Content Menu
● Understanding Aluminum Extrusion Defects
● Common Types of Aluminum Extrusion Surface Defects
● Identifying Surface Defects
● The Importance of Early Detection
● Fixing Aluminum Extrusion Surface Defects
>> Prevention Strategies
>> Rectification Techniques
● The Role of Technology in Detecting Defects
● Conclusion
● Related Questions
>> 1. What are the most common types of aluminum extrusion defects?
>> 2. How can I prevent scratches on extruded aluminum profiles?
>> 3. What causes die lines in aluminum extrusions?
>> 4. How can I identify internal defects in aluminum extrusions?
>> 5. What treatments can improve the appearance of defective aluminum profiles?
Aluminum extrusion is a widely utilized manufacturing process that shapes aluminum into various profiles by forcing it through a die. While this process offers numerous advantages, including versatility and efficiency, it is not without its challenges. One of the most significant issues faced by manufacturers is the occurrence of surface defects in aluminum extrusions. Understanding how to identify and rectify these defects is crucial for maintaining product quality and meeting customer expectations.
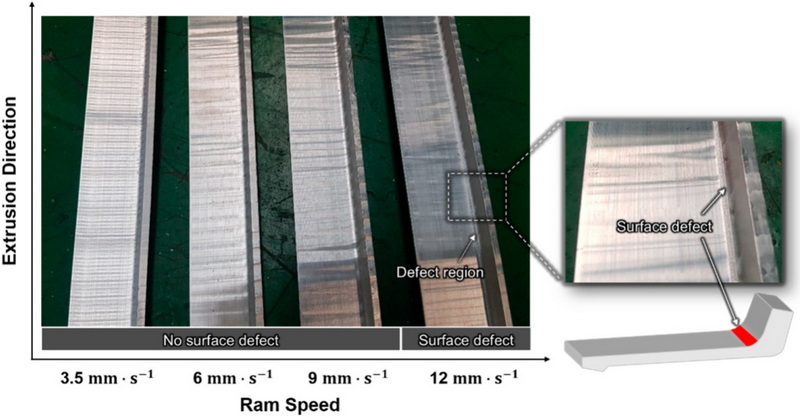
Understanding Aluminum Extrusion Defects
Aluminum extrusion defects can be broadly classified into three categories:
- Surface Defects: These affect the external appearance of the product and can include scratches, die lines, and blisters.
- Dimensional Defects: These refer to variations in size or shape that can impact the functionality of the extruded product.
- Internal Defects: These are not visible on the surface but can compromise the structural integrity of the extrusion.
This article will primarily focus on surface defects, which are often the most noticeable and can significantly affect the aesthetic appeal and usability of aluminum profiles.
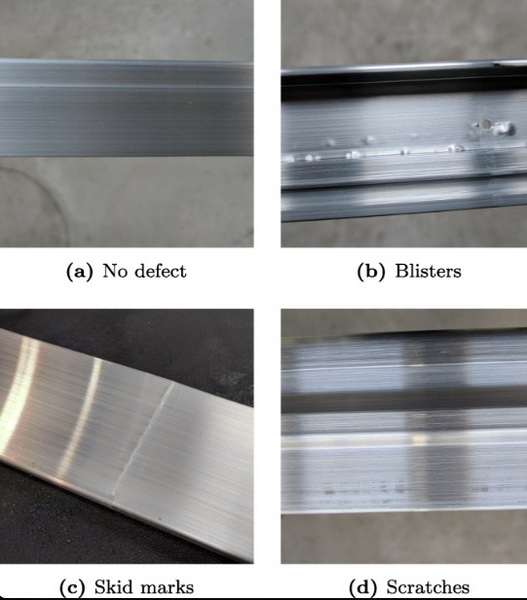
Common Types of Aluminum Extrusion Surface Defects
1. Scratches
- Description: Superficial abrasions or grooves on the surface.
- Causes: Poor handling, insufficient lubrication, or foreign particles in the die.
2. Die Lines
- Description: Longitudinal grooves or marks caused by imperfections on the die surface.
- Causes: Wear and tear on dies or improper die maintenance.
3. Blisters
- Description: Raised bubbles on the surface resulting from trapped gases or moisture.
- Causes: Inadequate preheating of billets or high moisture content in raw materials.
4. Pick-Ups
- Description: Small particles of aluminum that adhere to the surface, creating a rough texture.
- Causes: Contaminants on the die or insufficient cleaning during production.
5. Peeling
- Description: Separation between layers of aluminum due to trapped air or poor adhesion.
- Causes: Improper lubrication or contamination during extrusion.
