Content Menu
● Understanding the Extrusion Process
>> Types of Extrusion
>> Production Volume Estimates
● Factors Influencing Production Range
● Applications of Extrusion
● Advantages of Extrusion
● Challenges in Extrusion
● Detailed Examination of Extrusion Processes
>> Hot vs. Cold vs. Warm Extrusion
>> Hydrostatic Extrusion
● Industry-Specific Applications
>> Construction Industry
>> Automotive Industry
>> Packaging Sector
>> Medical Field
● Future Trends in Extrusion Technology
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What types of materials are commonly extruded?
>> 2. How does die design affect production?
>> 3. What is the difference between hot and cold extrusion?
>> 4. Can extrusion be used for food products?
>> 5. What are some common applications of plastic extrusion?
● Citations:
Extrusion is a widely used manufacturing process that transforms raw materials into specific shapes by forcing them through a die. This method is prevalent across various industries, including plastics, metals, and food products. The range of production in the extrusion method can vary significantly based on several factors, including the type of material being extruded, the design of the die, and the intended application of the final product.
Understanding the Extrusion Process
Extrusion involves pushing a material through a specially designed die to create an object with a fixed cross-sectional profile. The process can be applied to a variety of materials such as metals, polymers, ceramics, and food products.
Types of Extrusion
- Hot Extrusion: Conducted above the material's recrystallization temperature, allowing for easier deformation. Commonly used for metals like aluminum and copper.
- Cold Extrusion: Performed at or near room temperature, ideal for materials that maintain their properties without heat. It produces parts with excellent surface finishes and dimensional accuracy.
- Warm Extrusion: This process operates at temperatures between hot and cold extrusion, balancing formability and mechanical properties.
- Direct (Forward) Extrusion: The material flows in the same direction as the applied force, commonly used for creating simple shapes.
- Indirect (Backward) Extrusion: The material flows in the opposite direction of the applied force, which reduces friction and energy consumption.
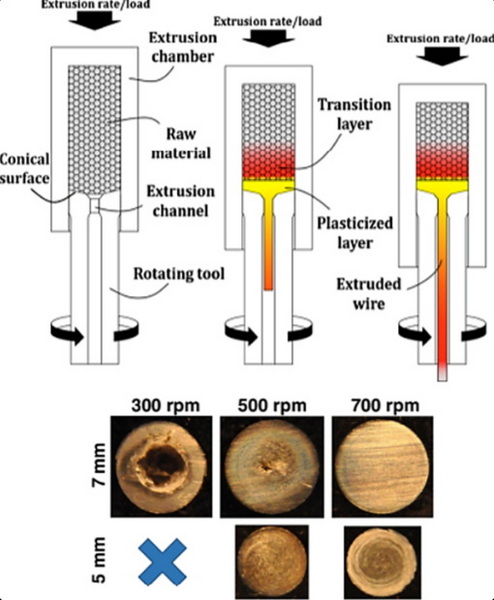
- Hydrostatic Extrusion: In this method, the billet is surrounded by a pressurized liquid, allowing for better control over the extrusion process and reducing friction.
Production Volume Estimates
- Plastic Extrusion: In plastic extrusion, production rates can range from 50 to 1,000 pounds per hour depending on the type of extruder and material used.
- Metal Extrusion: For metal extrusion, typical production rates vary widely based on material properties but can reach up to several tons per hour in high-capacity setups.
Factors Influencing Production Range
The range of production in extrusion is influenced by several key factors:
- Material Type: Different materials have varying flow characteristics and processing requirements. For instance, thermoplastics may allow for higher production rates compared to metals due to their lower viscosity when melted.
- Die Design: The complexity and size of the die affect how quickly and efficiently materials can be extruded. Custom dies can be designed for specific applications, impacting production volume.
- Extruder Capacity: The size and power of the extruder machinery determine how much material can be processed at once. Larger machines can handle higher volumes but may require more energy.
- Production Speed: The speed at which materials are fed into the extruder and pushed through the die significantly affects overall production rates. Faster speeds can lead to higher outputs but may compromise quality if not managed correctly.
Applications of Extrusion
The extrusion method is versatile and applicable in numerous industries:
- Construction: Producing window frames, door profiles, and structural components.
- Automotive: Manufacturing parts like weather seals, gaskets, and interior trim components.
- Packaging: Creating films, sheets, and containers that meet specific barrier properties.
- Medical Devices: Producing tubing and components that require precise dimensions and biocompatibility.
