Content Menu
● Understanding the Basics of Aluminum Extrusion
● The Aluminum Extrusion Process Flow Chart
● Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Aluminum Extrusion Process
>> 1. Die Preparation
>> 2. Billet Preheating
>> 3. Billet Transfer
>> 4. Extrusion
>> 5. Cooling and Quenching
>> 6. Stretching
>> 7. Cutting
>> 8. Heat Treatment (Aging)
● Advanced Techniques in Aluminum Extrusion
>> Taper Heating
>> Indirect Extrusion
● Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
● Environmental Considerations
● Future Trends in Aluminum Extrusion
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What is the difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
>> 2. How does the temperature affect the aluminum extrusion process?
>> 3. What are the advantages of aluminum extrusion over other manufacturing processes?
>> 4. How does the aging process affect extruded aluminum?
>> 5. Can all aluminum alloys be extruded?
● Citations:
Aluminum extrusion is a sophisticated manufacturing process that transforms raw aluminum into intricate shapes and profiles for various applications. This article will delve into the key steps of the aluminum extrusion process flow, providing a comprehensive overview of this fascinating industrial technique.
Understanding the Basics of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion is a process where aluminum alloy material is forced through a die with a specific cross-sectional profile[1]. The process can be likened to squeezing toothpaste out of a tube, where the opening of the tube acts like the extrusion die, shaping the material as it emerges[1].
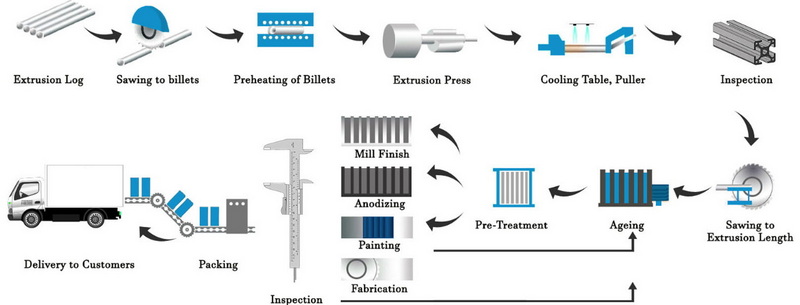
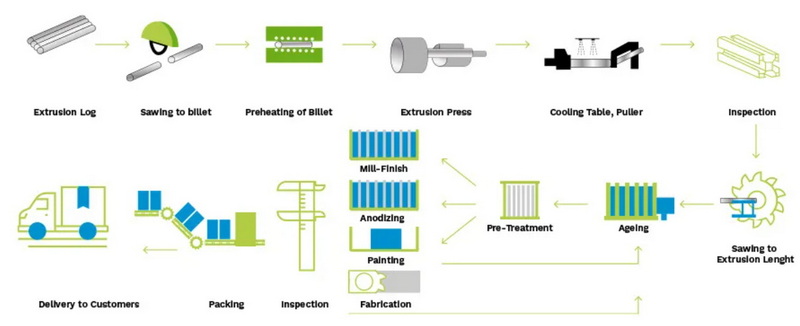
The Aluminum Extrusion Process Flow Chart
The aluminum extrusion process flow chart typically includes the following key steps:
1. Die preparation
2. Billet preheating
3. Billet transfer
4. Extrusion
5. Cooling and quenching
6. Stretching
7. Cutting
8. Heat treatment (aging)
Let's explore each of these steps in detail.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Aluminum Extrusion Process
1. Die Preparation
The process begins with the preparation of the extrusion die. This steel tool is designed with openings that will create the desired profile when the aluminum is pushed through[4]. The die is preheated to between 450-500 degrees Celsius to help maximize its life and ensure even metal flow[1].
2. Billet Preheating
An aluminum billet, which is a solid cylindrical length of alloy, is preheated in an oven to temperatures between 400-500 degrees Celsius[1][2]. This heating process makes the aluminum malleable enough for extrusion while still maintaining its solid form[4].
3. Billet Transfer
Once heated, the billet is transferred to the extrusion press. A lubricant or release agent is applied to both the billet and the extrusion ram to prevent sticking[1].
4. Extrusion
This is the core of the aluminum extrusion process flow. The preheated billet is loaded into the container of the extrusion press. A powerful hydraulic ram then applies pressure, pushing the billet into the container[2][4].
As pressure increases, the soft (but still solid) aluminum has nowhere else to go and begins to squeeze out through the shaped die, emerging on the other side as a fully formed profile[1][3].
5. Cooling and Quenching
After emerging from the die, the extrusion is quickly cooled or "quenched." This can be done using air, water, or a combination of both[1][2]. This rapid cooling is crucial for achieving the desired metallurgical properties[4].
6. Stretching
Once cooled, the extrusions are moved to a stretcher. Here, they are mechanically gripped on both ends and pulled until they are fully straight and brought into specification[1]. This process corrects any twisting that may have occurred during extrusion and cooling[2].
