Content Menu
● Understanding Extrusion Moulding
>> The Steps Involved in Extrusion Moulding
● Key Components of an Extrusion System
● Applications of Extrusion Moulding
>> Industry-Specific Applications
● Comparison Between Extrusion Moulding and Injection Moulding
● Advantages of Extrusion Moulding
● Limitations of Extrusion Moulding
● The Importance of Temperature Control
● Post-Extrusion Processing
● Environmental Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials are commonly used in extrusion moulding?
>> 2. How does extrusion differ from injection moulding?
>> 3. What types of products can be made using extrusion?
>> 4. What are the benefits of using extrusion moulding?
>> 5. Can extrusion be used for complex shapes?
● Citations:
Extrusion moulding is a vital process in plastic manufacturing that allows for the continuous production of various plastic products. This technique is widely utilized across multiple industries, including construction, automotive, and consumer goods, due to its efficiency and versatility. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of extrusion moulding, compare it with injection moulding, and examine its applications, advantages, and limitations.
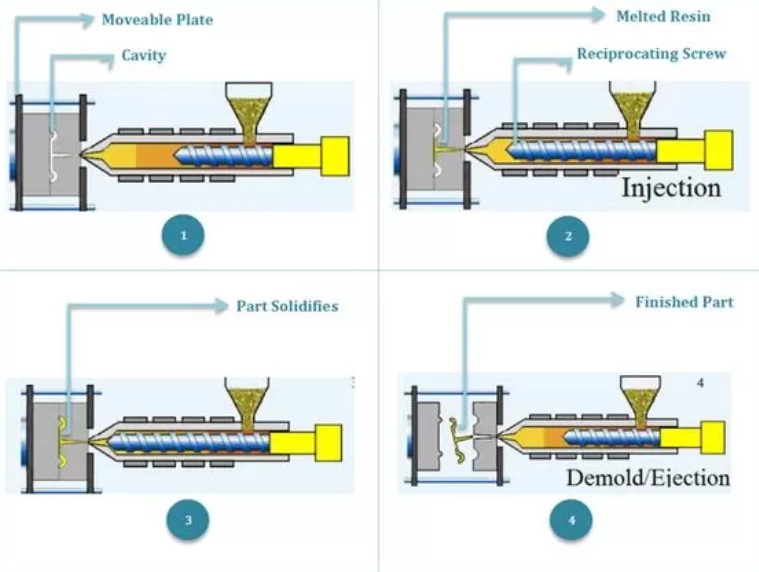
Understanding Extrusion Moulding
Extrusion moulding is a manufacturing process that involves melting plastic material and forcing it through a die to create a specific shape. The process begins with raw plastic materials, typically in pellet form, which are fed into an extruder. The extruder consists of a heated barrel and a rotating screw that melts the plastic and pushes it through the die.
The Steps Involved in Extrusion Moulding
1. Material Preparation: Plastic pellets are mixed with additives such as colorants, stabilizers, or flame retardants to enhance their properties.
2. Heating and Melting: The pellets are fed into the extruder's barrel, where they are subjected to heat from both the barrel's heaters and the friction generated by the rotating screw. This process transforms the solid pellets into a molten state.
3. Extrusion Through the Die: Once melted, the plastic is pushed through a die that shapes it into a continuous profile. The shape of the die determines the final product's cross-section.
4. Cooling: After exiting the die, the extruded plastic is cooled using air or water baths to solidify it into its final form.
5. Cutting and Finishing: The cooled extrudate is cut to the desired length and may undergo additional finishing processes if required.
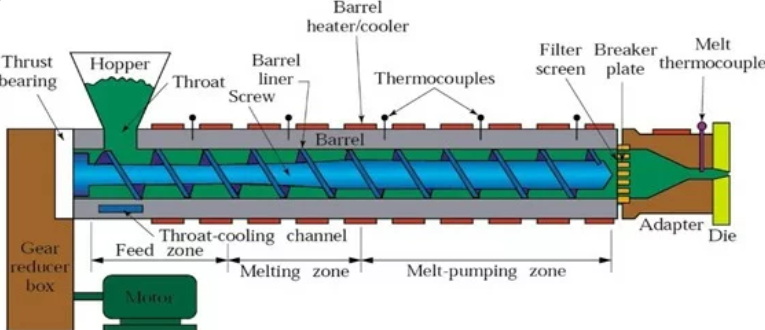
Key Components of an Extrusion System
Understanding the key components of an extrusion system can provide further insight into how extrusion moulding operates:
- Hopper: This component feeds raw materials into the extruder.
- Screw: The screw rotates within a heated barrel to melt and transport the plastic material.
- Barrel: A heated cylindrical chamber where melting occurs.
- Die: A specially shaped opening through which molten plastic is forced to create specific profiles.
- Cooling System: Often involves air or water baths to cool and solidify the extruded material.
Applications of Extrusion Moulding
Extrusion moulding is used to manufacture a wide range of products, including:
- Pipes and tubing
- Plastic sheets and films
- Weatherstripping
- Window frames
- Electrical conduits
This process is particularly advantageous for producing long lengths of uniform cross-section products.
Industry-Specific Applications
- Construction: Used for window frames, door profiles, and other architectural elements that require weather resistance and thermal efficiency.
- Automotive: Produces components like weather seals, gaskets, and interior trim parts that require durability against chemicals and temperature variations.
- Medical Devices: Utilizes extrusion for tubing in catheters or other medical applications where precise dimensions are critical.
- Packaging: Creates films and sheets for packaging materials that protect products and extend shelf life.
