strategies and considerations for optimizing designs for aluminum extrusion, ensuring efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and high-quality outcomes.
Understanding Aluminum Extrusion
Before diving into optimization strategies, it is essential to understand the basics of aluminum extrusion. The process begins with heating aluminum billets to a specific temperature, making them malleable. The heated billets are then pushed through a die using a hydraulic press, creating long lengths of aluminum profiles. These profiles can be cut to size and further processed for various applications.
Key Factors in Design Optimization
Material Selection
Choosing the right aluminum alloy is critical. Different alloys have varying mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and workability. Common alloys for extrusion include 6061, 6063, and 7075, each suited for specific applications. For instance, 6063 is often used for architectural applications due to its excellent finish and extrudability. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will guide you in selecting the most appropriate alloy.
Die Design
The die is a crucial component in the extrusion process. A well-designed die can significantly enhance the quality of the extruded product. Factors to consider include the die's shape, size, and the flow of material through the die. A balanced flow can minimize defects such as warping and surface imperfections. Additionally, the die should be designed to accommodate the thermal expansion of the aluminum during the extrusion process, ensuring consistent results.
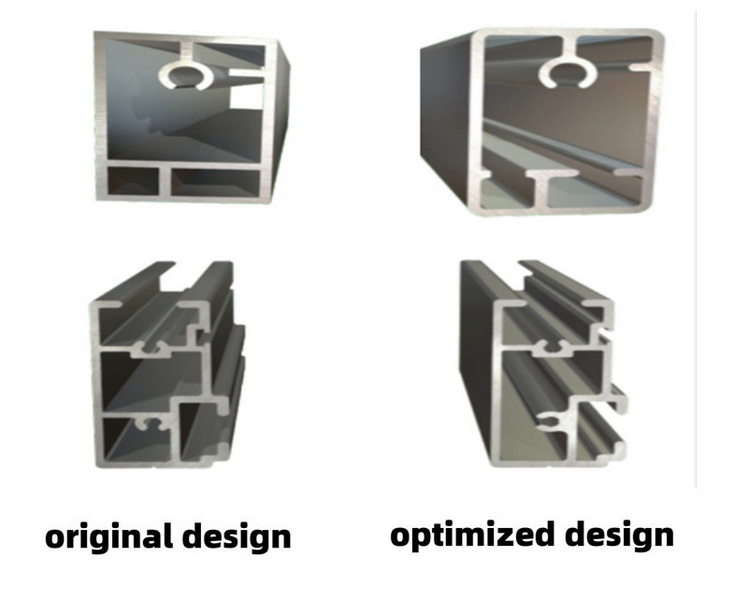
Profile Design
The geometry of the profile plays a vital role in the extrusion process. Simple shapes are easier to extrude and require less force, while complex shapes may lead to increased costs and potential defects. Designers should aim for a balance between functionality and manufacturability. For example, incorporating features like ribs or flanges can enhance the strength of the profile without significantly complicating the extrusion process.
Wall Thickness
Uniform wall thickness is essential for consistent extrusion quality. Varying wall thickness can lead to issues such as uneven cooling and distortion. Designers should strive for a consistent wall thickness throughout the profile, keeping in mind the minimum thickness requirements for structural integrity. It is also important to consider the effects of wall thickness on the overall weight and strength of the final product.
Draft Angles
Incorporating draft angles in the design can facilitate easier removal of the extruded profile from the die. A draft angle of 1-3 degrees is typically recommended, depending on the complexity of the shape. This consideration helps prevent damage to the profile and the die during the extraction process. Properly designed draft angles can also improve the surface finish of the extruded product.
Tolerances
Setting appropriate tolerances is crucial for ensuring that the extruded profiles meet the required specifications. Tight tolerances can lead to increased production costs and longer lead times. Designers should evaluate the necessary tolerances based on the application and consider using standard tolerances where possible. It is essential to communicate these tolerances clearly to the manufacturing team to avoid misunderstandings.
Surface Finish
The surface finish of the extruded profile can impact its aesthetic appeal and performance. Designers should consider the desired finish, whether it be anodized, painted, or mill finish, and how it affects the extrusion process. Certain finishes may require additional processing steps, which should be factored into the overall design. For instance, anodizing can enhance corrosion resistance but may require additional thickness in the design to accommodate the anodized layer.
Post-Processing Considerations
After extrusion, profiles may require additional processing such as cutting, machining, or assembly. Designers should consider these post-processing steps during the design phase to ensure compatibility and efficiency. For example, designing features that facilitate easy machining can save time and reduce costs. Additionally, understanding the capabilities of the post-processing equipment can help in designing profiles that are easier to work with.
