Content Menu
● Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
● Understanding the Aluminum Extrusion Process
>> Preparation of the Aluminum Billet
>> Preheating the Billet
>> Lubrication and Die Preparation
>> Extrusion Through the Die
>> Cooling and Stretching
>> Cutting and Heat Treatment
>> Finishing Processes
● Types of Aluminum Extrusion
● Aluminum Extrusion Die Design
● Applications of Aluminum Extrusions
● Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion
● Innovations in Aluminum Extrusion
● The Future of Aluminum Extrusion
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> Q1: What is the difference between aluminum extrusion and casting?
>> Q2: Can aluminum extrusions be welded?
>> Q3: How long can aluminum extrusions be?
>> Q4: Are aluminum extrusions environmentally friendly?
>> Q5: Can aluminum extrusions be bent or curved after production?
Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion is a fascinating manufacturing process that has revolutionized various industries, from construction to aerospace. This versatile technique allows for the creation of complex shapes and profiles with remarkable precision, making it an indispensable part of modern manufacturing. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve deep into the world of aluminum extrusion, exploring its processes, applications, and the science behind this innovative technique.
Understanding the Aluminum Extrusion Process
At its core, aluminum extrusion is a metal forming process that involves forcing heated aluminum alloy through a die with a specific cross-sectional profile. This process results in a long, straight piece of aluminum with a consistent cross-section that matches the die's shape. The beauty of this technique lies in its ability to create intricate designs and profiles that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods.
The aluminum extrusion process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Preparation of the aluminum billet
2. Preheating the billet
3. Lubrication of the die and other components
4. Extrusion through the die
5. Cooling and stretching of the extruded profile
6. Cutting to desired lengths
7. Heat treatment (if required)
8. Finishing processes
Preparation of the Aluminum Billet
The process begins with the preparation of an aluminum billet, which is a solid cylindrical block of aluminum alloy. The choice of alloy depends on the desired properties of the final product, such as strength, corrosion resistance, or conductivity. Common aluminum alloys used in extrusion include 6061, 6063, and 7075.
Preheating the Billet
Before extrusion, the billet is heated to temperatures ranging from 800°F to 925°F (427°C to 496°C). This heating process softens the aluminum, making it more malleable and easier to extrude without compromising its solid state.
Lubrication and Die Preparation
The extrusion die and other components are lubricated to reduce friction and wear during the extrusion process. This step is crucial for maintaining the quality of the extruded profile and extending the life of the equipment.
Extrusion Through the Die
The heated billet is then loaded into the extrusion press, where a powerful hydraulic ram forces it through the die. As the aluminum passes through the die, it takes on the shape of the die's opening. This is where the magic happens – complex shapes and profiles emerge from the die in a continuous stream.
Cooling and Stretching
As the hot aluminum exits the die, it is cooled using air or water. The cooling rate is carefully controlled to achieve the desired metallurgical properties. After cooling, the extruded profile is stretched to straighten it and relieve internal stresses.
Cutting and Heat Treatment
The continuous extrusion is then cut to the required lengths. Depending on the application, the cut pieces may undergo heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties.
Finishing Processes
Finally, the extruded profiles may undergo various finishing processes such as anodizing, painting, or powder coating to improve their appearance and durability.
Types of Aluminum Extrusion
There are two main types of aluminum extrusion:
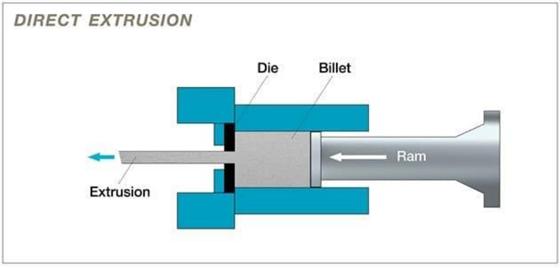
1. Direct Extrusion: In this method, the billet is pushed through the die by a ram, with the extruded profile emerging in the same direction as the ram's movement.
2. Indirect Extrusion: Here, the die moves against a stationary billet, with the extruded profile moving in the opposite direction of the die's movement.
Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the project.

Aluminum Extrusion Die Design
The heart of the aluminum extrusion process lies in the design of the extrusion die. These precision-engineered tools are crafted to create specific cross-sectional shapes and profiles. Die design is a complex art that requires a deep understanding of material flow, pressure distribution, and thermal management.
Modern die design often involves sophisticated computer simulations to optimize material flow and predict potential issues before the die is manufactured. This approach helps reduce trial and error, saving time and resources in the production process.
