Content Menu
● Understanding the Extrusion Process
● Types of Extrusion
● Applications of Production Extrusion
● Advantages of Production Extrusion
● Challenges in Production Extrusion
● Recent Advancements in Production Extrusion Technology
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials can be extruded?
>> 2. How does cooling affect the extrusion process?
>> 3. What are common applications of plastic extrusion?
>> 4. What are the main advantages of using extrusion?
>> 5. What challenges does production extrusion face?
● Citations:
Production extrusion is a widely utilized manufacturing process that transforms raw materials into continuous profiles by forcing them through a specially designed die. This method is primarily used for plastics and metals, allowing for the creation of a variety of products ranging from pipes and sheets to complex shapes used in various industries. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of production extrusion, its processes, applications, advantages, challenges, and recent advancements.
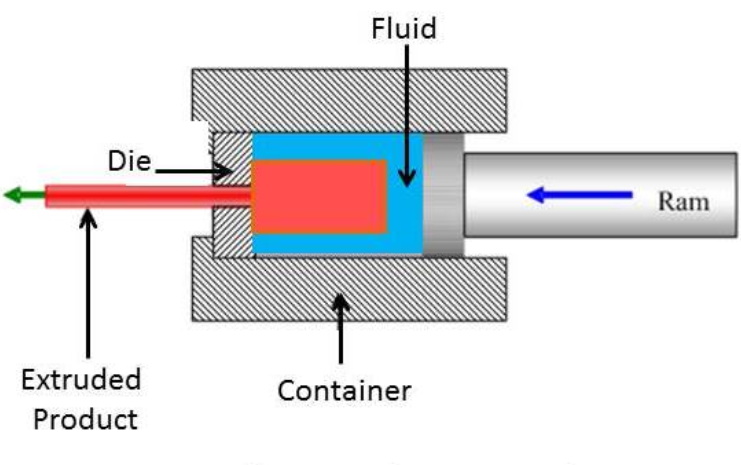
Understanding the Extrusion Process
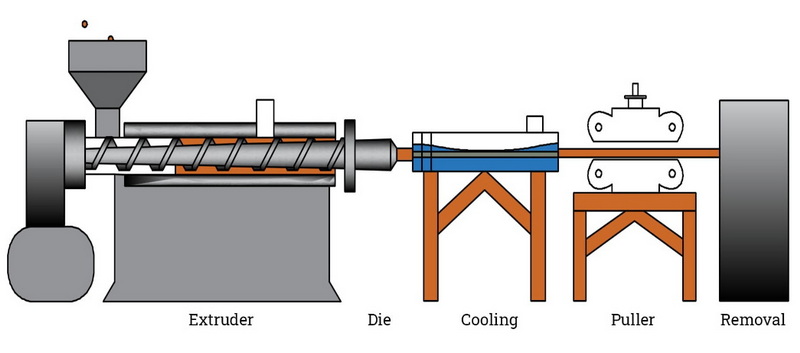
Extrusion involves several key stages that ensure the raw material is effectively transformed into the desired shape. The basic steps include:
1. Material Preparation: The raw material, typically in pellet or granule form, is fed into a hopper.
2. Heating and Melting: The material is then transported through a heated barrel where it is melted. This heating occurs in several zones to ensure even melting.
3. Screw Mechanism: A rotating screw pushes the molten material towards the die. The design of the screw can vary based on the material being processed.
4. Filtration and Pressure Maintenance: As the material approaches the die, it passes through a breaker plate with screens that filter out contaminants and maintain pressure.
5. Shaping: The molten material is forced through a die, which shapes it into a continuous profile.
6. Cooling: After exiting the die, the extrudate is cooled using water baths or air cooling systems to solidify it into its final form.
7. Cutting and Finishing: Finally, the extruded product is cut to length and may undergo additional finishing processes depending on its intended use.
Types of Extrusion
There are several types of extrusion processes, each suited for different materials and applications:
- Plastic Extrusion: This is the most common type of extrusion, used for producing plastic products like pipes, sheets, and films.
- Metal Extrusion: Used primarily for aluminum and other metals, this process can create solid or hollow shapes.
- Food Extrusion: A specialized form of extrusion used in food processing to create products like snacks and cereals by cooking and shaping ingredients simultaneously.
- Hot Extrusion: This process occurs above the recrystallization temperature of the material (approximately 50-60% of its melting temperature). It requires lower force compared to cold extrusion but may result in lower surface finish due to scale formation on extruded parts.
- Cold Extrusion: Conducted below recrystallization temperatures or at room temperature, this method produces high mechanical properties but requires higher force and may lead to strain hardening in the product.
Applications of Production Extrusion
Production extrusion has a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Construction: Used for creating window frames, door profiles, and piping systems.
- Automotive: Produces components such as dashboards and interior trim pieces.
