Content Menu
● Understanding Aluminum Extrusion
● The Role of CAD in Aluminum Extrusion Design
● Steps to Optimize Aluminum Extrusion Designs Using CAD
>> Step 1: Initial Sketching
>> Step 2: Refinement of Design
>> Step 3: 3D Visualization
>> Step 4: Simulation Testing
● Best Practices for Aluminum Extrusion Design Using CAD
● Advanced Techniques in CAD for Aluminum Extrusion Optimization
>> Custom Profiles
>> Integration with CAM
>> Iterative Design Process
● Additional Considerations for Effective Design
>> Material Selection
>> Understanding Extrusion Limits
>> Prototyping Techniques
● Visual Aids and Resources
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the importance of wall thickness in aluminum extrusion designs?
>> 2. How does simulation in CAD improve the design process?
>> 3. Can I create custom profiles using CAD?
>> 4. What are some common mistakes in aluminum extrusion design?
>> 5. How does integrating CAM with CAD benefit production?
Aluminum extrusion is a highly versatile manufacturing process that allows for the creation of complex shapes and profiles. The use of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software in this process has revolutionized how designers approach aluminum extrusion, enabling them to create precise and efficient designs that maximize the material's properties. This article will delve into the various strategies for optimizing aluminum extrusion designs using CAD, covering essential design principles, best practices, and advanced techniques.
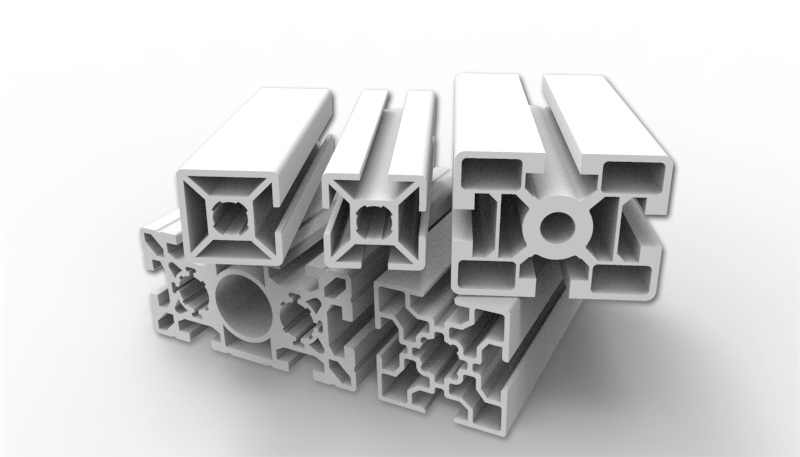
Understanding Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion involves forcing aluminum alloy through a die to create a specific cross-sectional shape. This process is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and consumer products due to aluminum's lightweight nature and excellent mechanical properties.
Key Benefits of Aluminum Extrusion:
- Design Flexibility: Designers can create intricate shapes that would be difficult or impossible with other manufacturing methods.
- Material Efficiency: The extrusion process minimizes waste by using only the necessary amount of material.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum extrusions provide high strength while remaining lightweight, making them ideal for structural applications.
The Role of CAD in Aluminum Extrusion Design
CAD software plays a crucial role in optimizing aluminum extrusion designs. It allows designers to visualize their ideas, make precise measurements, and simulate real-world conditions before production begins. Here are some essential functions of CAD in this context:
- Precision Design: CAD enables designers to achieve high accuracy in their dimensions, which is critical for ensuring that the extruded parts fit together correctly.
- 3D Visualization: With CAD, designers can view their models from multiple angles, helping identify potential issues early in the design process.
- Simulation Capabilities: Advanced CAD programs can simulate stress, heat, and other factors that affect the performance of the aluminum extrusions under real-world conditions.
Steps to Optimize Aluminum Extrusion Designs Using CAD
Step 1: Initial Sketching
Start by sketching your initial design idea on the CAD platform. This draft should capture the essential features of your desired extrusion profile without worrying about perfection.
Step 2: Refinement of Design
Use CAD's tools to refine your design. Considerations include:
- Wall Thickness: Ensure uniform wall thickness throughout the profile to avoid distortion during extrusion. As a general rule, keep wall thicknesses consistent and avoid sharp transitions.
- Shape Configuration: Design profiles that meet functional requirements while minimizing material usage. For instance, hollow shapes can reduce weight while maintaining strength.
Step 3: 3D Visualization
Visualize your design in 3D within the CAD software. Rotate and zoom into different areas to check for flaws or areas that may need modification. This step is crucial for identifying potential manufacturing challenges early on.
Step 4: Simulation Testing
Utilize built-in simulation tools to test your design under various conditions. For example:
- Stress Testing: Simulate how the profile will hold up under load.
- Thermal Analysis: Assess how different temperatures might affect material properties.
These simulations help predict performance issues before physical prototypes are created.
Best Practices for Aluminum Extrusion Design Using CAD
To optimize designs effectively, consider these best practices:
- Maintain Symmetry: Symmetrical designs help reduce internal stresses during the extrusion process.
- Smooth Transitions: Use generous radii at thick-thin junctions to minimize stress concentrations that could lead to failure.
- Incorporate Ribs and Webs: Adding ribs or webs can enhance structural integrity without significantly increasing weight.
