Content Menu
● Understanding Aluminum Extrusion
>> The Process of Aluminum Extrusion
● Benefits of Aluminum Extrusion Cut To Length
● Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
● Visual Representation of the Process
● Advantages of Using Aluminum in Manufacturing
● Challenges in Aluminum Extrusion
● Future Trends in Aluminum Extrusion
● Conclusion
● Related Questions and Answers
>> 1. What materials can be extruded besides aluminum?
>> 2. How does the extrusion process affect the mechanical properties of aluminum?
>> 3. What industries benefit most from aluminum extrusion?
>> 4. Can aluminum extrusions be recycled?
>> 5. What are some common shapes produced through aluminum extrusion?
Aluminum extrusion cut to length is a manufacturing process that involves shaping aluminum into specific profiles and then cutting these profiles to precise lengths according to project requirements. This method is widely utilized across various industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, due to its numerous advantages in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility.

Understanding Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion is a process where aluminum alloy is heated until it becomes pliable and then forced through a die with a specific cross-sectional shape. The resulting aluminum profile can be as simple as a straight bar or as complex as intricate designs tailored for specific applications. Once extruded, the aluminum is cooled and cut to the desired length, making it ready for use in various projects.
The Process of Aluminum Extrusion
1. Heating the Billet: A solid cylindrical piece of aluminum, known as a billet, is heated to approximately 900°F (482°C) until it becomes soft but not molten.
2. Extrusion: The heated billet is placed in an extrusion press where a ram pushes it through a shaped die. This creates a long length of aluminum with a uniform cross-section.
3. Cooling: After exiting the die, the extruded aluminum is cooled using water or air to solidify its shape.
4. Cutting to Length: The cooled extrusions are then cut to the specified lengths using precision saws.
5. Finishing: Finally, the extruded pieces may undergo additional processes such as machining or surface finishing to meet specific requirements.
Benefits of Aluminum Extrusion Cut To Length
The cut-to-length process offers several significant benefits for projects:
- Precision and Customization: Each piece can be cut to exact specifications, ensuring that components fit perfectly within assemblies or structures.
- Reduced Waste: By cutting profiles to length before shipping, manufacturers can minimize scrap material and reduce costs associated with excess material.
- Time Efficiency: Projects benefit from receiving ready-to-use components, which speeds up assembly and reduces labor costs on-site.
- Cost Savings: Cutting extrusions to length can lower shipping costs since shorter pieces can often be shipped via more economical methods like FedEx or UPS.
- Improved Quality Control: With precise cutting processes, manufacturers can maintain tight tolerances and ensure consistent quality across all pieces.
Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusions are used in a myriad of applications across different sectors:
- Construction and Architecture: Used for window frames, curtain walls, and structural supports due to their lightweight yet strong properties. Aluminum's resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for outdoor applications where durability is crucial.
- Automotive Industry: Utilized in vehicle frames and components where weight reduction is crucial for fuel efficiency. The ability to create complex shapes allows for innovative designs that enhance performance while maintaining safety standards.
- Consumer Products: Found in items such as furniture frames and appliances where design flexibility is needed. Manufacturers can create aesthetically pleasing products without sacrificing structural integrity.
- Electronics: Employed in heat sinks and enclosures that require efficient thermal management. The excellent thermal conductivity of aluminum helps dissipate heat effectively, prolonging the lifespan of electronic components.
- Aerospace: Used in aircraft structures where high strength-to-weight ratios are essential. Aluminum extrusions provide the necessary rigidity while keeping overall weight low, which is critical in aviation applications.
