Content Menu
● Understanding Extrusion
● Importance of Extrusion in Food Production
● Mechanisms of Nutritional Improvement through Extrusion
>> 1. Destruction of Anti-Nutritional Factors
>> 2. Gelatinization of Starches
>> 3. Protein Denaturation
>> 4. Fiber Enhancement
● Case Studies Illustrating Nutritional Benefits
● Challenges and Considerations
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
>> 1. What is extrusion in food processing?
>> 2. How does extrusion improve nutrient availability?
>> 3. Can all foods be extruded?
>> 4. What types of products are commonly made using extrusion?
>> 5. Are there any downsides to using extruded foods?
● Citations:
Extrusion is a versatile and efficient food processing technology that has gained significant attention for its ability to enhance the nutritional quality of various food products. This article explores how extrusion can improve the nutritional content of food, the mechanisms behind these improvements, and its importance in modern food production.
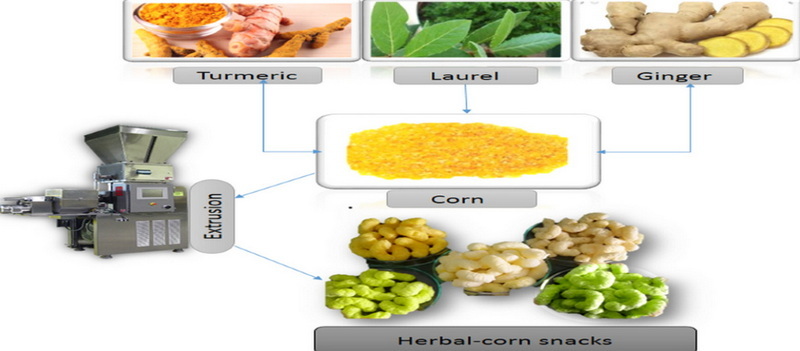
Understanding Extrusion
Extrusion is a high-temperature, short-time (HTST) process that combines cooking, mixing, and shaping into a single operation. Ingredients such as starches, proteins, and other additives are forced through a die under high pressure and temperature, resulting in a wide range of food products, including snacks, cereals, and meat analogs. The process not only alters the physical characteristics of food but also significantly impacts its nutritional profile.
Importance of Extrusion in Food Production
The significance of extrusion in food production cannot be overstated. It offers several advantages that contribute to improving the nutritional quality of food:
- Enhanced Nutrient Bioavailability: Extrusion can break down anti-nutritional factors present in raw materials, such as phytates and tannins. This breakdown enhances the bioavailability of essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and calcium, making them more accessible for absorption by the body[1][2].
- Retention of Heat-Sensitive Nutrients: Traditional cooking methods often lead to nutrient losses due to prolonged exposure to heat. However, the short processing time in extrusion minimizes the degradation of heat-sensitive vitamins such as vitamin C and several B vitamins[1][3].
- Improved Digestibility: The mechanical shear and heat applied during extrusion gelatinize starches and denature proteins, making them easier to digest. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with digestive issues or those requiring easily digestible foods[2][3].
- Incorporation of Functional Ingredients: Extrusion allows for the fortification of food products with additional nutrients and functional ingredients. Vitamins, minerals, and dietary fibers can be uniformly incorporated into extruded products during processing[1][2].
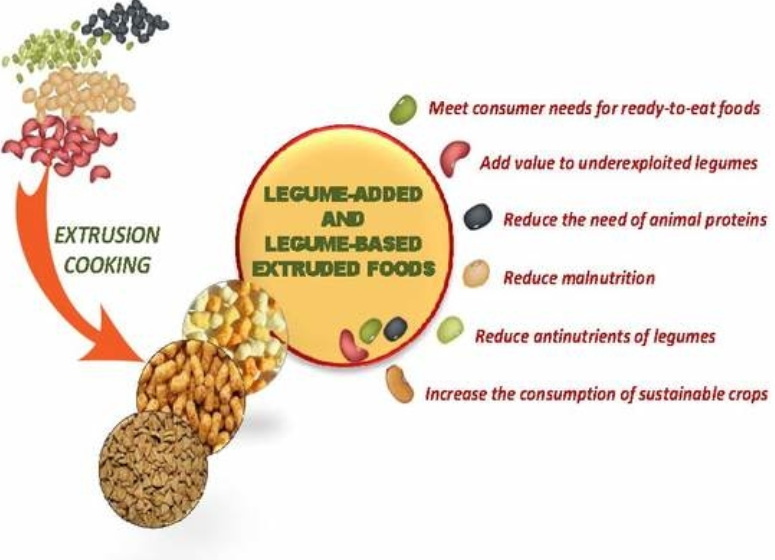
Mechanisms of Nutritional Improvement through Extrusion
The nutritional improvements achieved through extrusion can be attributed to several key mechanisms:
1. Destruction of Anti-Nutritional Factors
Extrusion effectively reduces anti-nutritional factors that inhibit nutrient absorption. For instance:
- Phytates: These compounds bind minerals like iron and zinc, reducing their bioavailability. Extrusion can hydrolyze phytates under high temperature and pressure conditions, thus enhancing mineral absorption[1][3].