- Packaging: Essential for manufacturing films and containers used in food packaging.
- Consumer Goods: Creates items like toys and household products.
- Medical Devices: Plastic extrusion is utilized to manufacture tubing and components for medical devices such as catheters due to its ability to produce precise dimensions with high consistency.
- Electrical Insulation: Extruded materials are used for wire insulation in electrical applications due to their durability and protective properties.
Advantages of Production Extrusion
The production extrusion process offers numerous benefits:
- High Efficiency: Capable of producing large volumes of products quickly with minimal waste due to recycling capabilities during production.
- Versatility: Can handle a wide range of materials including thermoplastics, metals, and food ingredients.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces waste by recycling scrap material during production; continuous production lowers operational costs.
- Customization: Allows for easy modification of product dimensions through die design changes; post-extrusion alterations can also be made while the product remains hot.
Challenges in Production Extrusion
Despite its advantages, production extrusion also faces challenges:
- Die Design Complexity: Designing dies for intricate shapes can be time-consuming and costly; precision in die design is crucial for maintaining product quality.
- Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for extrusion; some may degrade under high temperatures or require specific conditions for successful processing.
- Quality Control: Maintaining consistent quality throughout long production runs can be difficult; variations in raw materials can affect output stability.
Recent Advancements in Production Extrusion Technology
The field of production extrusion continues to evolve with technological advancements aimed at improving efficiency and product quality:
1. Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI algorithms analyze real-time data from machinery, allowing immediate adjustments during production to ensure that profiles meet exact specifications. This enhances product quality while contributing to resource efficiency[4].
2. Nano-Coating Technologies: These ultra-thin coatings provide an extra layer of protection against corrosion and abrasion on extruded profiles, significantly extending their lifespan across various applications[4].
3. Rapid Quench Systems: New cooling technologies ensure uniform cooling as extrusions exit the press, reducing deformations such as twisting and improving overall product quality[9].
4. Hybrid Extrusion Techniques: These methods combine traditional extrusion with advanced processes to optimize material properties, addressing demands for strength and formability in applications like aerospace[4].
5. Smart Extrusion Lines: Equipped with IoT technology, these lines allow seamless monitoring of production processes, optimizing efficiency while minimizing downtime[4].
6. Customization through 3D Printing Integration: The combination of aluminum extrusion with 3D printing technology enables intricate designs that meet specific customer requirements[4].
Conclusion
Production extrusion is an essential manufacturing process that enables the efficient creation of a wide variety of products across multiple industries. Its ability to produce high volumes with customization options makes it invaluable in today's manufacturing landscape. However, challenges such as die design complexity and material limitations must be carefully managed to ensure optimal results. With ongoing advancements in technology and practices aimed at improving sustainability and efficiency, production extrusion will continue to play a crucial role in modern manufacturing processes.

FAQ
1. What materials can be extruded?
Extrusion can be performed on various materials including thermoplastics (like polyethylene and polypropylene), metals (such as aluminum), and food ingredients (like cereals).
2. How does cooling affect the extrusion process?
Cooling solidifies the extrudate after it exits the die, ensuring it retains its shape. The cooling method (water bath or air cooling) can influence the final product's properties such as strength and surface finish.
3. What are common applications of plastic extrusion?
Plastic extrusion is commonly used in construction (pipes and profiles), automotive parts (dashboards), packaging materials (films), consumer goods (toys), medical devices (tubing), and electrical insulation (wire coatings).
4. What are the main advantages of using extrusion?
The main advantages include high efficiency in production rates, versatility in handling multiple materials, cost-effectiveness through reduced waste, customization options via die design modifications, and post-extrusion manipulation capabilities.
5. What challenges does production extrusion face?
Challenges include complex die design requirements, limitations on suitable materials due to thermal degradation risks, maintaining consistent quality across long production runs, and initial setup costs associated with custom dies.
Citations:
[1] https://paulmurphyplastics.com/industry-news-blog/extrusion-process-working-types-application-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[2] https://www.gabrian.com/what-is-aluminum-extrusion-process/
[3] https://www.chinaruicheng.com/news/the-role-of-extrusion-in-modern-manufacturing-applications-in-plastics-and-metals/
[4] https://yamunaind.com/innovation-spotlight-recent-advancements-in-aluminium-extrusion-technology/
[5] https://www.liveline.tech/case-studies
[6] https://www.tfgusa.com/understanding-extrusion-a-fundamental-manufacturing-process/
[7] https://fractory.com/metal-extrusion/
[8] https://www.clarkrandp.com/6-common-applications-of-plastic-extrusion/
[9] https://profileprecisionextrusions.com/the-evolution-of-aluminum-extrusions-emerging-trends-and-technologies/
[10] https://www.rayda.co.uk/blog/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-plastic-extrusion/






















