Content Menu
● Introduction to Automatic Extrusion
>> Key Components of Automatic Extrusion
● How Automatic Extrusion Works
● Applications of Automatic Extrusion
● Advantages of Automatic Extrusion
● Challenges and Future Developments
>> Material Limitations
>> Advanced Automation Technologies
>> Expanding Material Range
● Case Studies: Successful Applications of Automatic Extrusion
● Environmental Impact of Automatic Extrusion
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What is the primary advantage of using automatic extrusion?
>> 2. How does automatic extrusion differ from manual extrusion?
>> 3. What materials can be used in automatic extrusion?
>> 4. What role does the die play in the extrusion process?
>> 5. Can automatic extrusion be used for complex geometries?
Automatic extrusion is a highly advanced manufacturing process that utilizes machinery and automation to produce objects of fixed cross-sectional profiles. This process is widely used in various industries, including plastics, metals, and composites, to create a variety of products such as pipes, tubes, profiles, and more. In this article, we will delve into the principles of automatic extrusion, its applications, and how it works.
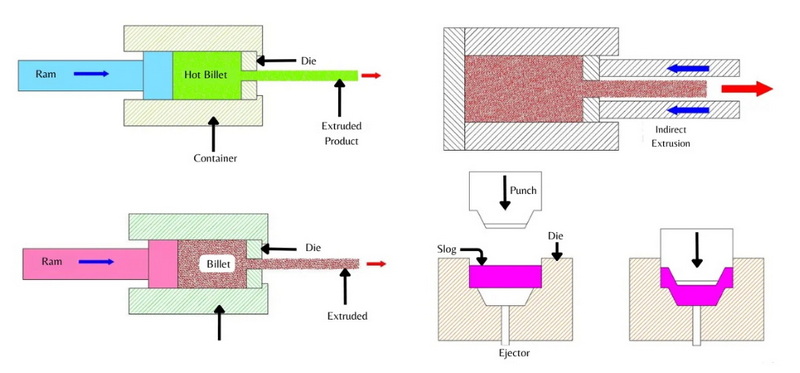
Introduction to Automatic Extrusion
Automatic extrusion involves the use of sophisticated machinery that can operate with minimal human intervention. The process begins with the preparation of raw materials, which are then fed into the extruder. For plastics, this typically involves thermoplastics like PVC, PE, PP, or PET, while metals require heating to a high temperature before extrusion.
Key Components of Automatic Extrusion
1. Extruder: This is the core machine that melts and pushes the material through a die.
2. Die: A specialized tool designed to shape the molten material into the desired form.
3. Automation Systems: These include PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), sensors, and software that control and monitor the process.
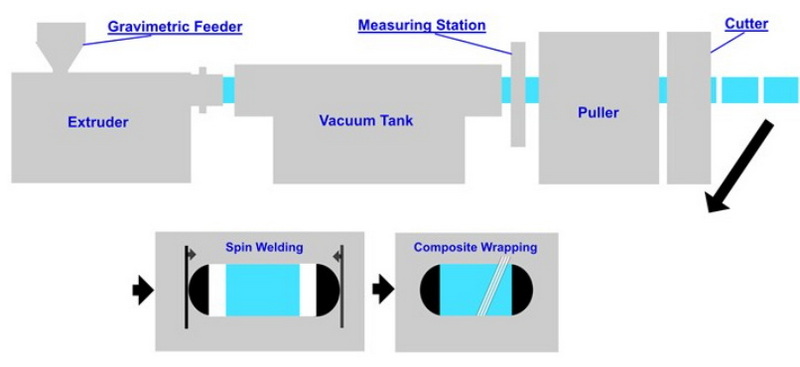
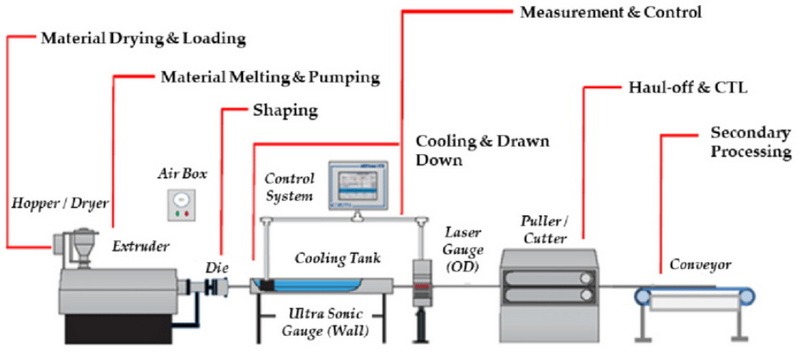
How Automatic Extrusion Works
The process of automatic extrusion can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Material Feeding: Raw materials are fed into the extruder through a hopper. This step is crucial as it ensures a consistent supply of material for the extrusion process.