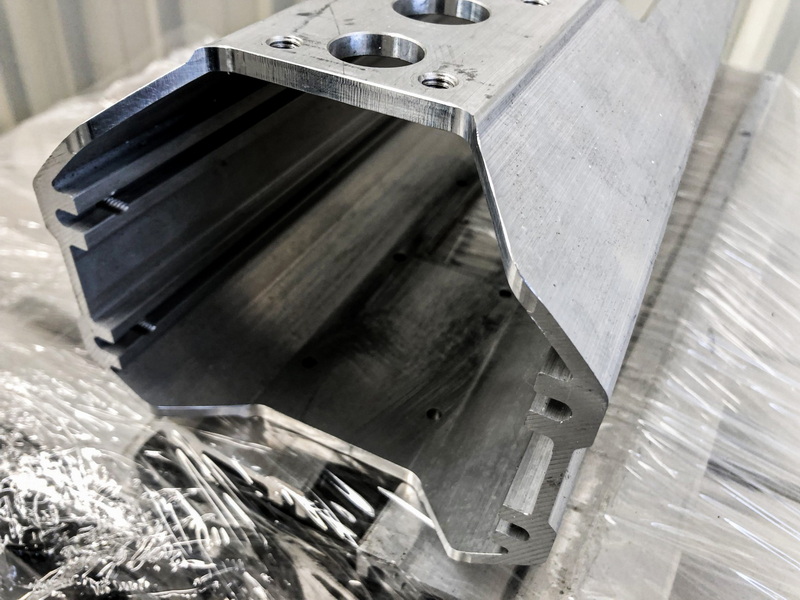

Best Practices for Design Optimization
Collaborate with Extrusion Experts
Engaging with experienced extrusion engineers during the design phase can provide valuable insights and help identify potential issues early in the process. Their expertise can guide material selection, die design, and profile geometry. Collaboration can also lead to innovative solutions that enhance the overall design.
Utilize CAD Software
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software can aid in visualizing and simulating the extrusion process. This technology allows designers to test different scenarios and optimize designs before production, reducing the likelihood of costly errors. Advanced CAD tools can also simulate the thermal and mechanical behavior of the extruded profiles, providing deeper insights into potential performance issues.
Prototype Testing
Creating prototypes of the extruded profiles can help identify design flaws and areas for improvement. Testing prototypes under real-world conditions can provide insights into performance and durability, allowing for necessary adjustments before full-scale production. Rapid prototyping techniques, such as 3D printing, can be particularly useful for testing complex designs quickly and cost-effectively.
Consider Sustainability
As industries move towards more sustainable practices, designers should consider the environmental impact of their designs. Using recycled aluminum and designing for recyclability can enhance the sustainability of the extrusion process. Additionally, optimizing designs to minimize waste during production can contribute to a more eco-friendly manufacturing process.
Continuous Improvement
The optimization of aluminum extrusion design is an ongoing process. Gathering feedback from production and end-users can help identify areas for improvement and drive innovation in future designs. Establishing a culture of continuous improvement within the design and manufacturing teams can lead to better products and processes over time.
Conclusion
Optimizing designs for aluminum extrusion is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of various factors, including material selection, die design, profile geometry, and post-processing needs. By following best practices and collaborating with experts, designers can create efficient, cost-effective, and high-quality aluminum extrusions that meet the demands of their applications.
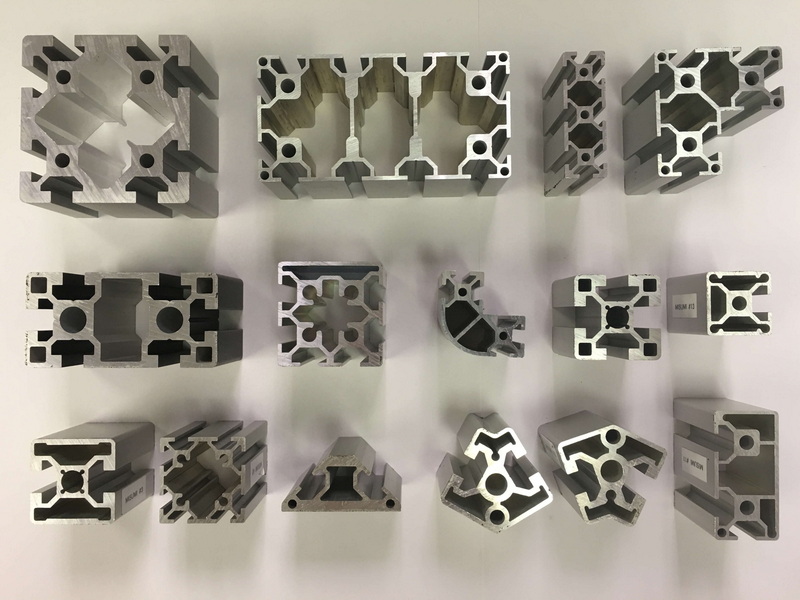

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most common aluminum alloy used for extrusion?
The most common aluminum alloys for extrusion are 6061 and 6063, known for their excellent extrudability and mechanical properties.
2. How does wall thickness affect the extrusion process?
Uniform wall thickness is crucial for consistent quality. Varying thickness can lead to defects and uneven cooling.
3. What role do draft angles play in extrusion?
Draft angles facilitate the removal of the extruded profile from the die, preventing damage during extraction.
4. Can CAD software help in optimizing extrusion designs?
Yes, CAD software allows designers to visualize and simulate the extrusion process, helping to identify potential issues early.
5. What are some post-processing steps for extruded aluminum profiles?
Common post-processing steps include cutting, machining, anodizing, and painting, depending on the application requirements.






















