Content Menu
● Understanding the Basics of Extrusion
>> Key Components of an Optical Grade Sheet Extrusion Line
● The Extrusion Process Explained
>> 1. Material Preparation
>> 2. Feeding the Extruder
>> 3. Melting and Mixing
>> 4. Extrusion Through the Die
>> 5. Cooling
>> 6. Winding
● Advantages of Optical Grade Sheet Extrusion Lines
● Applications of Optical Grade Sheets
● Advanced Technologies in Optical Grade Sheet Production
>> Multi-Layer Extrusion Technology
>> Precision Calendering Systems
>> Automated Quality Control Systems
● Challenges in Optical Grade Sheet Production
● Environmental Considerations in Optical Grade Sheet Production
● Future Trends in Optical Grade Sheet Manufacturing
>> Smart Manufacturing Integration
>> Customization Options
>> Sustainability Initiatives
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials are typically used in optical grade sheet extrusion?
>> 2. How does temperature affect the extrusion process?
>> 3. What is the significance of cooling in this process?
>> 4. Can different thicknesses be produced on one line?
>> 5. What quality control measures are implemented during production?
The production of optical grade sheets is a sophisticated process that involves a specialized extrusion line designed to create high-quality polycarbonate (PC) and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) sheets. These optical sheets are essential in various applications, including electronic displays, automotive components, and protective covers due to their excellent optical properties and durability. This article will delve into the workings of an optical grade sheet extrusion production line, covering its components, processes, and advantages.
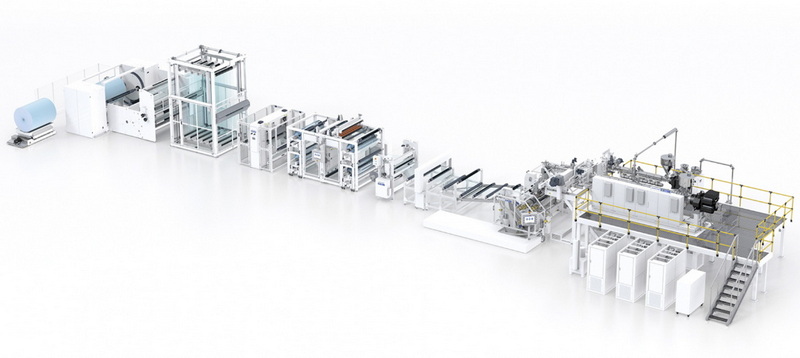
Understanding the Basics of Extrusion
Extrusion is a manufacturing process where raw materials are transformed into a continuous profile. In the case of optical grade sheets, thermoplastic materials like polycarbonate or PMMA are heated until they melt and then forced through a die to form sheets of desired thickness and width.
Key Components of an Optical Grade Sheet Extrusion Line
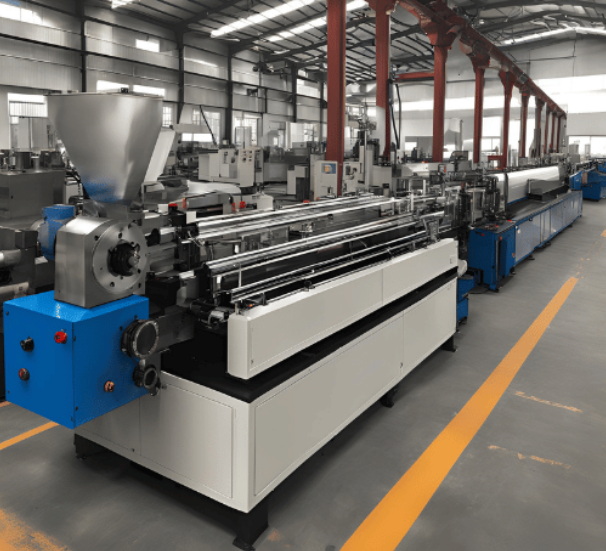
1. Extruder: The heart of the extrusion line, where raw materials are melted and mixed.
2. Die: A specially designed tool that shapes the molten material into sheets.
3. Cooling System: Maintains the temperature of the extruded sheet to prevent deformation.
4. Winding System: Rolls the finished product for storage or further processing.
5. Control Systems: Monitors and adjusts parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed throughout the process.
The Extrusion Process Explained
The extrusion process for optical grade sheets can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Material Preparation
Before extrusion begins, raw materials (usually in pellet form) are prepared. This involves:
- Drying: To remove moisture that can cause defects in the final product.
- Blending: Combining different materials or additives to achieve specific properties.
2. Feeding the Extruder
The prepared pellets are fed into the extruder through a hopper. The extruder consists of a barrel with a rotating screw that pushes the pellets forward.
3. Melting and Mixing
As the pellets move through the barrel:
- They are heated by electrical heaters along the barrel.
- The friction generated by the screw also contributes to melting.
- The material is mixed thoroughly to ensure uniformity.
4. Extrusion Through the Die
Once melted, the material is forced through a die:
- The die shapes the molten plastic into a flat sheet.
