Content Menu
● Understanding Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
>> What Is Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment?
>> Key Applications
● Benefits of Using Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
>> Enhanced Precision and Control
>> Cost-Effectiveness
>> Space Efficiency
>> Flexibility and Versatility
>> Scalability
● Types of Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
>> Single-Screw Lab Extruders
>> Twin-Screw Lab Extruders
>> Micro Lab Twin-Screw Extruders
>> Ram and Gear Pump Extruders
● Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Compact Extrusion Equipment
>> 1. Batch Size Compatibility
>> 2. Material Versatility
>> 3. Operational Efficiency
>> 4. Ease of Use and Maintenance
>> 5. Scale-Up Capabilities
>> 6. Space and Power Requirements
>> 7. Budget and Cost-Effectiveness
>> 8. Vendor Reputation and Support
● Comparing Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment to Standard-Sized Machines
● Steps to Select the Right Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
>> Step 1: Define Your Requirements
>> Step 2: Evaluate Equipment Types
>> Step 3: Assess Technical Specifications
>> Step 4: Consider Operational Factors
>> Step 5: Review Support and Scalability
>> Step 6: Analyze Cost and Value
● Advanced Features to Look For
● Common Pitfalls to Avoid
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the main advantages of using small laboratorial extrusion equipment in a lab setting?
>> 2. How do I decide between a single-screw and a twin-screw lab extruder?
>> 3. Can small laboratorial extrusion equipment be used for scale-up to industrial production?
>> 4. What maintenance considerations are important for small laboratorial extrusion equipment?
>> 5. What types of materials can be processed with small laboratorial extrusion equipment?
Choosing the right small laboratorial extrusion equipment is a crucial step for any laboratory engaged in research, development, or small-scale production. The proper compact extruder not only ensures accuracy and efficiency but also supports innovation and scalability in a laboratory environment where space, budget, and flexibility are often limited. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential considerations, types, and features to evaluate when selecting compact extrusion equipment for lab use, ensuring your investment delivers consistent results and supports your evolving scientific goals.
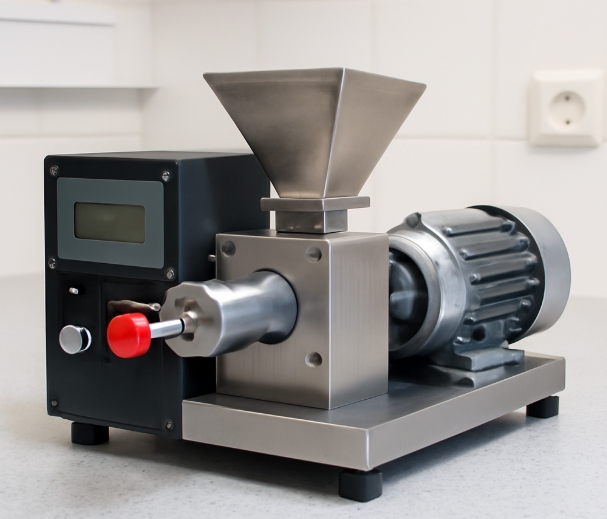

Understanding Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
What Is Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment?
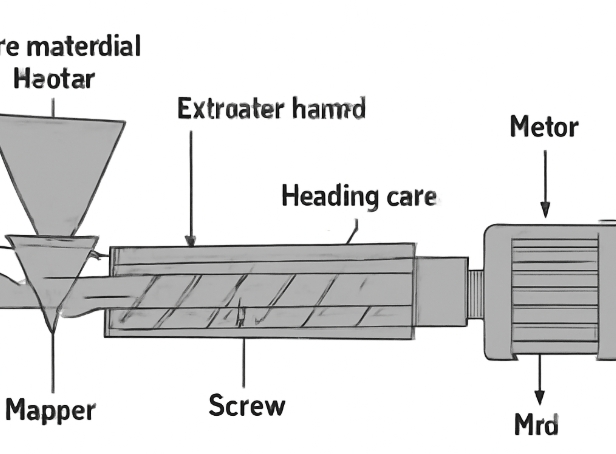
Small laboratorial extrusion equipment refers to compact, precision-engineered machines designed to process polymers or other materials in limited quantities. These machines are specifically tailored for laboratory use, where the focus is on flexibility, ease of operation, and precise control over process variables. Unlike industrial-scale extruders, small laboratorial extruders are optimized for research, formulation development, pilot-scale production, and educational applications.
