Content Menu
● Introduction to Aluminum MK8 Extruders
>> Advantages of Aluminum MK8 Extruders
● Direct Drive vs. Bowden Extruders
>> Direct Drive Extruders
>> Bowden Extruders
● Handling Flexible Filaments with Aluminum MK8 Extruders
>> Key Features for Flexible Filament Printing
● Benefits of Upgrading to Aluminum MK8 Extruders
● Optimizing Print Settings for Flexible Filaments
● Troubleshooting Common Issues
● Upgrading to Direct Drive
>> Steps for Upgrading to Direct Drive
● Additional Tips for Printing Flexible Filaments
● Advanced Techniques for Flexible Filament Printing
>> Dual Gear Direct Drive Extruders
>> High-Speed Printing with Flexible Filaments
>> Adjusting Infill Patterns for Flexibility
● Maintenance and Calibration
● Future Developments in Extruder Technology
● Advanced Filament Handling Techniques
>> Using Dual Gear Extruders for Enhanced Grip
>> High-Speed Printing with Flexible Filaments
>> Adjusting Infill Patterns for Flexibility
● Conclusion on Future Developments
● Additional Considerations for Flexible Filament Printing
>> Nozzle Size and Type
>> Bed Adhesion
>> Infill Patterns
>> Experimentation and Calibration
● Troubleshooting Tips for Aluminum MK8 Extruders
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What types of filaments can an aluminum MK8 extruder handle?
>> 2. Do I need a direct drive extruder for printing flexible filaments?
>> 3. How do I install an aluminum MK8 extruder on my 3D printer?
>> 4. Can I use an aluminum MK8 extruder in a dual-extrusion setup?
>> 5. What maintenance is required for an aluminum MK8 extruder?
● Citations:
The world of 3D printing has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in both hardware and software. One of the key components that have seen significant improvements is the extruder, particularly the aluminum MK8 extruder with direct drive. This article will delve into the capabilities of the aluminum MK8 extruder with direct drive in handling flexible filaments, exploring its design, advantages, and compatibility with various 3D printers.
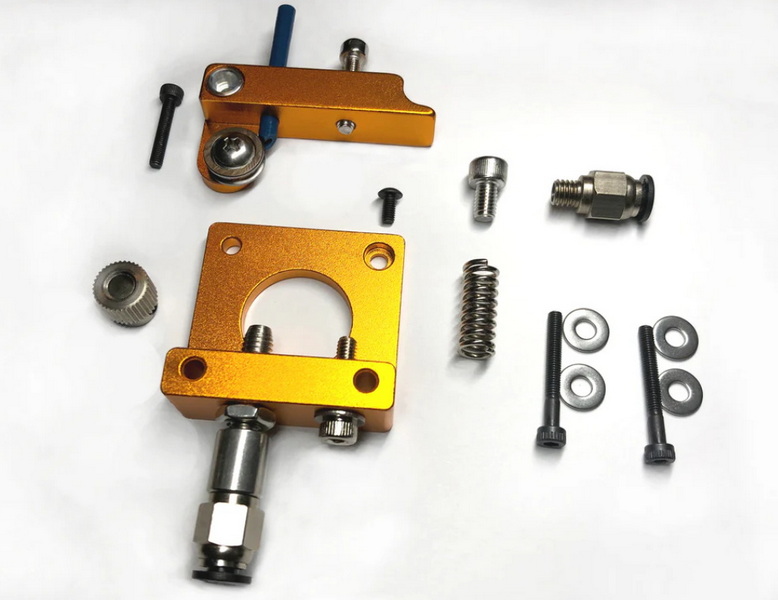

Introduction to Aluminum MK8 Extruders
The aluminum MK8 extruder is a popular upgrade among 3D printing enthusiasts due to its robust construction and improved performance compared to traditional plastic extruders. It is designed to handle 1.75mm filament and is widely compatible with many popular 3D printer models, including those from Creality, Anycubic, and more.
Advantages of Aluminum MK8 Extruders
1. Durability: Aluminum extruders are less prone to wear and tear compared to plastic ones, ensuring consistent performance over time.
2. Temperature Resistance: They can withstand higher temperatures without deforming, which is crucial for printing materials like ABS.
3. Filament Compatibility: Aluminum MK8 extruders can handle a wide range of filaments, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and flexible materials like TPU.
Direct Drive vs. Bowden Extruders
When it comes to printing flexible filaments, the choice between direct drive and Bowden extruders is often debated.
Direct Drive Extruders
- Definition: A direct drive extruder places the motor directly on the hotend, minimizing the distance the filament travels. This setup is beneficial for printing flexible filaments as it reduces the likelihood of filament buckling or escaping.
