Content Menu
● Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
● Materials Used in Aluminum Extrusion
● The Benefits of Using Aluminum Alloys
● The Aluminum Extrusion Process
● Applications of Aluminum Extrusions
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What types of materials can be extruded besides aluminum?
>> 2. How does temperature affect the aluminum extrusion process?
>> 3. What are some common defects found in extruded products?
>> 4. Can recycled aluminum be used in extrusion?
>> 5. What post-extrusion treatments are commonly applied?
● Citations:
Aluminum extrusion is a vital manufacturing process that transforms aluminum alloys into various shapes and profiles. This method is widely used across multiple industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Understanding the materials used in aluminum extrusion production is essential for optimizing product performance and ensuring sustainability. This article will explore the different materials involved in aluminum extrusion, the benefits of using aluminum alloys, and the steps in the extrusion process.
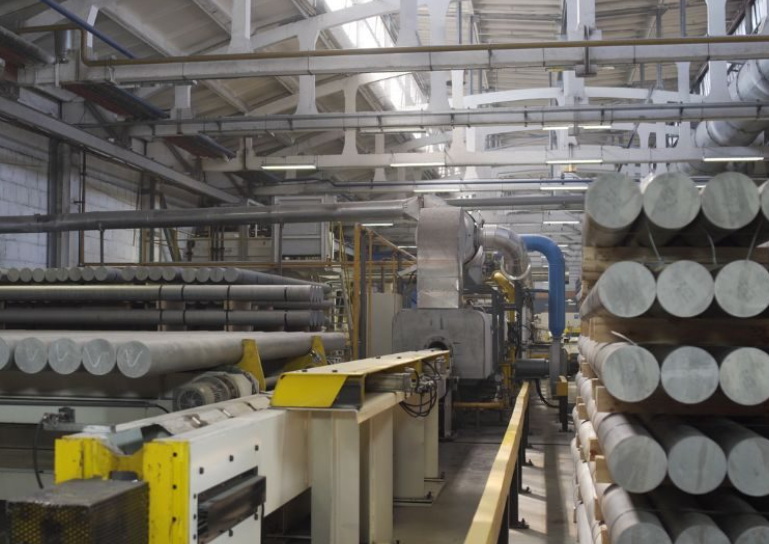

Introduction to Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion involves forcing a heated aluminum billet through a die to create a desired cross-sectional shape. The process is akin to squeezing toothpaste from a tube; as pressure is applied, the material emerges in the shape of the die opening. This technique allows for high precision and versatility in creating complex shapes that can be tailored to specific applications.
Materials Used in Aluminum Extrusion
The primary material used in aluminum extrusion is aluminum itself, specifically various aluminum alloys. These alloys are selected based on their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Below are some of the most commonly used aluminum alloys in extrusion production:
- 1xxx Series Alloys: These contain at least 99% aluminum and are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and high electrical conductivity. They are often used in applications requiring good workability and weldability.
- 2xxx Series Alloys: These alloys include copper as the primary alloying element. They are characterized by high strength but lower corrosion resistance compared to other series. Commonly used in aerospace applications.
- 3xxx Series Alloys: Manganese is the main alloying element in this series, providing good corrosion resistance and formability. These alloys are often used for manufacturing beverage cans and roofing sheets.
- 4xxx Series Alloys: Primarily composed of silicon, these alloys are known for their low melting points and excellent wear resistance. They are commonly used for welding wire and automotive applications.
- 5xxx Series Alloys: Magnesium is the key alloying element here, offering excellent corrosion resistance and weldability. These alloys are typically used in marine environments and for pressure vessels.
- 6xxx Series Alloys: This series includes magnesium and silicon as alloying elements, providing a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and workability. They are widely used in structural applications such as building frames and bridges.
- 7xxx Series Alloys: Zinc is the primary alloying element in these high-strength materials, often utilized in aerospace components due to their superior mechanical properties.
The Benefits of Using Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys offer several advantages over other materials, making them a preferred choice for many applications:
- Lightweight: Aluminum has a low density compared to steel or other metals, which contributes to weight savings in structures and vehicles.
- Corrosion Resistance: Many aluminum alloys naturally form a protective oxide layer that enhances their resistance to corrosion.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum's strength combined with its lightweight nature allows for efficient designs without sacrificing structural integrity.
- Good Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum is an excellent conductor of heat, making it suitable for heat exchangers and cooling systems.
