Content Menu
● Understanding Tubing Extrusion Equipment
● Categories of Materials Used in Tubing Extrusion
>> Plastics and Polymers
>>> Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
>>> Polyethylene (PE): HDPE and LDPE
>>> Polyurethane
>>> Nylon (Polyamide)
>>> Silicone
>>> Polyester (PET)
>>> Polyether Block Amide (PEBAX®)
>>> Fluoropolymers: FEP, PFA, ETFE, PTFE
>>> Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
>>> Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
>>> Other Plastics
>> Metals
>>> Aluminum and Its Alloys
>>> Copper and Copper Alloys
>>> Other Metals
>> Specialty Compounds and Composite Materials
>>> Tri-Extrusion and Co-Extrusion
>>> Reinforced Tubing
● Factors Influencing Material Selection for Tubing Extrusion Equipment
● Applications of Extruded Tubing by Material
● Innovations in Tubing Extrusion Equipment and Materials
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the most commonly used material in tubing extrusion equipment?
>> 2. Can tubing extrusion equipment process metals as well as plastics?
>> 3. What are the advantages of using fluoropolymers in tubing extrusion?
>> 4. How does tri-extrusion benefit tubing design?
>> 5. What factors should be considered when selecting a material for tubing extrusion equipment?
Tubing extrusion equipment is a fundamental component in the manufacturing sector, enabling the production of consistent, high-quality tubes for a vast range of industries. The true versatility of tubing extrusion equipment is demonstrated by its ability to process a wide variety of materials, each offering unique properties and advantages for the final product. Understanding which materials can be used with tubing extrusion equipment is essential for engineers, designers, and manufacturers who are seeking optimal performance, cost efficiency, and compliance with industry standards.
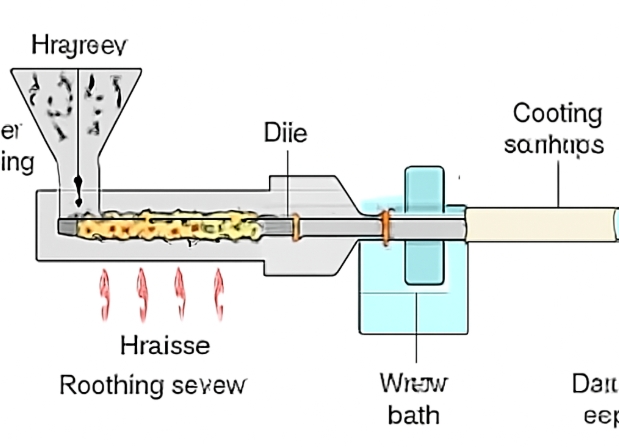
Understanding Tubing Extrusion Equipment
Tubing extrusion equipment is specifically engineered to shape raw materials into continuous tube profiles through a process that involves melting, shaping, and cooling. The equipment typically consists of a hopper for feeding raw materials, an extruder with a screw and barrel to melt and move the material, a die to shape the tube, a cooling system, and downstream handling components. The choice of material directly influences the extrusion parameters, the final properties of the tube, and the range of applications for which the tubing can be used.
Categories of Materials Used in Tubing Extrusion
The materials suitable for tubing extrusion equipment can be broadly classified into plastics (including thermoplastics and thermosets), metals, and specialty compounds. Each category encompasses a variety of specific materials, tailored for different environments and end uses.
Plastics and Polymers
Plastics are the most commonly extruded materials for tubing due to their processability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Within plastics, there are numerous options, each with distinct characteristics.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is one of the most widely used materials in tubing extrusion equipment. It is valued for its chemical resistance, durability, and affordability. PVC tubing is found in plumbing, electrical insulation, and medical applications. It is available in both rigid and flexible forms, allowing for a broad spectrum of uses.
Polyethylene (PE): HDPE and LDPE
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) are popular choices for their flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of processing. HDPE is particularly valued for its strength and rigidity, making it suitable for applications requiring durability, such as water and gas pipelines. LDPE, being more flexible, is often used where pliability is needed.
Polyurethane
Polyurethane tubing is known for its exceptional flexibility, abrasion resistance, and ability to soften at body temperature. It is widely used in pneumatic systems, medical devices, and environments where elasticity and durability are crucial. Polyurethane can be compounded with additives to enhance its properties further.
