Content Menu
● Understanding Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
>> Key Characteristics of Aluminum Extrusion
● The Aluminum Extrusion Process
● Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
● Applications of Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
● Detailed Steps in Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
>> Preparation of the Die
>> Heating the Aluminum Billet
>> Extrusion Process
>> Cooling Techniques
>> Stretching and Cutting
>> Finishing Processes
● Innovations in Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
● Visualizing the Process
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials can be extruded besides aluminum?
>> 2. How does the cost of aluminum extrusion compare to other manufacturing methods?
>> 3. Can custom shapes be created with aluminum extrusion?
>> 4. What industries benefit most from aluminum extrusion?
>> 5. Is recycled aluminum used in the extrusion process?
● Citations:
Aluminum extrusion drawing is a vital manufacturing process that transforms aluminum into various shapes and profiles. This method is widely used across multiple industries due to its versatility, efficiency, and the unique properties of aluminum. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of aluminum extrusion drawing, its benefits, applications, and the steps involved in the process.
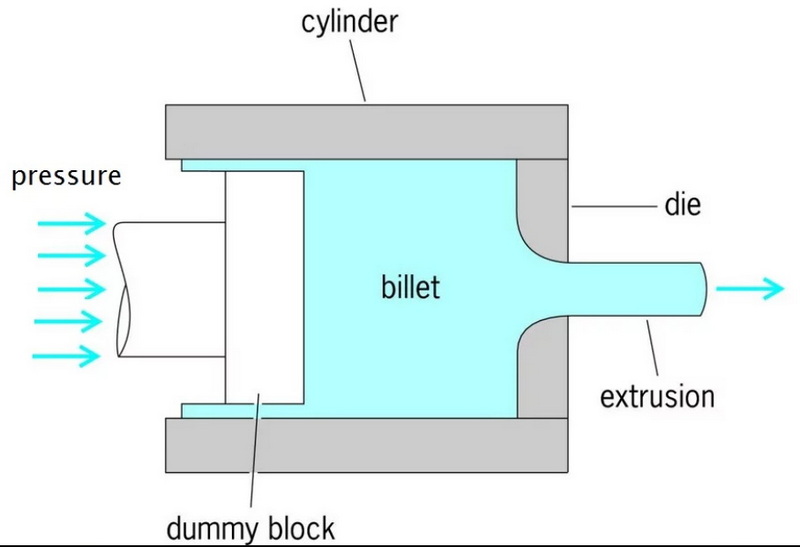
Understanding Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
Aluminum extrusion drawing involves forcing heated aluminum alloy through a die with a specific cross-sectional shape. The process is similar to squeezing toothpaste from a tube; as the aluminum is pushed through the die, it takes on the shape of the opening. This technique allows for the creation of long lengths of aluminum profiles ranging from simple bars to complex geometries.
Key Characteristics of Aluminum Extrusion
- Versatility: Aluminum can be extruded into various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for numerous applications.
- Lightweight: Aluminum has a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive where reducing weight is essential.
- Corrosion Resistance: The natural oxide layer that forms on aluminum provides excellent resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
- Design Flexibility: Designers can create intricate profiles with precise dimensions, enabling innovative designs that meet specific requirements.
The Aluminum Extrusion Process
The aluminum extrusion process consists of several key steps:
1. Preparation of the Die: The first step involves designing and machining a die that will shape the aluminum. The die is preheated to maintain an even flow of metal during extrusion.
2. Heating the Aluminum Billet: The aluminum billet is heated in a furnace until it reaches a malleable state, typically between 750°F to 925°F (400°C to 500°C). This heating process softens the metal, allowing it to be easily extruded.
3. Extrusion: A hydraulic ram applies significant pressure (up to 15,000 tons) to push the heated billet through the die. As the aluminum flows through the die, it takes on its desired shape.
4. Cooling: After exiting the die, the extruded profile is cooled using air or water sprays to solidify it quickly and maintain its shape.