- Advantages: Offers better control over retraction and can handle flexible filaments more effectively due to the constrained filament path.
- Example: The Micro Swiss Direct Drive Extruder is designed for printers like the Ender 3 and CR-10, providing a plug-and-play solution for printing flexible filaments with high speed and accuracy.
Bowden Extruders
- Definition: Bowden extruders use a longer tube to guide the filament from the extruder to the hotend. While they are generally more cost-effective and lighter, they can struggle with flexible filaments unless properly optimized.
- Challenges: The longer filament path can lead to issues with flexible filaments, such as buckling or escaping from the tube.
Handling Flexible Filaments with Aluminum MK8 Extruders
Flexible filaments, like TPU, require careful handling due to their tendency to buckle or escape from the extruder. The aluminum MK8 extruder with direct drive can effectively manage these challenges by providing a tightly constrained filament path and consistent extrusion pressure.
Key Features for Flexible Filament Printing
1. Constrained Filament Path: Ensures that the filament is guided smoothly into the hotend without buckling or escaping.
2. Consistent Extrusion Pressure: Critical for maintaining even flow and preventing slippage or grinding of the filament.
3. Adjustable Tension: Allows users to fine-tune the grip on the filament, which is essential for handling flexible materials.
Benefits of Upgrading to Aluminum MK8 Extruders
Upgrading to an aluminum MK8 extruder with direct drive offers several benefits:
- Improved Print Quality: Better filament control and consistent extrusion pressure lead to fewer defects and more consistent prints.
- Long-Term Cost Efficiency: Although initially more expensive, aluminum extruders last longer and require fewer replacements.
- Enhanced Filament Compatibility: Handles a wide range of filaments, including flexible ones, with ease.
Optimizing Print Settings for Flexible Filaments
To achieve the best results with flexible filaments, optimizing print settings is crucial:
- Print Speed: Slowing down the print speed can help prevent issues related to filament buckling and ensure better layer adhesion. A speed of 20-40 mm/s is generally recommended for flexible filaments.
- Temperature: Flexible filaments typically require higher printing temperatures than rigid materials. Refer to the filament manufacturer's recommendations for the optimal temperature range.
- Retraction: Adjusting retraction settings is essential for minimizing stringing and oozing. Lower retraction distances and speeds are generally recommended for flexible filaments.
- Layer Height: A smaller layer height can improve the surface finish and overall quality of the print. A layer height of 0.1-0.2 mm is often used for flexible filaments.
- Infill: Adjusting the infill density and pattern can affect the flexibility and strength of the printed part. Experiment with different settings to achieve the desired properties.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When printing with flexible filaments, several issues may arise:
1. Filament Jamming: If you experience jamming during printing, check if the filament path is clear and ensure that there are no obstructions in the nozzle or feeding mechanism.
2. Inconsistent Extrusion: If extrusion seems inconsistent, verify that your tension settings on the drive gear are properly adjusted; too much tension can crush filaments while too little can lead to slippage.
3. Temperature Settings: Ensure that your temperature settings match those recommended for your specific filament type; incorrect temperatures can lead to poor adhesion or excessive stringing in prints.
4. Calibration Issues: Regularly calibrate your printer after making any changes or upgrades; this helps maintain optimal performance across different materials and setups.
5. Print Speed: Print slowly, around 15-20mm/s, and turn the heat up a tad if needed.
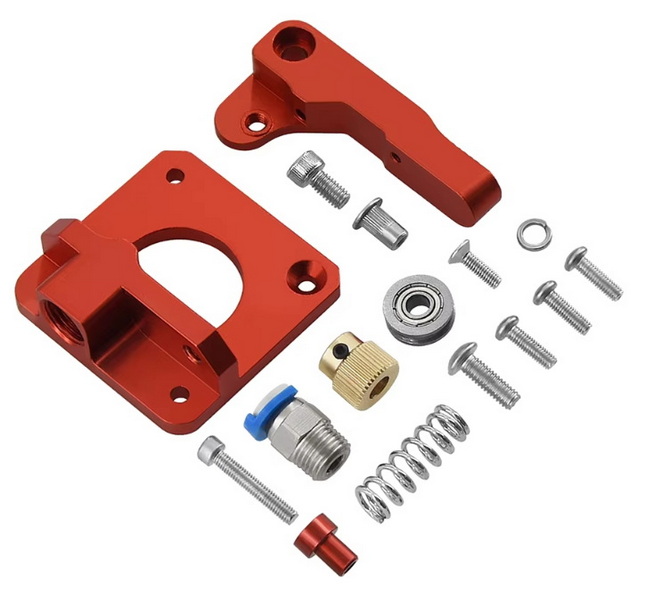
Upgrading to Direct Drive
If you encounter persistent issues with flexible materials using a Bowden setup, consider upgrading to a direct drive system where feasible. This setup minimizes the distance between the motor and hotend, improving control over filament feeding.
