Content Menu
● Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
● Understanding the Aluminum Extrusion Process
● Extrusion Press Operation
● Extrusion Die Design
● Hollow Profile Extrusion
● Aluminum Alloy Selection
● Quality Control in Extrusion
● Extruded Aluminum Applications
● Advancements in Aluminum Extrusion Technology
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> Q1: What is the main difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
>> Q2: How does the choice of aluminum alloy affect the extrusion process?
>> Q3: What are the advantages of aluminum extrusion over other manufacturing processes?
>> Q4: How is quality control maintained in the aluminum extrusion process?
>> Q5: What recent advancements have been made in aluminum extrusion technology?
Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion is a versatile manufacturing process that has revolutionized various industries, from construction to aerospace. This technique allows for the creation of complex shapes and profiles with exceptional precision, making it an indispensable method in modern manufacturing. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of the Aluminum Extrusion Process, exploring its methods, applications, and the science behind this remarkable technology.
Understanding the Aluminum Extrusion Process
The Aluminum Extrusion Process is a method of shaping aluminum by forcing it through a die with a specific cross-sectional profile. This process can be likened to squeezing toothpaste out of a tube, where the shape of the nozzle determines the shape of the extruded paste. In the case of aluminum extrusion, the "toothpaste" is a heated aluminum billet, and the "nozzle" is a carefully designed extrusion die.
The process begins with Billet Preparation. A billet is a solid cylinder of aluminum alloy that serves as the raw material for extrusion. These billets are cut to specific lengths depending on the desired length of the final extruded product. The billet is then preheated to a temperature range of 800°F to 925°F (427°C to 496°C), which makes the aluminum malleable enough for extrusion without melting it completely.
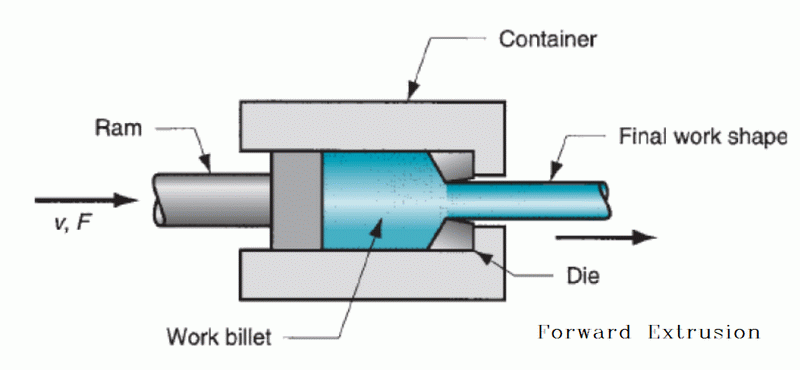
Extrusion Press Operation
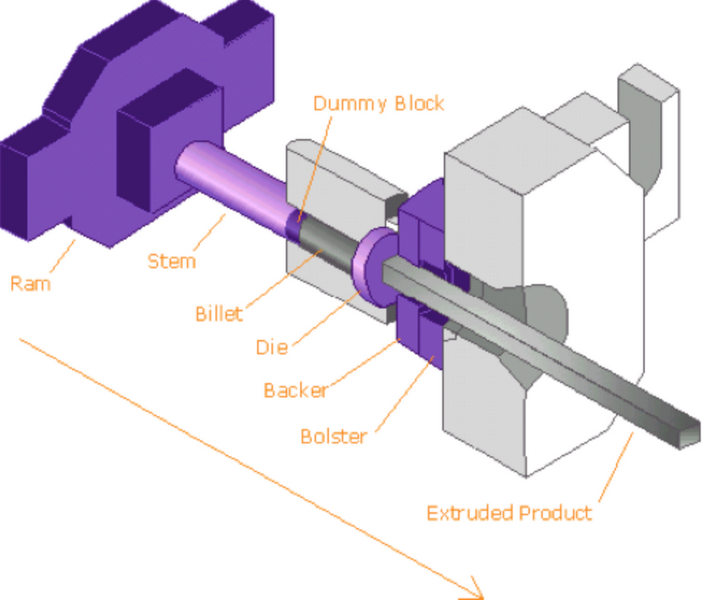
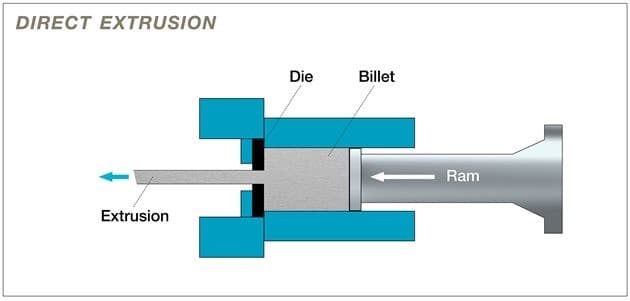
Once the billet is heated, it is transferred to the extrusion press. The Extrusion Press Operation is at the heart of the aluminum extrusion process. There are two primary methods of extrusion: the Direct Extrusion Method and the Indirect Extrusion Technique.
In the Direct Extrusion Method, which is more common, the heated billet is placed into a container in the extrusion press. A ram then pushes the billet, forcing the softened aluminum through a die. The die is a precisely engineered tool with an opening that matches the desired cross-section of the final product. As the aluminum is forced through the die, it takes on the shape of the die's opening, emerging on the other side as a fully formed profile.
The Indirect Extrusion Technique, on the other hand, involves a stationary billet while the die and ram move towards the billet. This method reduces friction and allows for the extrusion of more complex shapes, but it is less commonly used due to limitations in billet length and increased complexity of the machinery.
