Content Menu
● Understanding Extrusion
● Types of Extrusion Processes
● The Extrusion Process Steps
● Detailed Explanation of Each Step
>> 1. Preparation of Raw Material
>> 2. Heating
>> 3. Feeding into the Extruder
>> 4. Shaping through the Die
>> 5. Cooling
>> 6. Cutting and Finishing
● Applications of Extrusion
● Advantages of Extrusion
● Challenges in Extrusion
● Emerging Technologies in Extrusion
● Future Trends in Extrusion Production
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials can be extruded?
>> 2. How does temperature affect the extrusion process?
>> 3. What is the difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
>> 4. Can recycled materials be used in extrusion?
>> 5. How do manufacturers ensure quality during extrusion?
● Citations:
The extrusion production process is a fundamental manufacturing method used across various industries, including plastics, metals, and food. This article will delve into the intricacies of the extrusion process, exploring its types, applications, advantages, and challenges. We will also provide visual aids and video links to enhance understanding.
Understanding Extrusion
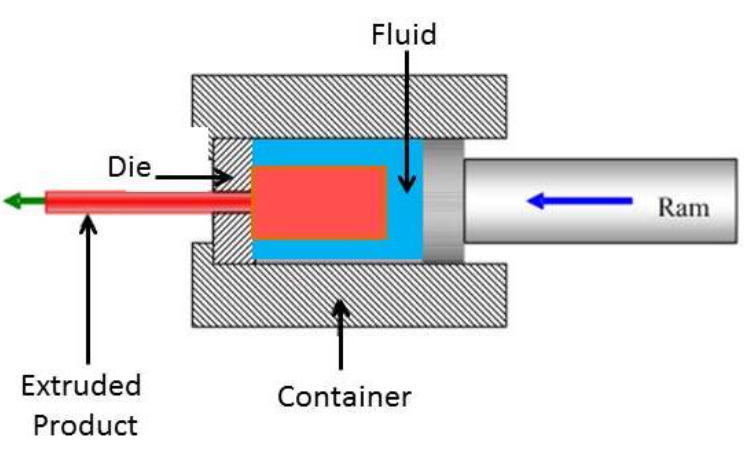
Extrusion is a process where raw materials are forced through a die to create objects with a fixed cross-sectional profile. This method is widely utilized for producing continuous shapes such as pipes, sheets, and profiles in both plastic and metal forms.
Types of Extrusion Processes
There are several types of extrusion processes, each suited for different materials and applications:
- Direct Extrusion: The most common method where the material is pushed through the die.
- Indirect Extrusion: The die moves with the ram, reducing friction and allowing for more complex shapes.
- Cold Extrusion: Conducted at or near room temperature, ideal for materials requiring high strength.
- Hot Extrusion: Involves heating the material before extrusion to enhance flow characteristics.
- Plastic Extrusion: A high-volume manufacturing process where thermoplastic materials are melted and formed continuously.
The Extrusion Process Steps
The extrusion process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Preparation of Raw Material: The raw material, either metal or plastic, is prepared in specific forms such as billets or pellets.
2. Heating: For metals like aluminum, the billets are heated to a temperature that makes them malleable but not molten. For plastics, pellets are heated until they melt.
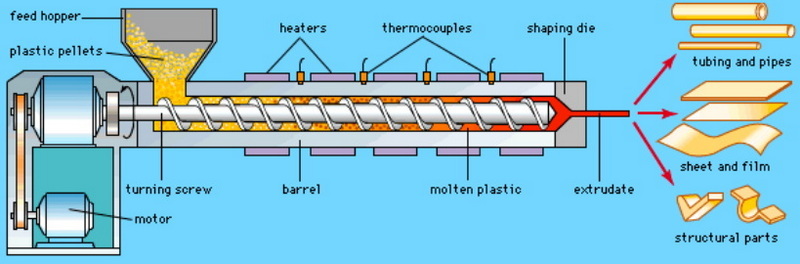
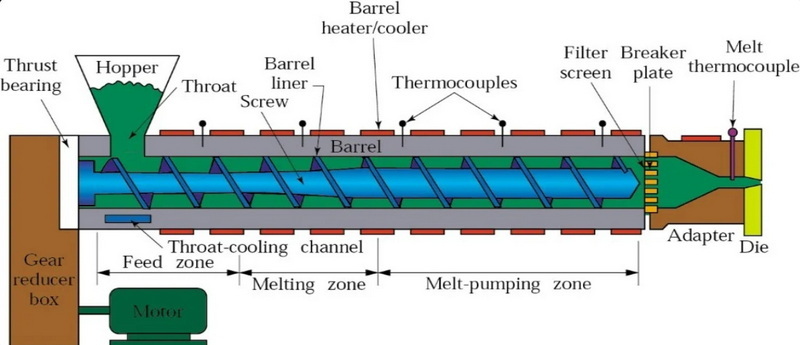
3. Feeding into the Extruder: The prepared material is fed into an extruder where it is subjected to heat and pressure.
4. Shaping through the Die: The molten material is forced through a die that shapes it into the desired profile.
5. Cooling: After exiting the die, the extrudate is cooled to solidify it into its final form.
6. Cutting and Finishing: The extruded product is cut to length and may undergo additional finishing processes such as machining or surface treatment.
Detailed Explanation of Each Step
1. Preparation of Raw Material
In metal extrusion, a billet (a solid cylindrical piece) is used as the raw material. For plastic extrusion, granules or pellets are prepared with any necessary additives like colorants or UV inhibitors.