Identifying Surface Defects
Identifying surface defects in aluminum extrusions involves a combination of visual inspection and testing methods:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly examining extruded profiles for visible defects such as scratches, blisters, and die lines. This should be done under good lighting conditions to ensure all imperfections are detected.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing can help identify internal defects that may not be visible on the surface but could affect performance.
- Surface Roughness Measurement: Tools such as profilometers can quantify surface roughness, providing a more objective assessment of defect severity.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of surface defects is vital for minimizing waste and reducing production costs. By identifying issues at an early stage, manufacturers can take corrective actions before large quantities of defective products are produced. Implementing a robust quality control system that includes regular inspections and testing can help catch defects before they become significant problems.
Fixing Aluminum Extrusion Surface Defects
Addressing surface defects requires a systematic approach that includes prevention, identification, and rectification strategies:
Prevention Strategies
1. Material Quality Control:
- Ensure that raw materials are free from impurities and meet quality standards before extrusion begins. This includes verifying alloy composition and checking for any signs of contamination.
2. Die Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect and clean dies to prevent wear and contamination that can lead to die lines and pick-ups. Implementing a scheduled maintenance program can help prolong die life and maintain product quality.
3. Proper Lubrication:
- Use high-quality lubricants to minimize friction between the aluminum and die surfaces, reducing scratches and other defects. Regularly check lubricant levels and ensure that lubrication systems are functioning correctly.
4. Temperature Control:
- Maintain optimal temperatures during extrusion to prevent issues like blistering and peeling. Preheat billets adequately to remove moisture, which can lead to gas entrapment during extrusion.
5. Handling Procedures:
- Implement strict handling protocols to avoid scratches during transportation and storage of extruded profiles. Use protective coverings or padding when moving profiles to prevent contact with hard surfaces.
6. Training Personnel:
- Train employees on best practices for handling aluminum extrusions, including how to recognize potential sources of defects during production.
Rectification Techniques
1. Surface Treatment:
- Use processes such as anodizing or polishing to improve surface quality after extrusion. Anodizing not only enhances appearance but also increases corrosion resistance, making it an effective solution for many surface defects.
2. Reworking Defective Profiles:
- For significant defects, rework may be necessary. This could involve cutting out defective sections or re-extruding parts of the profile if feasible. In some cases, welding may be employed to repair damaged areas before finishing treatments are applied.
3. Quality Audits:
- Conduct regular audits of production processes to identify areas for improvement in defect prevention strategies. This includes reviewing inspection records, analyzing defect data, and implementing corrective actions based on findings.
4. Feedback Loop:
- Establish a feedback loop between production teams and quality control personnel to ensure that any identified issues are communicated effectively and addressed promptly.
5. Investing in Technology:
- Utilize advanced technologies such as machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance of equipment used in extrusion processes. This proactive approach can help prevent defects caused by equipment failure or wear over time.
The Role of Technology in Detecting Defects
The integration of technology into defect detection processes has proven beneficial for manufacturers:
- Automated Inspection Systems: Utilizing cameras equipped with image recognition software allows for real-time monitoring of extruded profiles as they exit the line, enabling immediate identification of visible defects like scratches or blisters.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing historical defect data helps identify patterns in defect occurrences, allowing manufacturers to address root causes systematically rather than just treating symptoms.
- Simulation Software: Advanced simulation tools can model the extrusion process under various conditions, helping engineers predict potential defect formation before actual production begins.
Conclusion
Identifying and fixing aluminum extrusion surface defects is essential for maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction. By understanding common types of defects, implementing effective prevention strategies, employing rectification techniques when necessary, and leveraging modern technology for detection and analysis, manufacturers can significantly reduce the occurrence of these issues. Continuous monitoring and improvement of processes will ensure high-quality aluminum profiles that meet industry standards while minimizing waste and enhancing overall productivity.
Related Questions
1. What are the most common types of aluminum extrusion defects?
The most common types include scratches, die lines, blisters, pick-ups, and peeling.
2. How can I prevent scratches on extruded aluminum profiles?
Prevent scratches by ensuring proper lubrication during extrusion, implementing careful handling procedures, using high-quality raw materials, and training personnel in best practices for handling profiles.
3. What causes die lines in aluminum extrusions?
Die lines are typically caused by wear on the die surfaces or contamination during production processes; regular maintenance is critical to minimize these issues.
4. How can I identify internal defects in aluminum extrusions?
Internal defects can be identified using non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing or through careful visual inspections for signs of structural weakness; integrating automated inspection systems can enhance detection capabilities further.
5. What treatments can improve the appearance of defective aluminum profiles?
Treatments such as anodizing or polishing can enhance surface quality by removing minor imperfections while improving corrosion resistance; reworking defective sections may also be necessary depending on defect severity.






