Steps for Upgrading to Direct Drive
1. Assess Compatibility: Ensure that your printer model supports a direct drive conversion. Some printers may require additional adapters or modifications.
2. Choose a Conversion Kit: Select a conversion kit that is specifically designed for your printer model and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully during installation.
3. Install the New Extruder: Remove the old extruder, assemble the new direct drive extruder if necessary, and secure it to the printer's mount.
Additional Tips for Printing Flexible Filaments
- Use High-Quality Filaments: Experiment with different brands and types of flexible filaments to find those that work best with your setup.
- Optimize Retraction Settings: Start with low retraction distances (1-2 mm) and slow retraction speeds (20-30 mm/s). Gradually adjust these settings based on print quality.
- Closed Travel Path: Ensure that the filament path is closed from the extruder gear to the hotend to prevent kinking.
Advanced Techniques for Flexible Filament Printing
Dual Gear Direct Drive Extruders
Dual gear direct drive extruders offer superior filament grip, reducing the chance of slippage and grinding, especially with softer or more flexible materials. This setup allows for more consistent extrusion and can handle a wider range of filament types, including highly flexible or abrasive materials.
High-Speed Printing with Flexible Filaments
While flexible filaments are typically printed at slower speeds, some advanced extruders like the E3D Hemera can maintain high speeds without compromising print quality. This is achieved by keeping the filament tightly constrained and minimizing kinks in the filament path.
Adjusting Infill Patterns for Flexibility
Adjusting the infill density and pattern can significantly affect the flexibility and strength of the printed part. For flexible filaments, using a lower infill density and a simple infill pattern is often recommended to maintain flexibility while ensuring structural integrity.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance and calibration are crucial for maintaining optimal performance with an aluminum MK8 extruder with direct drive:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean any debris from around the nozzle area to prevent clogs.
- Tension Adjustment: Periodically check and adjust tension settings based on the current filament type.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitor temperature settings closely during prints; adjust as necessary based on material being used.
Future Developments in Extruder Technology
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in extruder design. These developments may include more efficient heat management systems, improved filament grip mechanisms, and enhanced compatibility with a broader range of materials.
Advanced Filament Handling Techniques
Using Dual Gear Extruders for Enhanced Grip
Dual gear extruders provide a superior grip on the filament, reducing slippage and grinding issues, especially with flexible materials. This setup allows for more consistent extrusion and can handle a wider range of filament types, including highly flexible or abrasive materials.
High-Speed Printing with Flexible Filaments
While flexible filaments are typically printed at slower speeds, some advanced extruders like the E3D Hemera can maintain high speeds without compromising print quality. This is achieved by keeping the filament tightly constrained and minimizing kinks in the filament path.
Adjusting Infill Patterns for Flexibility
Adjusting the infill density and pattern can significantly affect the flexibility and strength of the printed part. For flexible filaments, using a lower infill density and a simple infill pattern is often recommended to maintain flexibility while ensuring structural integrity.
Conclusion on Future Developments
The future of 3D printing extruders holds much promise, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving performance, efficiency, and material compatibility. Upgrading to an aluminum MK8 extruder with direct drive is a step towards leveraging these advancements and achieving high-quality prints with flexible filaments.
Additional Considerations for Flexible Filament Printing
Nozzle Size and Type
Using a slightly larger nozzle can improve the flow of flexible filaments and reduce the risk of clogging. Nozzles with a diameter of 0.6mm or 0.8mm are often recommended for printing flexible materials like TPU.
Bed Adhesion
Flexible filaments tend to stick well to the build plate, but ensuring a smooth and clean surface is crucial. A build plate coated with PEI or similar materials works well for maintaining adhesion without causing damage to the print during removal.
Infill Patterns
Adjusting the infill density and pattern can significantly affect the flexibility and strength of the printed part. For flexible filaments, using a lower infill density and a simple infill pattern is often recommended to maintain flexibility while ensuring structural integrity.
Experimentation and Calibration
Experimenting with different print settings and calibrating your printer regularly are key to achieving high-quality prints with flexible filaments. This includes adjusting extrusion multipliers, retraction settings, and temperature profiles to match the specific requirements of the filament being used.