7. Cutting
After stretching, the extrusions are moved to a finish saw where they are cut to pre-specified lengths, typically between 8 and 21 feet long[1][2].
8. Heat Treatment (Aging)
The final step in the aluminum extrusion process flow is heat treatment or aging. This process further strengthens the aluminum and can be done naturally at room temperature or artificially in an aging oven[1][4]. The aging process affects the metallurgical structure of the alloys, yielding maximum strength, hardness, and elasticity for the profile[4].
Advanced Techniques in Aluminum Extrusion
While the basic aluminum extrusion process flow remains consistent, there are several advanced techniques that can be employed to enhance the quality and efficiency of the extrusion process.
Taper Heating
One such technique is taper heating of the billet. In this method, the front end of the billet is heated to a higher temperature than the rear. This compensates for the additional heat generated by friction and deformation as the billet progressively deforms in the press[7].
Indirect Extrusion
Another advanced technique is indirect extrusion. Unlike direct extrusion where the die is stationary and the ram forces the alloy through it, in indirect extrusion, the die is contained within a hollow ram. This method can reduce friction and allow for faster extrusion speeds for certain profiles[9].
Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
The versatility of the aluminum extrusion process flow allows for the creation of a wide range of products used in various industries. Some common applications include:
1. Construction: Window frames, door frames, roofing, and structural components
2. Transportation: Automotive parts, railway car components, bicycle frames
3. Electronics: Heat sinks, LED light housings
4. Consumer goods: Furniture, appliances, sporting goods
Environmental Considerations
One of the significant advantages of the aluminum extrusion process is its environmental friendliness. Aluminum is 100% recyclable, and the extrusion process itself produces minimal waste. Any scrap produced during the process, such as the remnants left in the container after extrusion, can be recycled and used in future extrusions[9].
Future Trends in Aluminum Extrusion
As technology advances, so does the aluminum extrusion process. Some emerging trends include:
1. Increased automation and robotics in the extrusion process
2. Development of new aluminum alloys for specific applications
3. Advancements in die design for more complex profiles
4. Integration of 3D printing technology in prototype development
Conclusion
The aluminum extrusion process flow is a complex yet fascinating manufacturing technique that allows for the creation of intricate aluminum profiles. From die preparation to the final aging process, each step plays a crucial role in producing high-quality extruded products. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further refinements and innovations in this process, leading to even more efficient and versatile aluminum extrusion capabilities.
Understanding the intricacies of the aluminum extrusion process flow is essential for anyone involved in manufacturing or engineering fields where aluminum components are used. By grasping the key steps and principles behind this process, professionals can make more informed decisions about material selection, design considerations, and production methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
Direct extrusion is the most common method where the die is stationary and the ram forces the alloy through the die. In indirect extrusion, the die is contained within a hollow ram, which can reduce friction and allow for faster extrusion speeds for certain profiles.
2. How does the temperature affect the aluminum extrusion process?
Temperature plays a crucial role in the extrusion process. The billet is typically heated to 400-500°C to make it malleable enough for extrusion while still maintaining its solid form. The die is also preheated to 450-500°C to help maximize its life and ensure even metal flow.
3. What are the advantages of aluminum extrusion over other manufacturing processes?
Aluminum extrusion offers several advantages, including the ability to create complex shapes with consistent cross-sections, high production speeds, excellent surface finish, and the ability to produce both solid and hollow profiles. It's also a cost-effective process for medium to high volume production.
4. How does the aging process affect extruded aluminum?
The aging process, whether natural or artificial, affects the metallurgical structure of the aluminum alloys. It yields maximum strength, hardness, and elasticity for the profile. Different aging times and temperatures can produce different tempers (T5, T6, etc.) with varying mechanical properties.
5. Can all aluminum alloys be extruded?
While many aluminum alloys can be extruded, some are more suitable for extrusion than others. Alloys in the 6000 series (aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys) are most commonly used for extrusion due to their excellent extrudability and good mechanical properties after heat treatment.
Citations:
[1] https://www.gabrian.com/what-is-aluminum-extrusion-process/
[2] https://americandouglasmetals.com/2024/05/19/understanding-the-aluminum-extrusion-process/
[3] https://aec.org/aluminum-extrusion-process
[4] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iiGlq7408ME
[5] https://proax.ca/en/blog/post/aluminum-extrusion-process-step-by-step-guide
[6] https://www.atieuno.com/2023/07/17/aluminium-extrusion-process-guide/
[7] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vHkwq_2yY9E
[8] https://www.rapiddirect.com/blog/aluminum-extrusion-process/
[9] https://midstal.com/sft1242/aluminum_extrusion_process_overview.pdf
[10] https://www.impol.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-aluminum-extrusion/






