2. Heating
For metals like aluminum, billets are typically heated to around 900°F (482°C) to soften them without melting. In plastic extrusion, temperatures vary based on the type of polymer used but generally range from 350°F to 500°F (177°C to 260°C).
3. Feeding into the Extruder
The extruder consists of a barrel with a rotating screw that pushes the material forward while applying heat. This process ensures that the material melts uniformly before reaching the die.
4. Shaping through the Die
As pressure builds up within the extruder, the molten material is forced through a die that has been designed specifically for the desired shape. This die can create various profiles depending on its design—ranging from simple rods to complex shapes like tubes or sheets.
5. Cooling
Once the extrudate exits the die, it must be cooled quickly to maintain its shape. Cooling methods can include air cooling or water baths (quenching), depending on the material being processed.
6. Cutting and Finishing
After cooling, the extruded product is cut to specified lengths using saws or other cutting equipment. Further finishing processes may include surface treatments such as anodizing for metals or printing for plastics.
Applications of Extrusion
Extrusion has a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Construction: Aluminum profiles for windows and doors.
- Automotive: Components made from lightweight materials for fuel efficiency.
- Packaging: Plastic films and sheets for food packaging.
- Electronics: Insulation for wires and cables.
- Medical: Tubing for medical devices.
Advantages of Extrusion
The extrusion process offers numerous benefits:
- High Efficiency: Continuous production leads to less waste compared to other manufacturing methods.
- Versatility: Can be used with various materials including metals and plastics.
- Complex Shapes: Capable of producing intricate designs that would be difficult with other methods.
- Cost-effective: Lower production costs due to reduced labor and material waste.
Challenges in Extrusion
Despite its advantages, extrusion also faces certain challenges:
- Material Limitations: Not all materials can be extruded effectively.
- Die Wear: Constant pressure can wear down dies over time, requiring replacements.
- Quality Control: Maintaining consistent quality can be challenging due to variations in material properties or processing conditions.
Emerging Technologies in Extrusion
As industries evolve, so does technology within extrusion processes. Several emerging technologies are shaping how extrusion is performed today:
- 3D Printing Integration: This allows for creating complex dies that were previously difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into extrusion processes for predictive maintenance, optimizing operations, and improving quality control by identifying defects early in production.
- Hybrid Processes: Combining traditional extrusion with additive manufacturing techniques allows for greater design flexibility and reduces waste by enabling intricate internal geometries that would otherwise require additional manufacturing steps.
- Rapid Quench Systems: These systems improve cooling efficiency after extrusion, which enhances product quality by ensuring uniform cooling across all sections of an extruded profile.
Future Trends in Extrusion Production
The future of extrusion production looks promising with ongoing advancements aimed at improving efficiency and sustainability:
- Sustainability Initiatives: Many companies are focusing on reducing carbon emissions throughout their production processes by utilizing recycled materials more effectively and adopting greener technologies.
- Enhanced Material Properties: Research into new aluminum alloys and composite materials promises stronger yet lighter products suitable for demanding applications in automotive and aerospace industries.
- Automation and Robotics: Increasing automation in production lines will streamline operations further while reducing labor costs and human error in quality control processes.
Conclusion
The extrusion production process is a vital manufacturing technique that plays a significant role in various industries by enabling efficient production of complex shapes from both metals and plastics. Understanding its workings allows industries to optimize their production techniques while maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency. As technology continues to advance within this field, we can expect further innovations that will enhance productivity while addressing environmental concerns associated with manufacturing processes.
FAQ
1. What materials can be extruded?
Extrusion can be performed on various materials including metals (like aluminum), thermoplastics (like PVC), and even food products.
2. How does temperature affect the extrusion process?
Temperature significantly impacts material flow; higher temperatures generally improve flow characteristics but may also affect mechanical properties if too high.
3. What is the difference between direct and indirect extrusion?
In direct extrusion, material is pushed directly through a stationary die; in indirect extrusion, the die moves with the ram which reduces friction during processing.
4. Can recycled materials be used in extrusion?
Yes, many manufacturers incorporate recycled materials into their extrusion processes which helps reduce waste and costs.
5. How do manufacturers ensure quality during extrusion?
Quality control measures include monitoring temperature, pressure settings, and conducting regular inspections of finished products for consistency in dimensions and properties.
Citations:
[1] https://paulmurphyplastics.com/industry-news-blog/extrusion-process-working-types-application-advantages-and-disadvantages/
[2] https://midstal.com/sft1242/aluminum_extrusion_process_overview.pdf
[3] https://www.clarkrandp.com/6-common-applications-of-plastic-extrusion/
[4] https://www.rayda.co.uk/blog/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-plastic-extrusion/
[5] https://profileprecisionextrusions.com/the-evolution-of-aluminum-extrusions-emerging-trends-and-technologies/
[6] https://www.gabrian.com/what-is-aluminum-extrusion-process/
[7] https://onlytrainings.com/Polymer-Extrusion-Quick-Overview-Of-Extrusion-Process-and-Parameters
[8] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-common-applications-industrial-aluminum
[9] https://globalaluminium.com/the-future-of-aluminium-extrusion-emerging-technologies-and-innovations/
[10] https://www.tfgusa.com/understanding-extrusion-a-fundamental-manufacturing-process/






