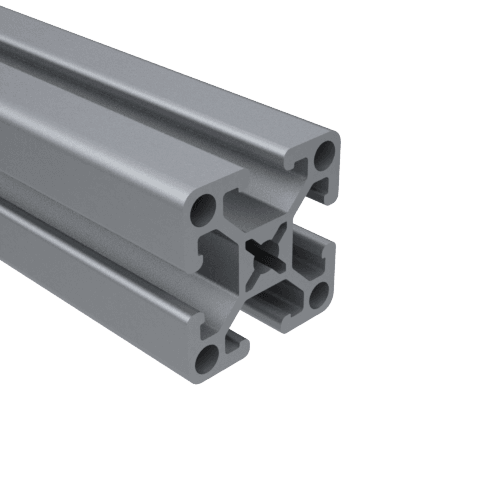
Visual Representation of the Process
To better understand the aluminum extrusion process, here are some images that illustrate each step:
"Heating the aluminum billet before extrusion."
"The extrusion press pushing the heated billet through the die."
"Cooling the extruded aluminum profiles."
"Cutting the cooled extrusions to specified lengths."
Advantages of Using Aluminum in Manufacturing
Aluminum offers several advantages that make it an ideal choice for various manufacturing processes:
- Lightweight: Aluminum is significantly lighter than many other metals, making it easier to handle and transport without compromising strength.
- Corrosion Resistance: The natural oxide layer that forms on aluminum protects it from corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor applications and environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
- Recyclability: Aluminum can be recycled repeatedly without losing its properties. This sustainability aspect appeals to environmentally conscious manufacturers and consumers alike.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has excellent thermal conductivity properties, making it ideal for applications requiring heat dissipation like electronics and automotive parts.
- Versatility: The ability to create complex shapes through extrusion allows manufacturers to innovate continuously while meeting specific design requirements.
Challenges in Aluminum Extrusion
While aluminum extrusion offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges associated with the process:
- Initial Setup Costs: The cost of creating custom dies for specific profiles can be high. However, this cost is often offset by the long-term savings achieved through reduced waste and increased efficiency.
- Limited Wall Thickness: Achieving very thin wall sections can be challenging during the extrusion process. Designers must consider this limitation when planning their projects.
- Quality Control Requirements: Maintaining consistent quality throughout production requires stringent quality control measures. Variations in temperature or pressure during extrusion can affect the final product's properties.
Future Trends in Aluminum Extrusion
As technology advances, several trends are emerging in the field of aluminum extrusion:
- Increased Automation: Automation technologies are being integrated into manufacturing processes to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs. Automated systems can enhance precision during cutting and finishing operations.
- Sustainability Initiatives: With growing awareness around environmental issues, manufacturers are focusing on sustainable practices such as using recycled aluminum and reducing energy consumption during production.
- Innovative Alloys: Research into new aluminum alloys continues to expand possibilities for enhanced performance in specific applications. These alloys may offer improved strength or corrosion resistance compared to traditional options.
- 3D Printing Integration: Combining traditional extrusion techniques with 3D printing allows for greater design flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities. This integration could revolutionize how components are designed and manufactured across industries.
Conclusion
Aluminum extrusion cut to length is an essential process that provides numerous advantages for various industries. Its ability to create customized profiles while minimizing waste and reducing costs makes it an invaluable manufacturing method. As industries continue to seek efficient solutions for their projects, the demand for aluminum extrusion will likely grow, further establishing its significance in modern manufacturing practices.

Related Questions and Answers
1. What materials can be extruded besides aluminum?
Aluminum is the most common material used for extrusion; however, other materials such as copper, magnesium, and certain plastics can also be extruded depending on their properties and intended applications.
2. How does the extrusion process affect the mechanical properties of aluminum?
The extrusion process enhances certain mechanical properties of aluminum by aligning its grain structure, which improves strength and durability compared to cast or wrought forms of aluminum.
3. What industries benefit most from aluminum extrusion?
Industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods benefit significantly from aluminum extrusion due to its lightweight nature and design flexibility.
4. Can aluminum extrusions be recycled?
Yes! Aluminum extrusions are highly recyclable without losing their properties. Recycling helps reduce energy consumption compared to producing new aluminum from ore.
5. What are some common shapes produced through aluminum extrusion?
Common shapes include bars, tubes, angles, channels, and custom profiles designed for specific applications such as heat sinks or structural components.






