Nylon (Polyamide)
Nylon is a hard, wear-resistant material that offers excellent rigidity and a high flexural modulus. It is used in both reinforced and unreinforced tubing, often in automotive, industrial, and medical applications. Nylon's hygroscopic nature (tendency to absorb moisture) should be considered during material selection.
Silicone
Silicone tubing is prized for its biocompatibility, high temperature resistance, and flexibility. It is extensively used in medical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries. Silicone's ability to withstand sterilization and its inertness make it ideal for sensitive applications.
Polyester (PET)
Polyester, particularly PET (polyethylene terephthalate), is a lightweight thermoplastic with excellent dielectric strength, UV resistance, and wear resistance. PET tubing is commonly used in medical devices, especially where optical clarity and thin walls are required. PET can also be used as reinforcement in other tubing materials for added strength and kink resistance.
Polyether Block Amide (PEBAX®)
PEBAX® is a specialty thermoplastic elastomer that combines flexibility with excellent temperature stability and a low coefficient of friction. It is widely used in medical tubing, especially for multi-lumen and reinforced designs, due to its processability and performance.
Fluoropolymers: FEP, PFA, ETFE, PTFE
Fluoropolymers such as FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene), PFA (perfluoroalkoxy), ETFE (ethylene tetrafluoroethylene), and PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) offer outstanding chemical resistance, low friction, and high thermal stability. These materials are chosen for demanding environments, including chemical processing, electronics, and medical applications. Their unique properties allow for thin-walled, multi-lumen, and reinforced tubing designs.
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
PEEK is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its rigidity, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It is used in applications where strength and durability are paramount, such as aerospace, medical implants, and high-pressure fluid transfer. PEEK can be cost-prohibitive but offers unmatched performance in critical environments.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
TPEs offer a combination of flexibility, high elongation, and ease of processing. They are used in multi-lumen tubing, medical devices, and consumer products where soft touch and stretchability are desired.
Other Plastics
Other plastics suitable for tubing extrusion equipment include acrylic, ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), polycarbonate, polypropylene, polystyrene, and Grilamid®. Each material brings unique features such as optical clarity, impact resistance, or specific mechanical properties, expanding the range of possible tubing applications.
Metals
While plastics dominate tubing extrusion, metals are also extruded using specialized tubing extrusion equipment, particularly in applications requiring high strength, conductivity, or resistance to extreme conditions.
Aluminum and Its Alloys
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to extrude. It is widely used in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries for structural tubing and heat exchangers.
Copper and Copper Alloys
Copper offers excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for plumbing, HVAC, and electrical applications. Copper alloys can enhance strength and corrosion resistance.
Other Metals
Other metals such as steel, stainless steel, magnesium, titanium, nickel, and their alloys can also be extruded, though the process parameters differ significantly from plastics. These materials are chosen for their mechanical strength, temperature resistance, and application-specific properties.
Specialty Compounds and Composite Materials
Modern tubing extrusion equipment can process composite materials and specialty compounds, often combining multiple materials to achieve tailored properties.
Tri-Extrusion and Co-Extrusion
Tri-extrusion and co-extrusion technologies allow for the simultaneous extrusion of two or three different materials. This enables the creation of tubing with multiple layers, each providing distinct physical or chemical properties, such as a soft outer layer for comfort and a rigid inner layer for strength. These advanced techniques are widely used in medical, automotive, and industrial tubing.
Reinforced Tubing
Materials like PET monofilaments, braided or coiled, can be embedded within the tubing wall to provide reinforcement. This enhances strength, kink resistance, and torque transmission, especially in medical catheters and industrial hoses.
