Content Menu
● 1. Overview of Aluminum Extrusion
● 2. Key Components of an Aluminum Extrusion Press
● 3. Detailed Functions of Each Component
>> Main Cylinder
>> Ram
>> Dummy Block
>> Container
>> Die Holder
>> Die
>> Press Platen
>> Tie Rods
>> Run Out Table
>> Cooling System
● 4. The Extrusion Process in Action
● 5. Additional Considerations in Aluminum Extrusion
>> Material Selection
>> Die Design
>> Process Parameters
>> Maintenance Practices
● 6. Innovations in Aluminum Extrusion Technology
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials can be extruded using this process?
>> 2. How does temperature affect aluminum extrusion?
>> 3. What types of dies are used in aluminum extrusion?
>> 4. How long does it take to complete an extrusion cycle?
>> 5. Can I customize my extruded profiles?
Aluminum extrusion is a vital manufacturing process used to create complex shapes and profiles from aluminum alloys. This technique involves forcing heated aluminum billets through a die to produce continuous lengths of material with a specific cross-section. Understanding the main parts of an aluminum extrusion press is essential for anyone involved in the industry, as these components work together to ensure efficient and effective production. In this article, we will explore the various parts of an aluminum extrusion press, their functions, and how they contribute to the extrusion process.
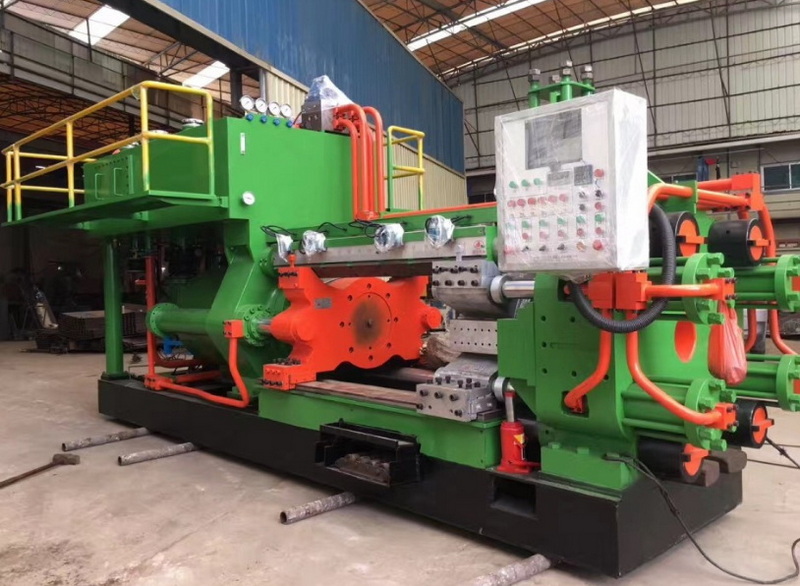

1. Overview of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion is widely used in various industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and consumer products. The process begins with an aluminum billet, which is a solid cylindrical piece of aluminum that is heated to a malleable state. Once heated, the billet is placed into an extrusion press where it is forced through a die by a hydraulic ram. The result is a continuous profile that can be cut to desired lengths.
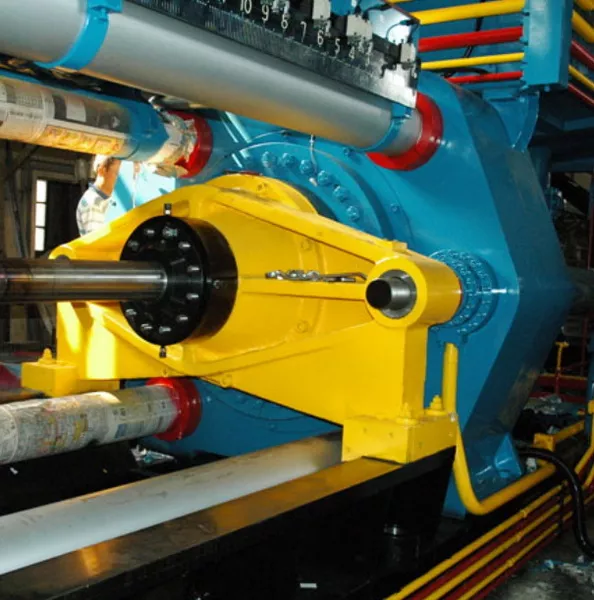
2. Key Components of an Aluminum Extrusion Press
The aluminum extrusion press consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in the extrusion process. Below are the main parts of an aluminum extrusion press:
| Component | Description |
| Main Cylinder | The chamber where hydraulic fluid is pumped to generate pressure for moving the ram. |
| Ram | A steel rod that pushes the aluminum billet into the container and applies pressure during extrusion. |
| Dummy Block | A tight-fitting block attached to the ram that seals the billet in the container to prevent leaks. |
| Container | Holds the heated aluminum billet while it is being pushed through the die. |
| Die Holder | Secures the die assembly, which shapes the extruded profile. |
| Die | The tool that defines the cross-sectional shape of the extruded material. |
| Press Platen | The front and back sections of the press that hold everything together and support the operation. |
| Tie Rods | Connects and stabilizes the front and back platens of the press. |
| Run Out Table | Supports extrusions as they exit the die and helps guide them for cooling and further processing. |
| Cooling System | Cools down extruded profiles using water or air to achieve desired mechanical properties (quenching). |
3. Detailed Functions of Each Component
Main Cylinder
The main cylinder is essential for generating hydraulic pressure within the press. It contains hydraulic fluid that is pumped into it, creating pressure that moves the ram forward at specified pounds per square inch (PSI). This pressure must be carefully controlled to avoid damaging both the billet and the components of the press.