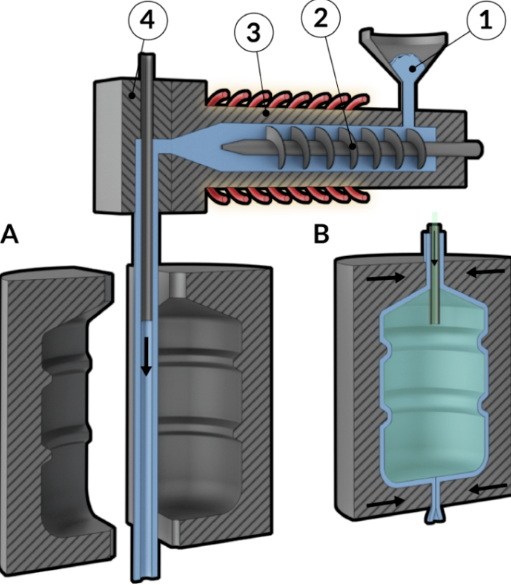
Comparison Between Extrusion Moulding and Injection Moulding
While both extrusion and injection moulding are popular methods for shaping plastics, they differ significantly in their processes and applications.
| Feature | Extrusion Moulding | Injection Moulding |
| Shape Produced | Continuous linear shapes (2D) | Complex three-dimensional shapes (3D) |
| Process Type | Continuous | Batch |
| Mould/Dies Used | Die for continuous profile | Mould for specific shapes |
| Cycle Time | Generally faster due to continuous nature | Slower due to batch processing |
| Setup Cost | Lower setup costs | Higher setup costs due to custom moulds |
Advantages of Extrusion Moulding
- High Production Efficiency: The continuous nature of extrusion allows for high-volume production rates.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower tooling costs compared to injection moulding make extrusion more economical for certain applications.
- Versatility in Shapes: Custom dies can produce various profiles, accommodating diverse product requirements.
- Smooth Surface Finish: Extruded products often have a smooth finish that requires little post-processing.
Limitations of Extrusion Moulding
- Shape Complexity: Limited to simpler shapes; intricate designs may not be feasible.
- Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for extrusion; thermoplastics work best.
- Cooling Challenges: Uneven cooling can lead to warping or dimensional inaccuracies in some cases.
The Importance of Temperature Control
Temperature control during the extrusion process is crucial for ensuring product quality.
- If the temperature is too low, the material may not melt completely, leading to blockages or inconsistencies in flow.
- Conversely, excessive heat can degrade the polymer properties, resulting in poor mechanical performance or discoloration.
Maintaining optimal temperatures ensures uniform melting and consistent product quality throughout production runs.
Post-Extrusion Processing
After extrusion, additional processes may be necessary to achieve desired specifications:
- Cutting: Products are often cut to length based on customer requirements.
- Coating or Printing: Some products may undergo surface treatments for aesthetics or functionality.
- Thermal Treatment: Certain applications might require annealing or other thermal processes to enhance material properties.
Environmental Considerations
The extrusion process can also be designed with sustainability in mind:
- Many thermoplastics used in extrusion are recyclable.
- Manufacturers can implement closed-loop systems where waste material is reprocessed back into production lines.
This focus on sustainability not only reduces environmental impact but also lowers production costs by minimizing waste.
Conclusion
Extrusion moulding is an essential process in plastic manufacturing that offers numerous advantages for producing continuous profiles efficiently. While it shares similarities with injection moulding, each method has its unique strengths and weaknesses tailored to specific applications. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers choose the right process for their needs. As technology evolves, advancements in extrusion techniques continue to expand its capabilities across various industries while promoting sustainable practices.
FAQ
1. What materials are commonly used in extrusion moulding?
Extrusion moulding primarily uses thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
2. How does extrusion differ from injection moulding?
Extrusion produces continuous shapes by pushing molten plastic through a die, while injection moulding fills a mold cavity with molten plastic to create discrete parts.
3. What types of products can be made using extrusion?
Common products include pipes, sheets, films, weatherstripping, window frames, and various custom profiles.
4. What are the benefits of using extrusion moulding?
Benefits include high production efficiency, lower setup costs compared to injection moulding, versatility in shapes, and smooth surface finishes.
5. Can extrusion be used for complex shapes?
No, extrusion is limited to simpler two-dimensional shapes; complex three-dimensional designs are better suited for injection moulding.
Citations:
[1] https://paulmurphyplastics.com/industry-news-blog/the-plastic-extrusion-process-explained-in-5-steps/
[2] https://www.clarkrandp.com/6-common-applications-of-plastic-extrusion/
[3] https://haluminium.com/Product/aluminum-extrusion-molding/
[4] https://www.goodfishgroup.com/the-step-by-step-process-of-plastic-extrusion
[5] https://plasticextrusiontech.net/applications/
[6] https://www.wangbrand.com/en/faq_02.htm
[7] https://adrecoplastics.co.uk/extrusion-moulding/
[8] https://cbmplasticsusa.com/plastic-extrusion-process-materials-and-applications/
[9] https://www.howardprecision.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-direct-extrusion/
[10] https://www.rayda.co.uk/blog/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-plastic-extrusion/
[11] https://stonermolding.com/blog/knowledge-base/2024/06/24/what-is-extrusion-molding-and-how-does-it-work
[12] https://www.3erp.com/blog/plastic-extrusion/
[13] https://khatabook.com/blog/extrusion-process-working-types-application-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[14] https://www.pbsplastics.com/what-is-the-difference-between-plastics-extrusion-and-injection-molding/
[15] https://paulmurphyplastics.com/industry-news-blog/extrusion-process-working-types-application-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[16] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extrusion_moulding
[17] https://www.longshengmfg.com/what-is-extrusion-moulding-process/
[18] https://waykenrm.com/blogs/plastic-extrusion-process/
[19] https://www.xometry.com/resources/injection-molding/injection-molding-vs.-extrusion/






