Troubleshooting Tips for Aluminum MK8 Extruders
When using an aluminum MK8 extruder, common issues may include jamming or inconsistent extrusion. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
1. Filament Jamming: Check for obstructions in the nozzle or feeding mechanism and ensure the filament path is clear.
2. Inconsistent Extrusion: Adjust tension settings on the drive gear to prevent slippage or crushing of the filament.
3. Temperature Settings: Ensure temperature settings match the filament type to prevent poor adhesion or excessive stringing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the aluminum MK8 extruder with direct drive is well-suited for handling flexible filaments due to its robust design, consistent extrusion pressure, and tightly constrained filament path. While it may not be universally compatible with all 3D printers, it offers significant improvements in print quality and durability for those who upgrade.
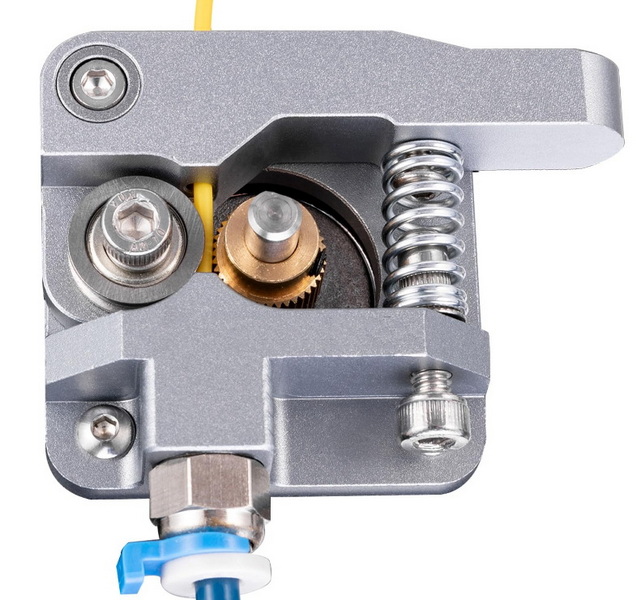
FAQ
1. What types of filaments can an aluminum MK8 extruder handle?
An aluminum MK8 extruder can handle a variety of filaments, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and flexible materials like TPU.
2. Do I need a direct drive extruder for printing flexible filaments?
While a direct drive extruder is highly recommended for flexible filaments, it is not strictly necessary. A well-optimized Bowden setup with good quality PTFE tubing and precise temperature control can also work effectively.
3. How do I install an aluminum MK8 extruder on my 3D printer?
Installation typically involves removing the old extruder, assembling the new one if necessary, and securing it to the printer's mount. Tools like Allen wrenches and screwdrivers are usually required.
4. Can I use an aluminum MK8 extruder in a dual-extrusion setup?
Yes, you can use two different MK8 extruders in a dual-extrusion setup as long as they are compatible with your printer's configuration.
5. What maintenance is required for an aluminum MK8 extruder?
Regular cleaning of the nozzle and feeding mechanism, checking tension settings, and applying lubricant to moving parts as needed are recommended for optimal performance.
Citations:
[1] https://www.yjing-extrusion.com/can-an-aluminum-alloy-bowden-extruder-be-used-for-flexible-filaments.html
[2] https://www.simplify3d.com/resources/materials-guide/flexible/
[3] https://forum.v1e.com/t/mk8-extruder-issues/5113
[4] https://www.yjing-extrusion.com/is-the-aluminum-mk8-extruder-compatible-with-all-3d-printers.html
[5] https://kingroon.com/blogs/3d-print-101/what-is-the-advantage-of-a-direct-drive-extruder
[6] https://www.yjing-extrusion.com/can-an-mk8-aluminum-extruder-reduce-jamming-issues.html
[7] https://www.matterhackers.com/articles/how-to-succeed-when-printing-with-flexible-filament
[8] https://www.reddit.com/r/ender3/comments/ad43gb/trying_out_an_adjustable_aftermarket_extruder/
[9] https://macewen3d.com/products/mk8-extruder-aluminum-drive-feed-for-cr-10-cr-10-s4-and-cr-10-s5
[10] https://colorfabb.com/nl/blog/post/how-to-print-with-colorfabb-ngen_flex
[11] https://www.reddit.com/r/ender3v2/comments/o90cgl/design_flaw_in_mk8_aluminum_metal_extruder/
[12] https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005004923874649.html
[13] https://www.3dmeta.com.au/blogs/news/flexible-filaments-a-guide-to-3d-printing-flexible-parts
[14] https://forum.v1e.com/t/problem-with-mk8-extruder/6793
[15] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Npuocf_f0jk
[16] https://mfg.trimech.com/ultimate-guide-to-flexible-3d-printer-filament/
[17] https://www.crealityexperts.com/creality-extruder-guide
[18] https://forum.makerforums.info/t/what-do-you-all-think-about-the-mk8-extruder/2638
[19] https://3dactions.com/blog/3dprint-tpu-guide/
[20] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c6JmCdovE0U






