Key Applications
Small laboratorial extrusion equipment is used in a variety of laboratory settings:
- Research and development of new materials, compounds, or blends
- Quality control and testing of raw materials or finished products
- Educational and training purposes for students and professionals
- Pilot-scale production to bridge the gap between laboratory research and full-scale manufacturing
- Prototyping of custom or niche products that require small-batch processing
Benefits of Using Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
Enhanced Precision and Control
Compact extruders designed for laboratory use offer highly precise control over processing parameters such as temperature, screw speed, and pressure. This level of control is essential for replicating production conditions on a smaller scale, developing new materials, and ensuring the consistency of experimental results.
Cost-Effectiveness
Operating small laboratorial extrusion equipment requires significantly less material, energy, and maintenance compared to industrial-scale machines. This translates to substantial cost savings, particularly during early-stage research or when only small quantities are needed for testing or prototyping.
Space Efficiency
The compact footprint of these machines allows them to fit easily into laboratory environments, making the most of limited space and enabling integration with other laboratory equipment for analysis and testing.
Flexibility and Versatility
Small laboratorial extrusion equipment is often designed to handle a wide range of materials and can be quickly adapted to different formulations or processes. This makes them ideal for laboratories that need to conduct diverse experiments or frequently switch between projects.
Scalability
Data and results obtained from small laboratorial extrusion equipment can be used to predict and scale up to full production, ensuring a smooth transition from research and development to manufacturing.
Types of Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
Single-Screw Lab Extruders
Single-screw extruders are the most common type used in laboratories. They are suitable for a wide range of materials and straightforward processes. Their simple design makes them easy to operate, clean, and maintain, making them a popular choice for general laboratory applications.
Twin-Screw Lab Extruders
Twin-screw extruders provide superior mixing capabilities and are more suitable for complex formulations or materials that require intensive blending. They offer greater flexibility, allowing for more advanced processing tasks, but are generally more expensive and complex to operate than single-screw models.
Micro Lab Twin-Screw Extruders
Micro twin-screw extruders are specifically designed for ultra-small batch processing. These machines are ideal for high-value materials or when only minimal sample quantities are available, such as in pharmaceutical or specialty polymer research.
Ram and Gear Pump Extruders
Ram extruders excel at processing high-viscosity materials, while gear pump extruders provide high precision and are used when consistent output and pressure are required. Both types are specialized solutions for specific laboratory needs.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Compact Extrusion Equipment
1. Batch Size Compatibility
The chosen equipment must efficiently handle the volume of material you intend to process. For laboratory applications, this often means the ability to run very small batches without excessive waste or loss, which is critical for high-value or limited-quantity materials.
2. Material Versatility
Ensure that the extruder can process the full range of materials you plan to use. Some equipment is optimized for standard polymers, while others are designed for specialty compounds, ceramics, pharmaceuticals, or food products. Consider the specific requirements of your materials, such as temperature range, shear sensitivity, and viscosity.
3. Operational Efficiency
Look for features that enhance throughput, minimize downtime, and reduce energy consumption. Efficient machines will save both time and operational costs in the long run, especially in busy laboratory environments.
4. Ease of Use and Maintenance
User-friendly controls, straightforward cleaning procedures, and accessible maintenance points are essential in a laboratory setting, where staff may not be specialized machine operators. Equipment that is easy to use and maintain will reduce downtime and improve productivity.
5. Scale-Up Capabilities
Choose equipment that allows for easy scaling of processes. This ensures that results obtained in the lab can be replicated in larger production runs without significant adjustments, facilitating a smoother transition from research to manufacturing.
6. Space and Power Requirements
Assess the available space in your laboratory and ensure the equipment's footprint and power needs are compatible. Compact models are specifically designed to fit into tight spaces and often run on standard laboratory power supplies.
7. Budget and Cost-Effectiveness
While it's important not to compromise on quality, the chosen equipment should provide good value for money, considering both the initial investment and ongoing operational costs. Factor in potential savings from reduced waste, energy efficiency, and minimal downtime.
8. Vendor Reputation and Support
Select a supplier with a proven track record, robust after-sales support, and the ability to provide training, spare parts, and technical assistance as needed. Reliable vendor support can make a significant difference in the long-term performance and reliability of your equipment.