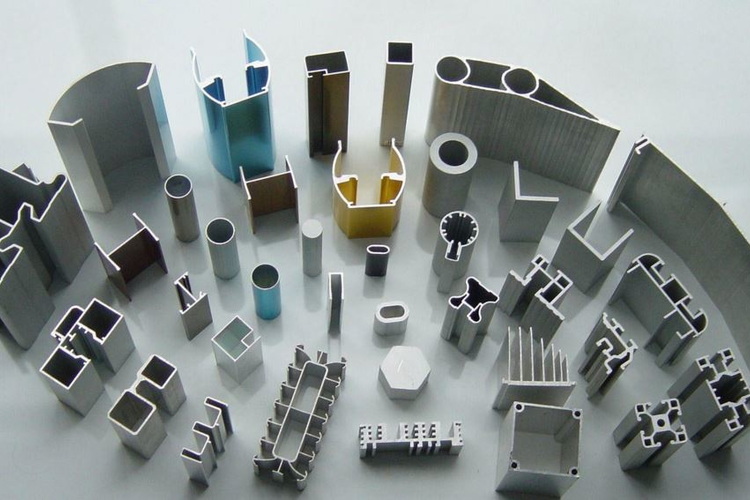
Applications of Aluminum Extrusions
The versatility of aluminum extrusions has led to their widespread use across numerous industries:
1. Construction: Window frames, door frames, curtain walls, and structural components.
2. Transportation: Automotive body parts, railway car components, and aerospace structures.
3. Electronics: Heat sinks, LED housings, and electronic enclosures.
4. Renewable Energy: Solar panel frames and wind turbine components.
5. Consumer Goods: Furniture, appliances, and sporting equipment.
The ability to create custom profiles allows designers and engineers to optimize parts for specific applications, often reducing weight, improving performance, and lowering costs compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion offers several key advantages:
1. Design Flexibility: Complex shapes can be created in a single piece, reducing the need for assembly.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: For medium to high volume production, extrusion can be more economical than other manufacturing methods.
3. Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum's excellent strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for lightweight, durable structures.
4. Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, enhancing its resistance to corrosion.
5. Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum's conductive properties make it suitable for heat sinks and electrical applications.
6. Sustainability: Aluminum is 100% recyclable, making extrusions an environmentally friendly choice.
Innovations in Aluminum Extrusion
The aluminum extrusion industry continues to evolve, with ongoing innovations enhancing the process and expanding its capabilities:
1. Multi-Hole Dies: These allow for the simultaneous extrusion of multiple profiles, increasing productivity.
2. Micro-Extrusion: Advancements in die technology enable the production of extremely small and precise profiles for miniature components.
3. Composite Extrusion: Combining aluminum with other materials during extrusion creates profiles with enhanced properties.
4. Smart Manufacturing: Integration of IoT and AI technologies for real-time process optimization and quality control.
The Future of Aluminum Extrusion
As industries continue to demand lighter, stronger, and more complex components, aluminum extrusion is poised to play an increasingly important role. Future developments may include:
1. Advanced Alloys: Development of new aluminum alloys with enhanced properties for specific applications.
2. Sustainable Practices: Increased focus on energy-efficient extrusion processes and the use of recycled aluminum.
3. Additive Manufacturing Integration: Combining extrusion with 3D printing technologies for hybrid manufacturing solutions.
4. Nanotechnology: Incorporation of nanoparticles in aluminum alloys to create extrusions with superior properties.
Conclusion
Aluminum extrusion is a remarkable manufacturing process that combines art, science, and engineering to create products that touch nearly every aspect of our lives. From the buildings we live and work in to the vehicles we travel in, aluminum extrusions play a crucial role in shaping our modern world. As technology advances and new challenges emerge, the aluminum extrusion industry will undoubtedly continue to innovate, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in manufacturing and design.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between aluminum extrusion and casting?
A1: Aluminum extrusion involves forcing heated aluminum through a die to create a specific shape, resulting in a continuous profile. Casting, on the other hand, involves pouring molten aluminum into a mold and allowing it to solidify. Extrusion typically produces stronger parts with a more consistent grain structure, while casting can create more complex 3D shapes.
Q2: Can aluminum extrusions be welded?
A2: Yes, aluminum extrusions can be welded using various methods such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding or MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding. However, welding aluminum requires specific techniques and expertise due to its unique properties, such as its low melting point and high thermal conductivity.
Q3: How long can aluminum extrusions be?
A3: The length of aluminum extrusions can vary depending on the extrusion press capabilities and the specific profile being extruded. Typical maximum lengths range from 20 to 100 feet (6 to 30 meters). However, some specialized presses can produce even longer extrusions.
Q4: Are aluminum extrusions environmentally friendly?
A4: Yes, aluminum extrusions are considered environmentally friendly for several reasons. Aluminum is 100% recyclable without loss of quality, and recycling aluminum requires only about 5% of the energy needed to produce primary aluminum. Additionally, the long lifespan and lightweight nature of aluminum extrusions contribute to their sustainability.
Q5: Can aluminum extrusions be bent or curved after production?
A5: Yes, aluminum extrusions can be bent or curved after production using various methods such as roll bending, stretch forming, or press braking. The ability to bend an extrusion depends on factors like the alloy used, the profile shape, and the desired radius of curvature. Some profiles are specifically designed to be easily bent for applications like curved window frames or architectural features.






