5. Stretching and Cutting: Once cooled, the extrusions are stretched to eliminate any distortions and improve their mechanical properties. They are then cut to specified lengths for further processing or delivery.
6. Finishing: The final step may include additional treatments such as anodizing or painting to enhance appearance and corrosion resistance.
Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
The aluminum extrusion drawing process offers numerous advantages:
- Cost Efficiency: The method minimizes material waste and reduces production costs compared to traditional manufacturing techniques.
- High Production Rates: Aluminum extrusion can produce large volumes of products quickly, making it suitable for both small and large-scale production runs.
- Enhanced Mechanical Properties: The extrusion process improves the strength and durability of aluminum products, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Sustainability: Aluminum is recyclable without losing its properties, making it an environmentally friendly choice for manufacturers.
Applications of Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
Aluminum extrusions are used in various industries due to their unique properties:
- Construction: Used in window frames, curtain walls, and structural components due to their lightweight and durable nature.
- Automotive: Employed in vehicle frames, bumpers, and interior parts where weight reduction contributes to improved fuel efficiency.
- Aerospace: Utilized in structural components such as fuselage frames and wing structures where strength-to-weight ratio is critical.
- Electronics: Commonly used for heat sinks and enclosures due to excellent thermal conductivity.
- Transportation: Applied in rail and marine applications where lightweight materials are essential for performance.
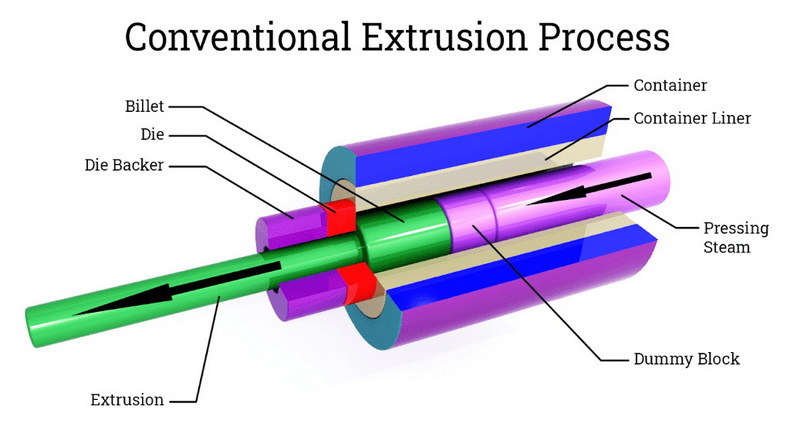
Detailed Steps in Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
To delve deeper into each step of the aluminum extrusion drawing process:
Preparation of the Die
The die design is crucial as it determines the final shape of the extruded product. Engineers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to create intricate designs that meet specific customer requirements. The die material must withstand high temperatures and pressures; thus, tool steel or carbide is often used.
Heating the Aluminum Billet
The heating phase is critical because improper heating can lead to defects in the final product. Billets are typically heated in a controlled environment where temperature uniformity ensures consistent flow characteristics during extrusion.
Extrusion Process
During extrusion, several factors affect product quality:
- Temperature Control: Maintaining optimal temperature ensures proper flow through the die.
- Ram Speed: The speed at which the ram pushes the billet affects surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Die Design: A well-designed die minimizes friction and wear during extrusion while ensuring uniform material flow.
Cooling Techniques
Cooling methods can significantly impact mechanical properties:
- Air Cooling: Slower cooling rates can enhance ductility but may lead to warping if not controlled properly.
- Water Quenching: Rapid cooling increases strength but may introduce internal stresses that require subsequent aging processes to relieve.
Stretching and Cutting
Stretching not only corrects any distortions but also aligns grain structures within the metal, enhancing strength. Cutting techniques vary based on profile type; saw cutting is common for larger sections while precision cutting methods are used for intricate shapes.