2. Melting: The material is heated and melted as it moves through the extruder barrel. This process involves precise temperature control to ensure the material reaches the optimal melting point.
3. Extrusion Through the Die: The molten material is forced through a die to achieve the desired shape. The die is designed to produce the specific cross-sectional profile required for the final product.
4. Cooling: The extruded product is cooled to solidify its shape. This can be done using air, water, or other cooling mediums depending on the material and desired properties.
5. Cutting and Finishing: The extruded product is cut to the required length and undergoes finishing processes such as grinding or coating.
Applications of Automatic Extrusion
Automatic extrusion is used in a wide range of industries:
- Plastics Industry: Produces items like pipes, tubes, and packaging materials. Plastic extrusion is particularly common for creating PVC pipes used in plumbing and construction.
- Metal Industry: Creates aluminum profiles, lead pipes, and other metal components. Metal extrusion is often used in the automotive and aerospace sectors for lightweight yet strong components.
- Composite Materials: Used in manufacturing pressure tanks and other reinforced structures. Composite extrusion combines materials like carbon fiber with polymers to achieve high strength-to-weight ratios.
Advantages of Automatic Extrusion
1. High Efficiency: Automated systems can run continuously with minimal downtime, significantly increasing production rates compared to manual processes.
2. Consistency: Ensures uniformity in the final product, which is critical for maintaining quality standards in industries like aerospace and automotive.
3. Cost-Effective: Reduces labor costs and increases productivity, making it a preferred method for large-scale manufacturing.
4. Flexibility: Allows for the production of complex shapes and profiles that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods.
Challenges and Future Developments
Despite its advantages, automatic extrusion faces challenges such as material limitations and the need for precise control systems. Future developments are likely to focus on integrating more advanced automation technologies and expanding the range of materials that can be processed.
Material Limitations
One of the main challenges in automatic extrusion is the limitation of materials that can be processed. For instance, certain plastics may not be suitable for high-speed extrusion due to their melting properties. Similarly, metals require specific conditions to achieve the desired properties.
Advanced Automation Technologies
The integration of advanced automation technologies, such as AI and IoT, is expected to enhance the efficiency and precision of automatic extrusion. These technologies can optimize production parameters in real-time, reducing waste and improving product quality.
Expanding Material Range
Research is ongoing to expand the range of materials that can be extruded automatically. This includes developing new composite materials and improving the extrudability of existing materials like ceramics and glass.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Automatic Extrusion
1. Automotive Industry: Automatic extrusion is used to produce lightweight aluminum profiles for vehicle frames, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
2. Construction Industry: PVC pipes produced through automatic extrusion are widely used in plumbing systems due to their durability and resistance to corrosion.
3. Aerospace Industry: Composite extrusion is used to manufacture components for aircraft, where high strength-to-weight ratios are critical for performance and safety.
Environmental Impact of Automatic Extrusion
The environmental impact of automatic extrusion varies depending on the materials used and the energy efficiency of the process. However, it offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
- Reduced Waste: Automated systems can optimize material usage, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern extrusion machines are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process.
Conclusion
Automatic extrusion is a powerful tool in modern manufacturing, offering high efficiency, consistency, and cost-effectiveness. Its applications span multiple industries, from plastics to metals and composites. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated automation systems and expanded capabilities in the field of extrusion.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary advantage of using automatic extrusion?
- The primary advantage of automatic extrusion is its ability to operate with high efficiency and consistency, reducing labor costs and increasing productivity.
2. How does automatic extrusion differ from manual extrusion?
- Automatic extrusion uses machinery and automation to control the process, whereas manual extrusion relies on human intervention for each step.
3. What materials can be used in automatic extrusion?
- A variety of materials can be used, including thermoplastics like PVC and PE, metals such as aluminum and lead, and composite materials.
4. What role does the die play in the extrusion process?
- The die shapes the molten material into the desired form, determining the cross-sectional profile of the final product.
5. Can automatic extrusion be used for complex geometries?
- Yes, automatic extrusion can produce complex geometries, especially in hot extrusion processes where metals can be shaped into intricate profiles.






















