Content Menu
● Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
● What is Aluminum Extrusion?
● The Aluminum Extrusion Process: Step by Step
>> 1. Aluminum Billet Preparation
>> 2. Preheating the Billet
>> 3. Lubrication
>> 4. Extrusion
>>> Direct Extrusion Technique
>>> Indirect Extrusion Method
>> 5. Cooling and Stretching
>> 6. Cutting and Finishing
● Extrusion Die Design: The Key to Customization
● Aluminum Alloy Extrusion: Choosing the Right Material
● Applications of Extruded Aluminum Profiles
● Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion Manufacturing
● Innovations in Aluminum Profile Customization
● The Future of Aluminum Extrusion
● Video: Understanding the Aluminum Extrusion Process
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> Q1: What is the main difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
>> Q2: How does the choice of aluminum alloy affect the extrusion process?
>> Q3: What are some common applications of extruded aluminum profiles?
>> Q4: How does extrusion die design impact the final product?
>> Q5: What are the environmental benefits of aluminum extrusion?
Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion is a sophisticated manufacturing process that has revolutionized various industries, from construction to aerospace. This versatile technique allows for the creation of complex shapes and profiles with remarkable precision and efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the Aluminum Extrusion Process, exploring its methods, applications, and significance in modern manufacturing.
What is Aluminum Extrusion?
Aluminum Extrusion is a manufacturing technique where aluminum alloy is forced through a die with a specific cross-sectional profile. This process transforms a solid aluminum billet into a shaped product with a consistent cross-section. The resulting extruded aluminum profiles can be customized to meet various design specifications, making it an invaluable method for producing components for diverse applications.
The Aluminum Extrusion Process: Step by Step
1. Aluminum Billet Preparation
The process begins with Aluminum Billet Preparation. A billet is a solid, cylindrical block of aluminum alloy that serves as the raw material for extrusion. These billets are carefully selected based on the desired properties of the final product, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and formability.
2. Preheating the Billet
Before extrusion, the aluminum billet is preheated to temperatures ranging from 800°F to 925°F (425°C to 500°C). This heating process softens the aluminum, making it more malleable and easier to extrude without reaching its melting point.
3. Lubrication
The die and other components of the extrusion press are lubricated to reduce friction and ensure smooth material flow during the extrusion process. This step is crucial for maintaining the quality of the extruded product and prolonging the life of the equipment.
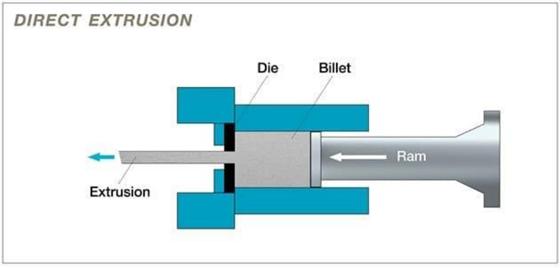
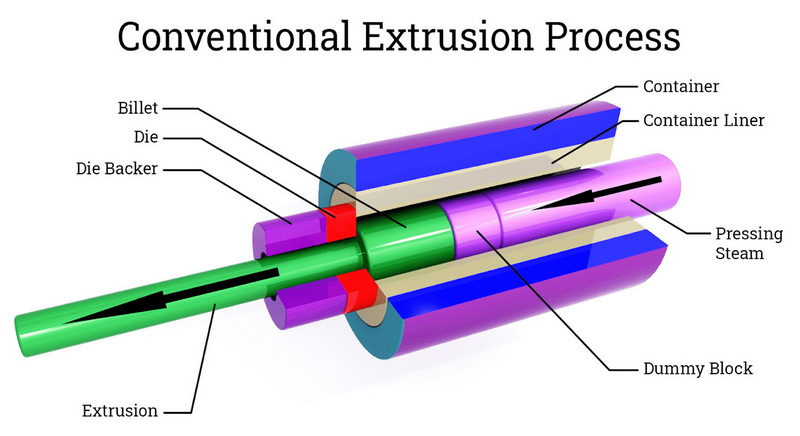
4. Extrusion
The heart of the Aluminum Extrusion Process lies in this step. There are two primary methods of extrusion:
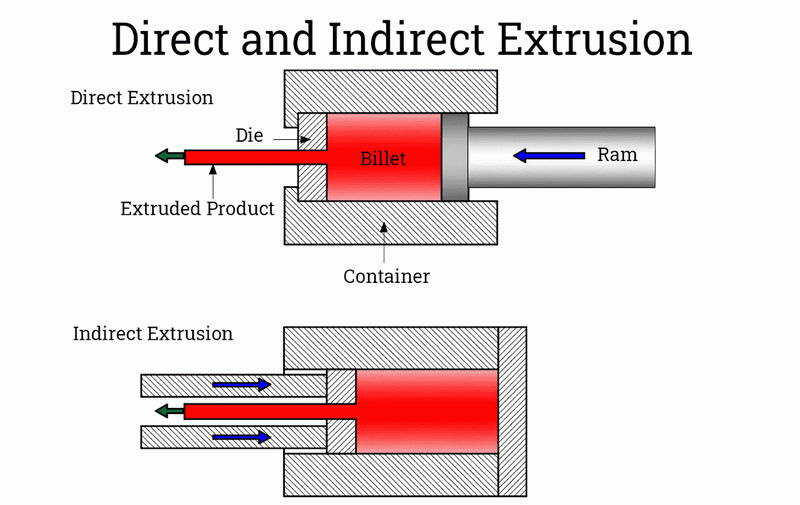
Direct Extrusion Technique
In the Direct Extrusion Technique, also known as forward extrusion, a ram pushes the heated billet through a stationary die. As the aluminum is forced through the die, it takes on the shape of the die's opening, creating the desired profile.