Extrusion Die Design
The Extrusion Die Design is crucial to the success of the aluminum extrusion process. Dies are typically made from tool steel and are designed to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the extrusion process. The design of the die determines not only the shape of the extruded profile but also affects the flow of aluminum during extrusion, which in turn influences the quality and properties of the final product.
There are several types of dies used in aluminum extrusion:
1. Solid dies: Used for creating solid profiles
2. Hollow dies: Used for creating hollow profiles
3. Semi-hollow dies: Used for profiles with partially enclosed voids
The design of these dies requires extensive expertise and often involves computer simulations to optimize metal flow and ensure the desired profile is achieved consistently.
Hollow Profile Extrusion
Hollow Profile Extrusion is a specialized technique that allows for the creation of complex shapes with internal cavities. This process is particularly useful for creating structural components that need to be lightweight yet strong, such as framing for windows and doors.
The process of hollow profile extrusion involves using a die with a mandrel. The mandrel is a tool that creates the internal shape of the hollow profile. As the aluminum flows around the mandrel and through the die, it forms a hollow shape. This technique requires precise control of metal flow and temperature to ensure the hollow sections are formed correctly without collapsing or deforming.
Aluminum Alloy Selection
Aluminum Alloy Selection is a critical aspect of the extrusion process. Different alloys have varying properties that affect their extrudability and the characteristics of the final product. Some common alloys used in extrusion include:
1. 6061: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good strength
2. 6063: Offers good extrudability and surface finish, commonly used in architectural applications
3. 7075: Provides high strength, often used in aerospace applications
The choice of alloy depends on the intended application of the extruded product, considering factors such as strength requirements, corrosion resistance, and surface finish needs.
Quality Control in Extrusion
Quality Control in Extrusion is essential to ensure that the extruded products meet the required specifications and standards. This involves several steps throughout the extrusion process:
1. Pre-extrusion checks: Ensuring the billet quality and proper die preparation
2. In-process monitoring: Controlling extrusion speed, temperature, and pressure
3. Post-extrusion inspection: Checking dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and mechanical properties
Advanced techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection may be used to detect internal defects in the extruded profiles.
Extruded Aluminum Applications
The versatility of the aluminum extrusion process has led to its widespread use across various industries. Some notable Extruded Aluminum Applications include:
1. Construction: Window frames, door frames, curtain walls
2. Transportation: Automotive body parts, railway car components
3. Electronics: Heat sinks, LED housings
4. Aerospace: Aircraft structural components
5. Consumer goods: Furniture, sporting equipment
The ability to create complex shapes with high precision and consistency makes aluminum extrusion an attractive manufacturing method for a wide range of products.
Advancements in Aluminum Extrusion Technology
The field of aluminum extrusion continues to evolve with technological advancements. Some recent developments include:
1. Computer-aided die design: Improving die efficiency and reducing trial-and-error in die manufacturing
2. Automated extrusion systems: Enhancing productivity and consistency in production
3. Advanced alloy development: Creating new alloys with improved extrudability and end-use properties
4. Sustainable practices: Implementing energy-efficient processes and increasing the use of recycled aluminum
These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what's possible with aluminum extrusion, opening up new applications and improving the efficiency of the process.
Conclusion
The Aluminum Extrusion Process is a fascinating blend of engineering, metallurgy, and precision manufacturing. From the initial Billet Preparation to the final Quality Control in Extrusion, each step of the process plays a crucial role in creating high-quality extruded products. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and improvements in this versatile manufacturing technique.
Whether you're an engineer designing new products, a manufacturer looking to optimize your processes, or simply someone curious about how things are made, understanding the aluminum extrusion process provides valuable insights into one of the most important manufacturing methods of our time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the main difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
A1: The main difference lies in the movement of components. In direct extrusion, the billet is pushed through a stationary die, while in indirect extrusion, the die moves towards a stationary billet. Direct extrusion is more common but can result in more friction, while indirect extrusion can produce more complex shapes but is limited in billet length.
Q2: How does the choice of aluminum alloy affect the extrusion process?
A2: The choice of aluminum alloy significantly impacts the extrusion process. Different alloys have varying extrudability, which affects the ease of extrusion and the quality of the final product. For example, 6063 alloy is known for its excellent extrudability and surface finish, making it ideal for architectural applications, while 7075 alloy offers high strength but is more challenging to extrude.
Q3: What are the advantages of aluminum extrusion over other manufacturing processes?
A3: Aluminum extrusion offers several advantages, including:
- Ability to create complex shapes in a single process
- High production speeds for long, continuous profiles
- Excellent surface finish without additional processing
- Cost-effectiveness for medium to high volume production
- Ability to easily customize profiles by changing dies
Q4: How is quality control maintained in the aluminum extrusion process?
A4: Quality control in aluminum extrusion involves multiple steps:
- Pre-extrusion checks of billet quality and die condition
- Monitoring of extrusion parameters like speed, temperature, and pressure during the process
- Post-extrusion inspections for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and mechanical properties
- Advanced testing methods like ultrasonic or X-ray inspection for internal defects
Q5: What recent advancements have been made in aluminum extrusion technology?
A5: Recent advancements in aluminum extrusion technology include:
- Computer-aided die design for improved efficiency
- Automated extrusion systems for enhanced productivity
- Development of new aluminum alloys with improved properties
- Implementation of sustainable practices, including energy-efficient processes and increased use of recycled aluminum
- Advanced simulation tools for optimizing metal flow and predicting extrusion outcomes






