Ram
The ram is a critical part of the extrusion process; it applies force to push the heated aluminum billet through the die. As pressure builds up, it compresses the billet against the die, causing it to flow out in the desired shape.
Dummy Block
Attached to the end of the ram, the dummy block prevents any backward flow of metal during extrusion. It ensures that all material moves forward through the die without leaking back into the container.
Container
The container holds the heated billet during extrusion. It must withstand high pressures while allowing smooth movement of aluminum as it transitions through various stages of shaping.
Die Holder
The die holder secures various dies used for different profiles. It must be robust enough to handle high pressures while allowing for easy changes between different dies depending on production needs.
Die
The die itself is crucial as it determines the final shape of the extruded profile. Dies can be customized for various applications, allowing manufacturers to produce a wide range of shapes from simple bars to complex geometries.
Press Platen
The press platen consists of two sections: front and back platens that are connected by tie rods. These platens provide structural support for all components during operation.
Tie Rods
Tie rods are essential for maintaining alignment between front and back platens under high pressure conditions during extrusion.
Run Out Table
Once extruded, profiles are guided along a run out table where they can be cooled and cut to length as needed. This table supports profiles immediately after they exit from the die.
Cooling System
Cooling systems are vital for rapidly reducing temperatures of extruded profiles after they exit from the die. This process, known as quenching, helps achieve desired mechanical properties by controlling how quickly materials cool down.
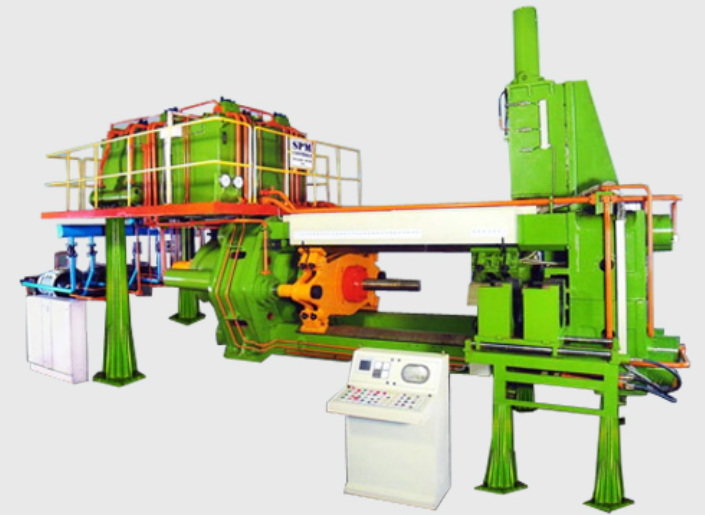

4. The Extrusion Process in Action
To better understand how these components work together, let's walk through a typical aluminum extrusion process:
1. Heating: The aluminum billet is heated in a furnace until it reaches approximately 900°F (482°C), making it malleable yet still solid.
2. Loading: The heated billet is loaded into the container of an extrusion press.
3. Pressing: The hydraulic ram applies pressure to push the billet through the die opening.
4. Shaping: As pressure builds up, aluminum flows through die openings, taking on its final shape.
5. Cooling: The extruded material exits through a run out table where it is cooled using water or air.
6. Cutting & Handling: After cooling, profiles are cut to specified lengths and prepared for further processing or shipping.
5. Additional Considerations in Aluminum Extrusion
While understanding individual components is crucial, it's also important to consider other factors that affect overall performance and efficiency in an aluminum extrusion press:
Material Selection
Choosing appropriate aluminum alloys can significantly impact both quality and performance characteristics of extruded products. Common alloys include 6061 (known for its good mechanical properties) and 6063 (often used for architectural applications).
Die Design
The design of dies plays an essential role in determining not just shape but also surface finish and tolerances of extruded profiles. Advanced software tools allow engineers to simulate flow patterns before physical production begins.
Process Parameters
Key parameters such as temperature control, ram speed, and cooling rates must be optimized based on specific applications to ensure high-quality outputs while minimizing waste.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance checks on hydraulic systems, alignment adjustments on tie rods, and inspections on dies can prolong equipment life and enhance operational efficiency.
6. Innovations in Aluminum Extrusion Technology
As industries evolve, so does technology related to aluminum extrusion presses:
- Automation: Modern presses often incorporate automated systems for loading billets and handling extrusions post-production.
- Real-time Monitoring Systems: Sensors can provide real-time data on temperature, pressure, and flow rates enabling immediate adjustments during production cycles.
- Sustainability Practices: Many manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices by recycling scrap material generated during production processes.
Conclusion
Understanding what makes up an aluminum extrusion press is crucial for optimizing production processes in various industries that rely on aluminum profiles. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring efficiency and quality throughout production—from heating billets to shaping them into complex designs.
FAQ
1. What materials can be extruded using this process?
Aluminum alloys are primarily used in extrusion due to their favorable properties such as lightweight and corrosion resistance.
2. How does temperature affect aluminum extrusion?
Temperature significantly affects malleability; higher temperatures allow easier shaping but require careful control to prevent defects.
3. What types of dies are used in aluminum extrusion?
There are various types of dies including solid dies for simple shapes and complex dies for intricate designs.
4. How long does it take to complete an extrusion cycle?
Cycle times vary depending on profile complexity but typically range from several minutes to hours including heating, pressing, cooling, and cutting.
5. Can I customize my extruded profiles?
Yes, manufacturers can design custom dies for specific shapes based on client specifications.






