- Design for Assembly: Consider how components will be assembled post-extrusion. Features like screw ports or alignment grooves can simplify assembly processes.
Advanced Techniques in CAD for Aluminum Extrusion Optimization
Custom Profiles
With CAD, creating custom profiles tailored to specific applications is straightforward. Designers can draft unique shapes that meet exact specifications while ensuring they fit seamlessly into larger assemblies. This customization is particularly valuable in industries where standard profiles may not meet specific performance criteria or aesthetic requirements.
Integration with CAM
Once an aluminum extrusion design is finalized in a CAD system, it can be directly integrated into Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. This integration streamlines the transition from design to production, reducing errors and improving efficiency. By linking CAD with CAM systems, manufacturers can automate processes such as cutting, machining, and assembly planning based on accurate digital models.
Iterative Design Process
The iterative nature of CAD allows designers to make quick adjustments based on feedback from simulations or prototype testing. This flexibility is vital for refining designs and achieving optimal results without incurring significant costs or delays. Continuous improvement through iteration ensures that any issues identified during testing are addressed promptly, leading to better final products.
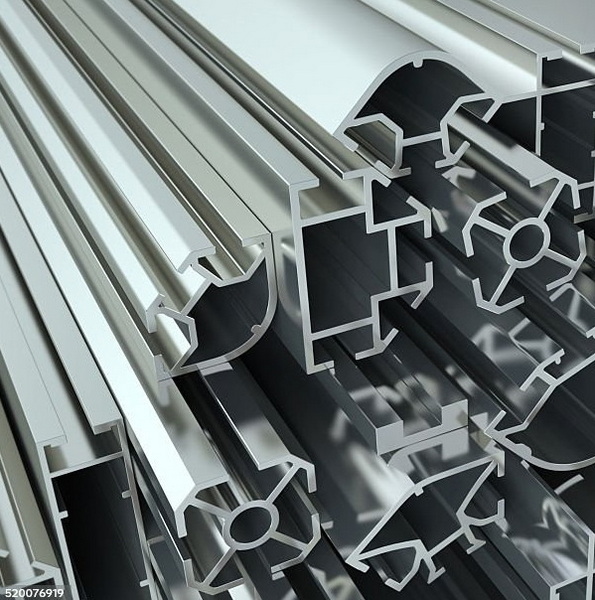

Additional Considerations for Effective Design
Material Selection
Choosing the right aluminum alloy is crucial for achieving desired mechanical properties and performance characteristics. Different alloys have varying strengths, corrosion resistance levels, and workability factors. Designers should consider these properties when selecting materials for their extrusions to ensure they meet the application requirements effectively.
Understanding Extrusion Limits
Each extrusion die has specific limitations regarding shape complexity and size due to factors like material flow and cooling rates. Being aware of these limits can help designers create feasible designs that are easier to manufacture without compromising quality or performance.
Prototyping Techniques
While CAD simulations provide valuable insights into design performance, physical prototypes remain an essential part of the development process. Rapid prototyping techniques such as 3D printing can be employed to create models quickly for testing fit and function before moving on to full-scale production.
Visual Aids and Resources
To further enhance understanding and application of these concepts, various resources such as videos and diagrams can be invaluable:
1. YouTube Tutorials: Numerous tutorials are available that demonstrate modeling techniques in popular CAD software like AutoCAD or FreeCAD specifically for aluminum extrusions.
2. Diagrams: Visual representations of successful aluminum profiles can provide inspiration and guidance on effective design strategies.
3. Webinars: Participating in webinars hosted by industry experts can offer insights into advanced techniques and emerging trends in aluminum extrusion design using CAD tools.
4. Online Forums: Engaging with online communities focused on CAD and aluminum extrusion can provide support and knowledge sharing among peers facing similar challenges.
5. Software Documentation: Most CAD software comes with extensive documentation that includes best practices for designing aluminum extrusions effectively.
Conclusion
Optimizing aluminum extrusion designs using CAD is a multifaceted process that combines creativity with technical precision. By leveraging advanced design tools and adhering to best practices, designers can create efficient, functional, and aesthetically pleasing aluminum profiles tailored to specific applications. The integration of simulation capabilities further enhances this process by allowing thorough testing before production begins. As industries continue to innovate, mastering these techniques will be crucial for staying competitive in the field of aluminum extrusion.

FAQ
1. What is the importance of wall thickness in aluminum extrusion designs?
Maintaining uniform wall thickness is crucial as it helps prevent distortion during the extrusion process and ensures structural integrity in the final product.
2. How does simulation in CAD improve the design process?
Simulation allows designers to test how their extrusions will perform under real-world conditions without needing physical prototypes, saving time and resources.
3. Can I create custom profiles using CAD?
Yes, CAD software enables designers to create custom profiles tailored specifically to their application requirements easily.
4. What are some common mistakes in aluminum extrusion design?
Common mistakes include neglecting wall thickness uniformity, failing to smooth transitions between different thicknesses, and not considering assembly processes during design.
5. How does integrating CAM with CAD benefit production?
Integrating CAM with CAD streamlines the manufacturing process by reducing errors during production setup and enhancing overall efficiency.






