- The thickness can be adjusted by changing the die gap.
5. Cooling
After exiting the die, the hot sheet passes through a cooling system:
- Typically involves chill rolls or water baths that cool the sheet quickly to solidify it.
- This step is crucial for maintaining optical clarity and preventing warping.
6. Winding
Finally, once cooled, the sheet is wound onto rolls using a winding system:
- Ensures that the sheets are stored properly without damage.
- Automated systems can adjust tension during winding for consistent quality.

Advantages of Optical Grade Sheet Extrusion Lines
Optical grade sheet extrusion lines offer several advantages:
- High Efficiency: Continuous production allows for large quantities to be produced quickly.
- Quality Control: Advanced monitoring systems ensure that each sheet meets stringent quality standards.
- Versatility: Capable of producing sheets with varying thicknesses and properties based on market demands.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces waste and maximizes material usage through precise control over processes.
Applications of Optical Grade Sheets
Optical grade sheets produced via extrusion find their applications in various sectors:
- Electronics: Used in displays for smartphones, tablets, and televisions due to their clarity and impact resistance.
- Automotive Industry: Employed in headlights and dashboards where durability and transparency are critical.
- Construction: Used in skylights and glazing where light transmission and UV resistance are required.
Advanced Technologies in Optical Grade Sheet Production
Recent advancements in technology have significantly improved the efficiency and quality of optical grade sheet production lines. Some notable innovations include:
Multi-Layer Extrusion Technology
Multi-layer extrusion allows manufacturers to combine different materials or additives during production. This results in composite materials with enhanced properties such as improved barrier performance against UV rays or moisture. For example, applying a UV protective layer during production can significantly extend the lifespan of outdoor applications like roofing or skylights.
Precision Calendering Systems
Calendering is crucial for achieving desired thicknesses and surface smoothness in optical sheets. Advanced calendering systems utilize high-temperature pressurized water circulation to maintain precise temperature control throughout the process. This ensures that even thin sheets maintain high optical quality without defects.
Automated Quality Control Systems
Modern extrusion lines incorporate sophisticated monitoring systems that provide real-time data on various parameters such as thickness, temperature, and pressure. This automation not only enhances product quality but also minimizes waste by allowing immediate adjustments during production.
Challenges in Optical Grade Sheet Production
Despite its advantages, producing optical grade sheets comes with challenges:
- Material Variability: Different batches of raw materials may exhibit variations that affect consistency in final products.
- Processing Conditions: Fluctuations in temperature or pressure during extrusion can lead to defects such as bubbles or uneven thickness.
- Market Demand Fluctuations: Changes in consumer preferences can lead to overproduction or underproduction if manufacturers do not adapt quickly enough.
Environmental Considerations in Optical Grade Sheet Production
With increasing awareness about environmental sustainability, manufacturers are focusing on reducing their ecological footprint during production processes. Some strategies include:
- Recycling Materials: Utilizing recycled plastics in production not only conserves resources but also reduces waste sent to landfills.
- Energy-Efficient Equipment: Investing in energy-efficient machinery reduces energy consumption during production, leading to lower operational costs and minimized environmental impact.
- Waste Management Practices: Implementing effective waste management practices ensures that scrap materials generated during production are recycled or repurposed rather than discarded.
Future Trends in Optical Grade Sheet Manufacturing
As technology continues to evolve, several trends are shaping the future of optical grade sheet manufacturing:
Smart Manufacturing Integration
The integration of smart manufacturing technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) will allow manufacturers to monitor equipment performance remotely, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes based on real-time data analytics.
Customization Options
There is an increasing demand for customized products tailored to specific customer needs. Manufacturers will likely invest more in flexible production lines capable of producing bespoke optical sheets with unique properties or designs.
Sustainability Initiatives
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, manufacturers will need to adopt sustainable practices not only in material sourcing but also throughout their entire supply chain—from production methods to packaging solutions.
Conclusion
The optical grade sheet extrusion production line is an intricate system that transforms raw thermoplastic materials into high-quality sheets used across multiple industries. By understanding how this process works—from material preparation to winding—the importance of precision engineering becomes clear. As technology advances, these systems will continue to evolve, offering even greater efficiency and quality in optical sheet production while addressing environmental concerns through sustainable practices.

FAQ
1. What materials are typically used in optical grade sheet extrusion?
Optical grade sheets are primarily made from polycarbonate (PC) and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) due to their excellent optical properties and durability.
2. How does temperature affect the extrusion process?
Temperature plays a crucial role in melting raw materials; too low may result in incomplete melting while too high can degrade material quality.
3. What is the significance of cooling in this process?
Cooling is essential to solidify extruded sheets quickly while maintaining their shape and preventing defects like warping or bubbles.
4. Can different thicknesses be produced on one line?
Yes, modern extrusion lines can produce sheets of varying thicknesses by adjusting die settings during operation.
5. What quality control measures are implemented during production?
Quality control measures include real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and thickness to ensure each sheet meets industry standards.






