Finishing Processes
Finishing treatments such as anodizing not only improve aesthetics but also enhance corrosion resistance by creating a thicker oxide layer on aluminum surfaces. Powder coating provides additional protection while allowing for color customization.
Innovations in Aluminum Extrusion Drawing
Recent advancements in technology have transformed how aluminum extrusion drawing is performed:
- 3D Printing Integration: Some manufacturers are exploring hybrid processes that combine 3D printing with traditional extrusion methods to create complex shapes that were previously impossible or cost-prohibitive.
- Smart Manufacturing Technologies: Implementing IoT devices allows real-time monitoring of extrusion parameters, leading to improved quality control and reduced downtime through predictive maintenance.
- Sustainable Practices: Innovations in recycling processes enable manufacturers to use post-consumer recycled aluminum without sacrificing quality or performance characteristics.
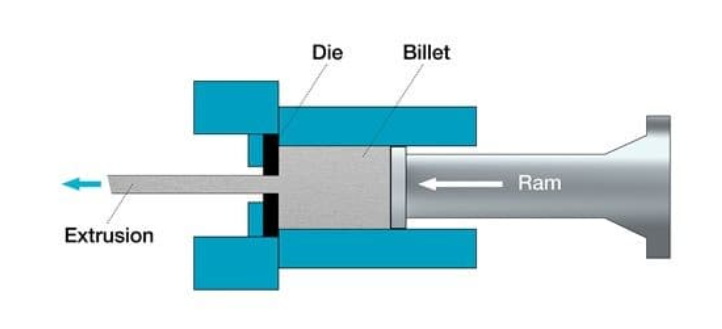
Visualizing the Process
To better understand aluminum extrusion drawing, visual aids such as diagrams or videos can be incredibly helpful. Below are suggested types of visuals that can enhance comprehension:
- Diagrams illustrating each step of the extrusion process.
- Videos demonstrating real-time aluminum extrusion operations.
- Images showcasing various aluminum profiles produced through extrusion drawing.
Conclusion
Aluminum extrusion drawing is a crucial manufacturing process that offers unparalleled versatility and efficiency across multiple industries. Its ability to produce complex shapes while maintaining strength and lightweight properties makes it an invaluable technique in modern manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve and demand innovative solutions, aluminum extrusion drawing will play a significant role in meeting these challenges. With ongoing advancements in technology and sustainable practices, this process remains at the forefront of manufacturing innovation.
FAQ
1. What materials can be extruded besides aluminum?
Aluminum is the most common material used for extrusion; however, other metals like copper, magnesium, and some plastics can also be extruded using similar processes.
2. How does the cost of aluminum extrusion compare to other manufacturing methods?
Aluminum extrusion tends to be more cost-effective than traditional methods due to reduced material waste and faster production rates.
3. Can custom shapes be created with aluminum extrusion?
Yes, one of the primary advantages of aluminum extrusion is its ability to create custom shapes tailored to specific design requirements.
4. What industries benefit most from aluminum extrusion?
Industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and transportation benefit significantly from aluminum extrusion due to its lightweight and durable properties.
5. Is recycled aluminum used in the extrusion process?
Yes, recycled aluminum can be used in the extrusion process without compromising quality or performance characteristics.
Citations:
[1] https://www.hydro.com/profiles/aluminum-extrusion-process
[2] https://waykenrm.com/blogs/aluminum-extrusion/
[3] https://asaluminum.com/blog/exploring-the-art-of-aluminum-extrusion-methods-advantages-and-applications/
[4] https://www.istockphoto.com/fr/photos/aluminum-extrusion
[5] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yqKK5SI2Gzg
[6] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vHkwq_2yY9E
[7] https://aec.org/aluminum-extrusion-process
[8] https://leadrp.net/blog/a-complete-guide-to-aluminum-extrusion/
[9] https://www.yjing-extrusion.com/what-are-the-key-benefits-of-aluminum-extrusion-design.html
[10] https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/aluminum-extrusion






