Indirect Extrusion Method
The Indirect Extrusion Method, or backward extrusion, involves a stationary ram and a moving container. The die is attached to the ram, and the container holding the billet moves towards the die, forcing the aluminum through it. This method typically results in less friction and can be more efficient for certain types of profiles.
5. Cooling and Stretching
After extrusion, the aluminum profile is cooled, either by air or water quenching, depending on the alloy and desired properties. The profile is then stretched to straighten it and relieve internal stresses, ensuring dimensional accuracy.
6. Cutting and Finishing
The extruded profiles are cut to the required lengths and may undergo additional finishing processes such as heat treatment, surface finishing, or machining to meet specific product requirements.
Extrusion Die Design: The Key to Customization
Extrusion Die Design plays a crucial role in the aluminum extrusion process. The die is a precision tool that determines the cross-sectional shape of the extruded profile. Skilled engineers design these dies to create a wide range of shapes, from simple geometric forms to complex, custom profiles.
Aluminum Alloy Extrusion: Choosing the Right Material
The choice of aluminum alloy significantly impacts the properties of the extruded product. Common alloys used in Aluminum Alloy Extrusion include:
- 6061: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good strength
- 6063: Offers a smooth surface finish, ideal for architectural applications
- 7075: Provides high strength, often used in aerospace components
Each alloy brings unique characteristics to the extruded product, allowing manufacturers to tailor the material properties to specific applications.
Applications of Extruded Aluminum Profiles
The versatility of Extruded Aluminum Profiles has led to their widespread use across various industries:
1. Construction: Window frames, door frames, and structural components
2. Transportation: Automotive body parts, railway car components
3. Electronics: Heat sinks, LED housings
4. Aerospace: Aircraft structural components
5. Renewable Energy: Solar panel frames, wind turbine components
Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion Manufacturing
Aluminum Extrusion Manufacturing offers several benefits:
1. Design Flexibility: Complex shapes can be created in a single process
2. Cost-Effectiveness: High production rates and minimal material waste
3. Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum's lightweight nature combined with the strength of extruded profiles
4. Sustainability: Aluminum is recyclable, making the process environmentally friendly
5. Surface Finish: Excellent surface quality straight from the extrusion process
Innovations in Aluminum Profile Customization
Advancements in technology have expanded the possibilities for Aluminum Profile Customization. Computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools allow engineers to optimize profile designs for specific performance requirements. Additionally, multi-hole dies and porthole dies enable the creation of hollow sections and more intricate shapes, further broadening the range of possible applications.
The Future of Aluminum Extrusion
As industries continue to demand lighter, stronger, and more efficient materials, the Aluminum Extrusion Process is poised for further innovation. Research into new alloys, improved die designs, and more efficient extrusion techniques promises to expand the capabilities of this versatile manufacturing method.
Video: Understanding the Aluminum Extrusion Process
To better visualize the Aluminum Extrusion Process, watch this informative video:
This video provides a clear explanation of the aluminum extrusion process, offering valuable insights into each step of the manufacturing technique.
Conclusion
The Aluminum Extrusion Process stands as a testament to human ingenuity in manufacturing. By understanding the intricacies of this process, from Aluminum Billet Preparation to the final Extruded Aluminum Applications, we can appreciate the complexity and versatility of this manufacturing technique. As technology advances and new challenges arise, aluminum extrusion will undoubtedly continue to play a crucial role in shaping our modern world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the main difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
A1: The main difference lies in the movement of components. In direct extrusion, the ram pushes the billet through a stationary die, while in indirect extrusion, the die moves towards a stationary billet. Indirect extrusion typically results in less friction and can be more efficient for certain profiles.
Q2: How does the choice of aluminum alloy affect the extrusion process?
A2: Different aluminum alloys have varying properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and formability. The choice of alloy affects the extrusion temperature, pressure required, and the final properties of the extruded product. For example, harder alloys may require higher extrusion pressures but result in stronger profiles.
Q3: What are some common applications of extruded aluminum profiles?
A3: Extruded aluminum profiles are widely used in construction (window frames, door frames), transportation (automotive parts), electronics (heat sinks), aerospace (structural components), and renewable energy (solar panel frames). Their versatility makes them suitable for numerous applications across various industries.
Q4: How does extrusion die design impact the final product?
A4: Extrusion die design is crucial as it determines the cross-sectional shape of the extruded profile. A well-designed die ensures proper material flow, consistent wall thickness, and the ability to create complex shapes. The die design also affects the extrusion speed and the quality of the final product.
Q5: What are the environmental benefits of aluminum extrusion?
A5: Aluminum extrusion is considered environmentally friendly for several reasons. Aluminum is 100% recyclable without loss of quality, and the extrusion process itself produces minimal waste. Additionally, extruded aluminum products are lightweight, which can lead to energy savings in transportation applications. The long lifespan of aluminum products also contributes to their sustainability.






