- Recyclability: Aluminum can be recycled repeatedly without losing its properties, contributing to sustainability efforts.
The Aluminum Extrusion Process
The aluminum extrusion process consists of several key steps that ensure high-quality production:
1. Billet Preparation: The first step involves selecting raw materials—either virgin aluminum or recycled scrap—and casting them into billets (cylindrical blocks).
2. Heating the Billet: The aluminum billets are heated to temperatures between 400°C to 500°C (750°F to 900°F) to make them malleable enough for extrusion.
3. Extrusion Die Preparation: A die with a specific cross-sectional profile is designed and preheated to ensure even metal flow during extrusion.
4. Extrusion Process: The heated billet is placed into an extrusion press where a hydraulic ram pushes it through the die under high pressure (up to 100,000 psi). This step shapes the aluminum into the desired profile.
5. Cooling: After exiting the die, the extruded material is cooled rapidly using water or air quenching methods to solidify its shape.
6. Stretching: The cooled extrusions may undergo stretching to eliminate any twists or distortions that occurred during cooling.
7. Cutting: The extruded profiles are cut into specific lengths using saws or cutting machines.
8. Heat Treatment (Aging): Depending on the alloy used, heat treatment may be applied to enhance mechanical properties such as strength and hardness.
9. Surface Finishing: Finally, extrusions may undergo surface treatments such as anodizing or powder coating for improved durability and aesthetics.
Applications of Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum extrusions find use in a wide range of applications due to their versatility:
- Construction: Used for window frames, curtain walls, roofing systems, and structural components.
- Automotive: Employed in vehicle frames, heat exchangers, and body panels due to their lightweight nature.
- Aerospace: Critical components like wing structures and fuselage sections benefit from high-strength aluminum alloys.
- Consumer Products: Items such as furniture frames, lighting fixtures, and electronic enclosures utilize extruded aluminum for design flexibility.
- Industrial Applications: Used in machinery parts, conveyor systems, and heat sinks due to their thermal conductivity.
Conclusion
In summary, aluminum extrusion production relies heavily on various aluminum alloys tailored to meet specific performance requirements across multiple industries. The lightweight nature of aluminum combined with its excellent mechanical properties makes it an ideal choice for numerous applications ranging from construction to aerospace. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in manufacturing processes, aluminum's recyclability further enhances its appeal as an environmentally friendly material choice.
FAQs
1. What types of materials can be extruded besides aluminum?
While aluminum is the most common material used in extrusion processes, other metals such as copper and magnesium can also be extruded depending on specific application requirements.
2. How does temperature affect the aluminum extrusion process?
Temperature plays a crucial role; if the billet is too cool, it may not extrude properly; if too hot, it could lose strength during processing. The optimal range is typically between 400°C to 500°C (750°F to 900°F).
3. What are some common defects found in extruded products?
Common defects include surface imperfections like scratches or pits, dimensional inaccuracies such as warping or twisting during cooling, and internal voids caused by improper heating or pressure application.
4. Can recycled aluminum be used in extrusion?
Yes! Recycled aluminum is commonly used in extrusion processes due to its favorable properties while promoting sustainability by reducing waste.
5. What post-extrusion treatments are commonly applied?
Post-extrusion treatments may include heat treatment (aging), anodizing for surface protection, powder coating for aesthetics, or machining for precise dimensions.
Citations:
[1] https://tri-stateal.com/resources/extrusion-guide/
[2] https://taberextrusions.com/aluminum-extrusions-material-comparisons/
[3] https://www.gabrian.com/aluminum-extrusion-alloys/
[4] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/aluminum-extrusion.html
[5] https://stock.adobe.com/search?k=%22aluminium+extrusion%22
[6] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ELgtjeJyFw8
[7] https://americandouglasmetals.com/2024/05/19/understanding-the-aluminum-extrusion-process/
[8] https://www.gabrian.com/what-is-aluminum-extrusion-process/
[9] https://waykenrm.com/blogs/aluminum-extrusion/
[10] https://www.richardsonmetals.com/resources/aluminum-extrusions-guide/
[11] https://www.dreamstime.com/photos-images/aluminum-extrusion.html
[12] https://leadrp.net/blog/a-complete-guide-to-aluminum-extrusion/
[13] https://kdmfab.com/aluminum-extrusion/






