- Tannins: Present in legumes and certain grains, tannins can interfere with protein digestion. The extrusion process reduces tannin levels, improving protein digestibility[1][2].
2. Gelatinization of Starches
During extrusion, starch granules undergo gelatinization—a process where they swell and lose their crystalline structure when exposed to heat and moisture. This transformation increases the solubility of starches, allowing for better digestion and absorption[3][4].
3. Protein Denaturation
The high temperatures involved in extrusion denature proteins, altering their structure so that they become more digestible. This process enhances the availability of essential amino acids necessary for human health[2][4].
4. Fiber Enhancement
Extrusion can increase the dietary fiber content of food products by incorporating fiber-rich ingredients such as whole grains or legumes. This not only improves digestive health but also contributes to satiety and overall well-being[3][4].
Case Studies Illustrating Nutritional Benefits
Several case studies highlight how extrusion has been successfully employed to enhance the nutritional quality of various food products:
- Fortified Breakfast Cereals: A leading cereal manufacturer utilized extrusion to fortify their products with essential vitamins and minerals. By adding these nutrients during the extrusion process, they ensured uniform distribution throughout the cereal, significantly improving its nutritional profile[1][2].
- Legume-Based Snacks: Research demonstrated that extruding legume flour significantly reduced anti-nutritional factors while enhancing protein digestibility. Snacks made from extruded legume flour showed improved nutrient profiles compared to traditional snacks made from refined flours[3][4].
Challenges and Considerations
While extrusion offers numerous benefits for enhancing nutritional content, it is essential to consider certain challenges:
- Control of Processing Parameters: The nutritional outcomes depend heavily on precise control over extrusion parameters such as temperature, moisture content, and feed composition. Improper settings can lead to nutrient losses or undesirable changes in product texture[2][3].
- Potential Nutrient Losses: Although extrusion minimizes losses compared to traditional cooking methods, some sensitive nutrients may still degrade during processing due to high temperatures or prolonged exposure[4][5].
Conclusion
Extrusion is a powerful tool in modern food production that significantly enhances the nutritional quality of various food products. By breaking down anti-nutritional factors, improving digestibility, and allowing for fortification with essential nutrients, this technology plays a crucial role in addressing dietary deficiencies and promoting overall health.
The importance of extrusion in food production lies not only in its ability to create diverse products but also in its potential to meet consumer demands for healthier options. As research continues to uncover new applications and benefits of extrusion technology, it will undoubtedly remain a vital component of sustainable food systems.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is extrusion in food processing?
Extrusion is a high-temperature cooking process that combines mixing and shaping ingredients under pressure to produce various food products.
2. How does extrusion improve nutrient availability?
Extrusion breaks down anti-nutritional factors like phytates and tannins while gelatinizing starches and denaturing proteins, enhancing nutrient absorption.
3. Can all foods be extruded?
Not all foods are suitable for extrusion; typically starchy or protein-rich materials work best due to their ability to withstand high temperatures.
4. What types of products are commonly made using extrusion?
Common extruded products include breakfast cereals, snacks (like puffed corn), pasta alternatives, pet foods, and meat analogs.
5. Are there any downsides to using extruded foods?
While extrusion improves many aspects of nutrition, it can also lead to some nutrient losses if not carefully controlled; thus proper processing parameters are crucial.
Citations:
[1] https://sga.com.au/extrusion-processing/
[2] https://cfaminternational.com/how-extrusion-has-changed-the-food-processing-industry/
[3] https://extruafrica.org.za/the-nutritional-benefits-of-extruded-food/
[4] https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/extruder
[5] https://loyalmachines.com/blog/the-manufacturing-process-of-extruded-food-products/
[6] https://www.academia.edu/99938042/Extrusion_problems_solved
[7] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/common-problems-use-extruder-amisy-fish
[8] https://iaras.org/iaras/filedownloads/fnsij/2023/013-0002(2023).pdf
[9] https://medcraveonline.com/MOJFPT/applications-of-food-extrusion-technology.html
[10] https://irispublishers.com/gjnfs/fulltext/how-does-extrusion-technology-help-the-development-of-foods-with-better-nutritional-value.ID.000511.php
[11] https://www.feedstrategy.com/blogs/feed-ingredient-insights/blog/15665541/extrusion-technologys-role-in-modern-feed-manufacturing
[12] https://rivalzsnacks.com/blogs/better-snacks/rivalz-extrusion-experts-help-improve-humanitarian-food-aid-offerings
[13] https://www.ift.org/news-and-publications/food-technology-magazine/issues/2017/july/columns/processing-extrusion-and-applications-in-food-industry
[14] https://www.ajol.info/index.php/najfnr/article/download/265858/250875
[15] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10905115/
[16] https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/MSD/Flyers/FL53327-interview-role-extrusion-within-sustainable-food-research.pdf
[17] https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=77cb54b2bd71cbc148c49ecc696859a8894c0203






