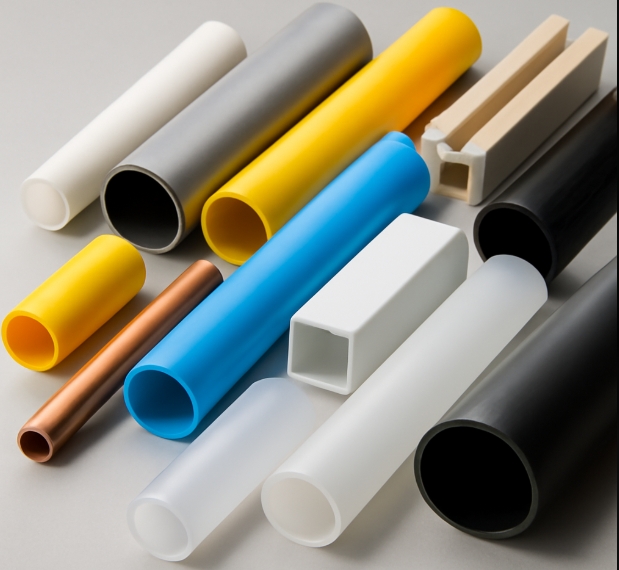

Factors Influencing Material Selection for Tubing Extrusion Equipment
Selecting the right material for tubing extrusion equipment involves balancing several factors:
- Chemical Resistance: The tubing must withstand exposure to chemicals, solvents, or fluids encountered in its application.
- Temperature Stability: The material should maintain its properties across the expected temperature range.
- Mechanical Properties: Flexibility, rigidity, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength are crucial for performance.
- Biocompatibility: For medical and food applications, the material must be non-toxic and compatible with sterilization methods.
- Cost and Processability: Material cost, ease of extrusion, and availability affect project feasibility.
- Regulatory Compliance: Materials must meet industry standards and regulations for safety and performance.
Applications of Extruded Tubing by Material
The choice of material for tubing extrusion equipment determines its suitability for specific applications:
- Medical Devices: Silicone, PEBAX®, PET, polyurethane, and fluoropolymers are common due to their biocompatibility and sterilization compatibility.
- Industrial and Automotive: PVC, nylon, polyurethane, and metals are selected for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to harsh environments.
- Construction and Plumbing: PVC, HDPE, copper, and aluminum are used for their strength, chemical resistance, and ease of installation.
- Consumer Products: TPEs, polycarbonate, and acrylic provide flexibility, optical clarity, and aesthetic appeal.
Innovations in Tubing Extrusion Equipment and Materials
Advancements in tubing extrusion equipment have expanded the range of processable materials and enabled complex tube designs. Modern extruders are equipped to handle high-performance polymers, multi-material co-extrusion, and precise dimensional control. The integration of automation, real-time monitoring, and custom die design allows manufacturers to meet stringent tolerances and produce tubing tailored to evolving industry needs.
Conclusion
Tubing extrusion equipment is remarkably versatile, capable of processing a diverse array of materials ranging from common plastics like PVC and polyethylene to high-performance polymers such as PEEK and fluoropolymers, as well as metals like aluminum and copper. The choice of material is dictated by the intended application, required properties, and regulatory considerations. As technology evolves, tubing extrusion equipment continues to adapt, enabling the creation of innovative tubing solutions for medical, industrial, automotive, and consumer markets.

FAQ
1. What is the most commonly used material in tubing extrusion equipment?
PVC is one of the most commonly used materials due to its affordability, chemical resistance, and versatility. It is used in both rigid and flexible forms across industries such as plumbing, electrical, and medical.
2. Can tubing extrusion equipment process metals as well as plastics?
Yes, specialized tubing extrusion equipment can process metals such as aluminum, copper, and steel. The extrusion process and parameters differ significantly from those used for plastics, but the principle of shaping material through a die remains the same.
3. What are the advantages of using fluoropolymers in tubing extrusion?
Fluoropolymers like FEP, PFA, and PTFE offer exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high temperature stability. These properties make them ideal for demanding applications in chemical processing, medical devices, and electronics.
4. How does tri-extrusion benefit tubing design?
Tri-extrusion allows the simultaneous extrusion of three different materials, enabling the creation of tubing with multiple layers. This can provide a combination of properties such as flexibility, strength, and chemical resistance within a single tube.
5. What factors should be considered when selecting a material for tubing extrusion equipment?
Key factors include chemical and temperature resistance, mechanical properties, biocompatibility (for medical and food applications), cost, processability, and compliance with industry regulations.






