Comparing Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment to Standard-Sized Machines
| Feature | Small Laboratorial Extruders | Standard-Sized Extruders |
| Footprint | Compact, space-saving | Large, requires more space |
| Throughput | Low, ideal for small batches | High, suited for mass production |
| Flexibility | Highly versatile | Less flexible, optimized for specific tasks |
| Cost | Lower initial and running costs | Higher purchase and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, simple controls | More complex, requires specialized operators |
| Waste | Minimal, efficient for R&D | More waste due to scale |
| Scalability | Ideal for prototyping and scale-up | Direct production, less suited for R&D |
Steps to Select the Right Small Laboratorial Extrusion Equipment
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
Start by identifying the types of materials and batch sizes you need to process. Clarify your primary applications, whether they are research and development, training, quality control, or pilot production.
Step 2: Evaluate Equipment Types
Compare single-screw, twin-screw, micro, ram, and gear pump extruders based on your process needs. Consider which type best matches your laboratory's workflow and the materials you plan to use.
Step 3: Assess Technical Specifications
Review technical details such as temperature control range, screw speed, pressure ratings, and compatibility with your materials. Ensure that the equipment can meet the specific processing requirements of your intended applications.
Step 4: Consider Operational Factors
Check for features that make operation and maintenance easier, such as intuitive user interfaces, quick-change components, and easy access for cleaning. Ensure the machine fits your laboratory's available space and infrastructure.
Step 5: Review Support and Scalability
Confirm that the manufacturer offers comprehensive technical support, training, and readily available spare parts. Also, ensure that the equipment's results can be scaled up to production levels, so your research can smoothly transition to manufacturing.
Step 6: Analyze Cost and Value
Consider both the purchase price and long-term operational costs. Evaluate potential savings from reduced waste, energy efficiency, and minimized downtime, as well as the overall value the equipment will bring to your laboratory.
Advanced Features to Look For
- Modular Design: Allows for easy upgrades or reconfiguration as research needs evolve.
- Integrated Sensors: Provide real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and torque for precise process control.
- Data Logging: Enables detailed analysis and documentation of experimental runs, which is essential for research and quality assurance.
- Quick Changeover: Facilitates rapid switching between different materials or formulations, increasing laboratory productivity and flexibility.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Selecting equipment that cannot handle your full range of materials or batch sizes.
- Overlooking the importance of after-sales support and spare parts availability.
- Focusing solely on initial cost rather than considering long-term operational efficiency and scalability.
- Ignoring the need for user-friendly controls and straightforward maintenance, which can lead to unnecessary downtime and frustration.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal small laboratorial extrusion equipment is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance your laboratory's capabilities, efficiency, and output. By focusing on batch size compatibility, material versatility, operational efficiency, ease of use, scalability, and vendor support, you can ensure your chosen extruder meets both current and future needs. Whether your focus is on research, training, or small-scale production, the right compact extruder will provide the foundation for innovation, quality, and growth in your laboratory operations.

FAQ
1. What are the main advantages of using small laboratorial extrusion equipment in a lab setting?
Small laboratorial extrusion equipment offers precise control, cost savings, space efficiency, and the flexibility to handle various materials and processes. This makes it ideal for research, development, and pilot production in laboratory environments.
2. How do I decide between a single-screw and a twin-screw lab extruder?
Single-screw extruders are generally easier to operate and suitable for standard materials and processes. Twin-screw extruders provide better mixing and are preferred for complex formulations or when working with challenging materials that require intensive blending.
3. Can small laboratorial extrusion equipment be used for scale-up to industrial production?
Yes, many compact lab extruders are designed to replicate production conditions, allowing results to be scaled up efficiently to larger manufacturing equipment. This ensures a smooth transition from laboratory research to full-scale production.
4. What maintenance considerations are important for small laboratorial extrusion equipment?
Look for equipment with accessible components, straightforward cleaning procedures, and support from the manufacturer for spare parts and technical assistance. Proper maintenance will minimize downtime and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
5. What types of materials can be processed with small laboratorial extrusion equipment?
These machines can handle a wide range of materials, including plastics, polymers, pharmaceuticals, food products, and specialty compounds. The specific materials that can be processed depend on the design and configuration of the extruder.