Advantages of Extrusion
The extrusion process offers several advantages:
- Cost Efficiency: High-volume production reduces costs per unit.
- Versatility: Capable of processing a wide range of materials into complex shapes.
- Quality Control: Provides consistent quality due to controlled processing conditions.
Challenges in Extrusion
Despite its benefits, extrusion also faces challenges:
- Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for extrusion; some may degrade or not flow properly through the die.
- Equipment Costs: Initial setup costs for extrusion equipment can be high.
Detailed Examination of Extrusion Processes
Hot vs. Cold vs. Warm Extrusion
The choice between hot, cold, or warm extrusion depends on the desired properties of the final product:
1. Hot Extrusion
- Performed above recrystallization temperatures.
- Allows for easier deformation.
- Commonly used for metals like aluminum.
- Can produce complex shapes with minimal defects.
- Typical temperature range is between 800 °F to 1800 °F (424 °C to 975 °C).
2. Cold Extrusion
- Conducted at or near room temperature.
- Ideal for producing high-strength components.
- Results in better surface finish and tighter tolerances.
- Suitable for materials that are sensitive to heat.
3. Warm Extrusion
- Operates between hot and cold temperatures.
- Balances ductility with strength.
- Useful for certain alloys that require specific mechanical properties post-extrusion.
Hydrostatic Extrusion
Hydrostatic extrusion employs a liquid medium to reduce friction during processing. This technique allows for:
- Increased control over material flow.
- Enhanced surface quality due to reduced wear on dies.
- Capability to extrude brittle materials that might fracture under traditional methods.
Industry-Specific Applications
The versatility of extrusion allows it to cater to various sectors:
Construction Industry
In construction, extrusion is utilized for creating profiles used in windows and doors. These products require durability against weather elements while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Automotive Industry
Automotive applications include manufacturing lightweight yet strong components such as chassis parts or interior trim pieces. The ability to produce complex geometries helps meet design specifications while optimizing weight efficiency.
Packaging Sector
In packaging, extrusion is critical for producing films that provide barrier properties against moisture or gases. This ensures product longevity while maintaining freshness.
Medical Field
The medical industry benefits from precision extruded tubing used in various applications such as catheters or IV lines where biocompatibility is essential.
Future Trends in Extrusion Technology
As technology advances, several trends are shaping the future of extrusion processes:
- Automation: Increased automation in extrusion lines enhances efficiency while reducing labor costs.
- Sustainability: There is a growing emphasis on using recycled materials in extrusion processes to minimize environmental impact.
- Smart Manufacturing: Integrating IoT technologies allows real-time monitoring of extruder performance metrics such as temperature and pressure, leading to improved quality control.
Conclusion
The range of production in the extrusion method is vast and varies significantly depending on multiple factors such as material type, die design, extruder capacity, and desired output speed. This versatility makes extrusion a preferred choice across various industries for producing consistent shapes efficiently. As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in extrusion processes that enhance production capabilities while maintaining quality standards.
FAQ
1. What types of materials are commonly extruded?
Commonly extruded materials include thermoplastics (like PVC and polyethylene), metals (such as aluminum), ceramics, and food products.
2. How does die design affect production?
Die design impacts flow characteristics and production rates; complex dies may slow down production while custom designs can optimize efficiency for specific applications.
3. What is the difference between hot and cold extrusion?
Hot extrusion occurs above recrystallization temperatures allowing easier deformation, while cold extrusion occurs at or near room temperature preserving material properties but requiring higher forces.
4. Can extrusion be used for food products?
Yes, food extrusion is widely used to produce snacks, cereals, and other food items by applying heat and pressure to raw ingredients.
5. What are some common applications of plastic extrusion?
Plastic extrusion is used in construction (window frames), automotive (gaskets), packaging (films), and medical devices (tubing).
Citations:
[1] https://www.tfgusa.com/understanding-extrusion-a-fundamental-manufacturing-process/
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extrude
[3] https://bonnellaluminum.com/tech-info-resources/aluminum-extrusion-process/
[4] https://www.3ds.com/make/guide/process/extrusion
[5] https://www.lubrizol.com/-/media/Lubrizol/Health/Literature/LSP-Extrusion-Guide.pdf
[6] https://hitechextrusions.com/extrusion-methods/
[7] https://onlytrainings.com/Polymer-Extrusion-Quick-Overview-Of-Extrusion-Process-and-Parameters
[8] https://scantech.com/information/the-extrusion-process/






















